Original author: Jonnyhimalaya
Original translation: Vernacular blockchain
This article explores some of the most promising Layer 1 Bitcoin decentralized exchanges (Dexs) and automated market makers (AMMs). Most of these markets are still under development, and some are only in the testnet stage. In general, these markets can be divided into two categories: order book exchanges and automated market makers. This article conducts research interviews with most of the teams involved.
DeFi on Bitcoin is coming. We have already seen the initial appearance of DeFi on Bitcoin, such as Ordinals, Runes, and the emergence of meta-protocols such as BRC 20 and TAP. The community wants to trade shitcoins on Bitcoin, but this situation is about to change!
Currently, the experience of trading tokens on Bitcoin is poor and full of friction. On markets such as Unisat and Magic Eden, sellers of tokens (BRC 20 or Runes) must list a specific number of tokens at a specific price and wait for buyers to buy the same number of tokens at the same price, which increases the friction of transactions.
Many teams are trying to solve this problem by bringing AMM and Dex-style transactions to Bitcoin, providing the trading experience we are used to on the EVM. Since Bitcoin uses the UTXO model instead of the account model used by the EVM, some functions need to be redesigned. In fact, UTXO has technical features that cannot be achieved by the EVM in terms of designing partially signed Bitcoin transactions (PSBT) to achieve atomic swaps.
When analyzing each market, I considered specific criteria: user experience when exchanging, degree of decentralization, whether permission is allowed, and other trade-offs.
Most teams are innovating in PSBT and signature hashes (Sighash). Signature hashes are the mechanism used to sign Bitcoin transaction inputs and outputs. There are six different types of signature hashes, ranging from the most secure but least flexible Sighash All to the least secure but most flexible Sighash None — Anyone Can Pay. Currently popular markets such as Unisat and Magic Eden use Sighash-Single to create their PSBTs. This means that not all outputs are signed, and transactions may therefore be affected by MEV sniping. Using Sighash-All means that all inputs and outputs are fully signed, and any transaction signed in this way can avoid MEV sniping.
There are many other factors to consider when analyzing a Dex or Swap, such as liquidity and slippage, maker and taker fees, liquidity provider incentives, trading volume, etc. However, since most of the analyzed markets are still in testing or early release stages, it will take time for these metrics to become relevant.
1. Fluid BTC
Website: https://btc.fluidtokens.com/swap
Twitter: https://x.com/FluidtokensXBT
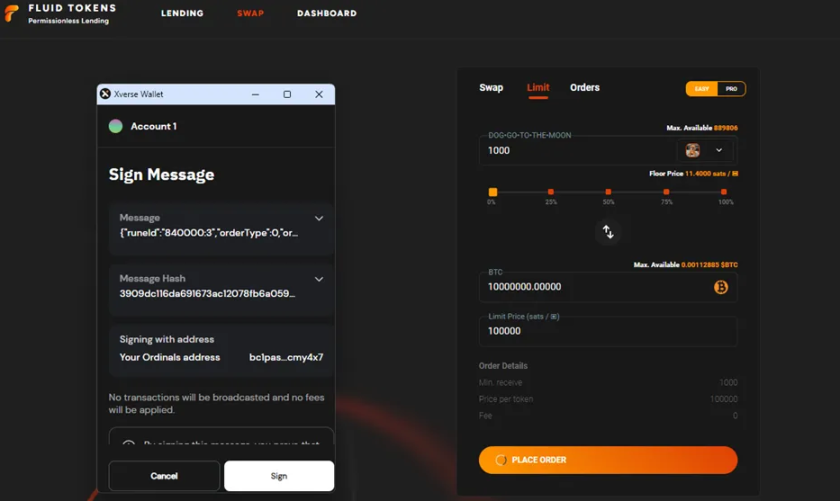
Fluid Tokens is an order book based decentralized exchange (DEX). Users can currently trade Runes-BTC, and the Runes-Runes feature is coming soon. Fluid is essentially a peer-to-peer trading market. When a trader wants to create an order (maker), they make an off-chain commitment (for example, I want to sell 1000 $DOG and exchange for 0.001 BTC). These commitments are published in the order book as limit orders. When a buyer (taker) accepts the order, that is, a market buy or sell, they initiate a PSBT (partially signed Bitcoin transaction) which details all the inputs and outputs promised by the maker. The original maker is then notified (via email or in-app) that their limit order has been matched, and then they sign the PSBT to broadcast the transaction to complete the transaction.
This trading design is completely permissionless and peer-to-peer. The market is essentially a facilitator of these trades. The trade-off is the round-trip in user experience. The maker makes a commitment, posts a limit order - the taker matches the order and initiates the PSBT - and then the maker signs and completes the PSBT. This friction inherently slows down the trading process and often does not meet the needs of traders to sell quickly. Another potential problem is the manipulation or spoofing of orders, for example, makers create orders that they have no intention of fulfilling in an attempt to manipulate prices. To mitigate this, the Fluid platform currently only allows one maker commitment order per address per trading pair. Therefore, it is not possible to gradually build positions through ladder orders for the time being, but this feature is on the development plan.
All transactions on Fluid are completely permissionless, and thanks to the ability to use Sighash All in PSBT, they are also MEV-protected and sniper-proof, meaning that transactions are only validated if both the maker and taker addresses participate in the transaction. Transactions cannot be sniped by third parties, which is a common occurrence with transactions on currently popular markets like Magic-Eden and Unisat. Fluid prioritizes completely permissionless and secure transactions, at the expense of a less fluid trading experience. Fluid will be launching their market in the coming weeks.
2. Saturn BTC
Website: https://www.saturnbtc.io/
Twitter: https://x.com/Saturn_btc
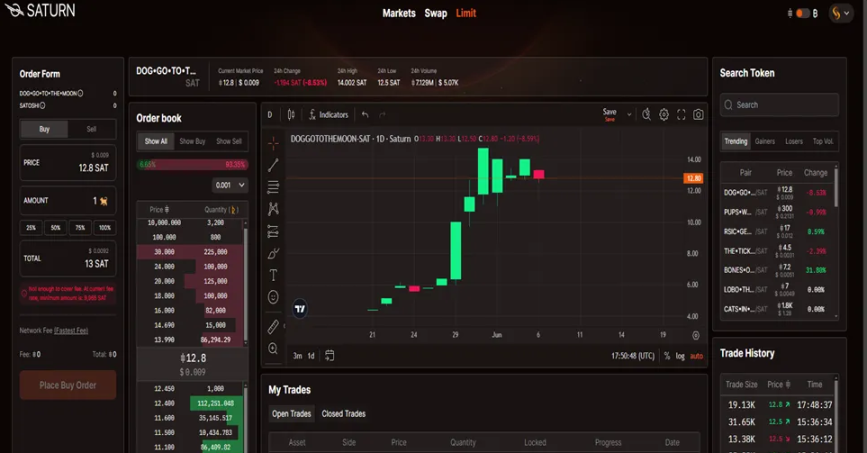
Saturn BTC is an orderbook based on-chain trading platform that was originally launched in the summer of 2023 for rare sats (the smallest unit of Bitcoin). They have just launched the Runes trading market. They are focused on creating a smooth trading experience similar to centralized exchanges. They have a peer-to-peer order book where users can place limit orders on-chain to fill the order book, and users can also make market buys, taking existing limit orders in the order book. This user experience is very smooth, especially since users dont have to worry about splitting UTXOs or matching the exact requirements of the orders placed by the maker. This is a big improvement over the traditional, more cumbersome Runes trading experience on Unisat and Magic Eden. Saturn also has a swap feature, but this is not an AMM-style liquidity pool swap. With a swap, users simply market buy the appropriate amount of sell orders in the order book, and vice versa.
To enable this improvement in trading experience and functionality, especially as it relates to limit orders and the matching engine, Saturn currently requires users to deposit funds into a trading account, which is a multi-signature account signed by the user and co-signed by Saturn. This trading wallet will be replaced by a one-time multi-signature in the next version. When a user creates a limit order, they sign a Sighash None PSBT, which technically hands control of the tokens/bitcoins involved in that specific order to the Saturn platform and matching engine in a 2/2 multi-signature manner. Transactions are finalized via Sighash All before being broadcast to the memory pool, ensuring protection against sniping. This trading process means that as long as the order remains open, the trader must trust Saturn to handle the specific funds involved. Therefore, the trading experience is not completely permissionless and has some centralized aspects.
Saturn takes an interesting and innovative approach by replicating the smooth trading experience of centralized exchanges directly on the Bitcoin Layer 1 chain. Their platform also offers full charting capabilities powered by Trading View. There is no need to split orders, the platform handles these, and there can be partial fills and multiple wallets in the same trade. Saturn is a very user-friendly and intuitive decentralized exchange with many product improvements and new features in its roadmap.
3. UniTap
Website: https://unitap.io/
Twitter: https://x.com/Uni_Tap
Unitap is a decentralized exchange (Dex) built for the TAP ecosystem. The TAP meta-protocol enables various DeFi functions and operations to be performed directly on Bitcoin Layer 1, using distributed indexers to assist in calculations and account balancing.
Unitap is building a marketplace not only for trading Tap-based assets, but also for Tap to Runes trading. They are developing a Runes to Tap bridge solution.
Unitap has designed a completely non-custodial exchange system. Users who wish to sell a token (e.g. $-tap) can create a PSBT using the “Sighash Single”, specifying the amount of token they wish to sell and what form (token and amount) they wish to receive in return. The return can be BTC or another Tap or Rune token. This creates a very specific sell order that can take some time to find a match, especially if market liquidity is low. To help overcome this friction, Unitap places this sell order into the market, matching it with all other orders that match the buyer of this specific sell order. For example, if I want to sell some $-tap, I can select that token and click on the “Give” tab. This will open a market with all the orders to buy $-tap, and sellers of other assets who are looking for $-tap in exchange for their assets (see screenshot above). This adds flexibility to the market and helps facilitate the quick sales that traders like. Currently, Tap-Tap assets are traded, and Tap-Runes and Runes-Tap swaps will be launched in the coming months.
Unitap will also launch its own wallet in the coming weeks, supporting all TAP operations and enabling cross-protocol swaps such as Tap-Runes or Tap-BRC 20.
4. Dotswap
Website: https://www.dotswap.app/
Twitter: https://x.com/dot_swap
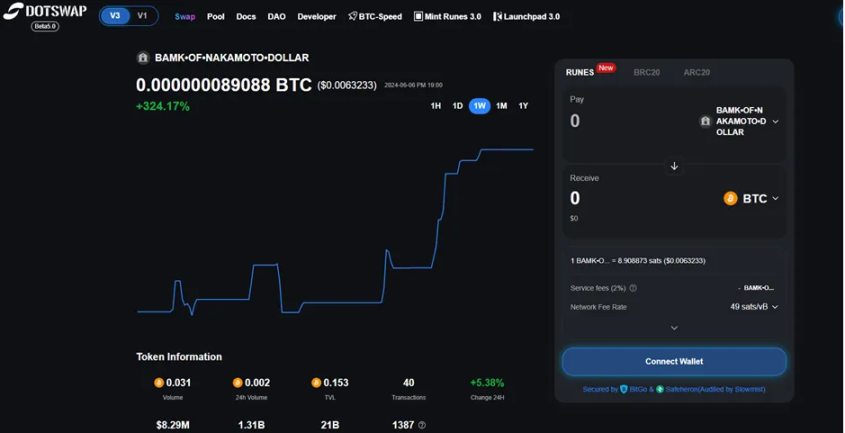
Dotswap is a native AMM-style trading platform based on Bitcoin Layer 1, supporting BRC 20, ARC 20, and Runes. Its trading experience is very similar to how Uniswap works. Users can already exchange between BRC 20/Bitcoin and Runes/Bitcoin, and Runes/Runes exchange is coming soon.
Atomic swaps are completely permissionless and non-custodial, using the Sighash All PSBT. Users select how much Bitcoin/token they wish to swap, and receive a corresponding amount of another token in the same transaction. Using Sighash-All means that all transactions are sniper-resistant.
The trade-off here is that liquidity pools are custodial. When liquidity providers deposit funds into a liquidity pool, those funds are stored in a multi-signature system because Bitcoin has no smart contracts to send funds to. Dotswaps unique MMM (Multi-layer Multi-signature Matrix) custody solution was developed in-house and run in partnership with custodians Safeheron and BitGo. The process of adding and removing liquidity is as simple as expected, similar to the experience of EVM AMMs. Dotswap is the first team on Bitcoin to implement a centralized serializer to protect transaction ordering (and therefore price ordering).
Dotswap has also developed a new Runes Token launch platform that operates similarly to pump.fun on Solana. At launch, participants use Bitcoin to purchase a specific Runes Token, most of which is used to seed a liquidity pool for that Token. Therefore, any Rune launched on this platform has an immediately available liquidity pool that users can exchange and trade in a completely permissionless manner. Contributors to the launch platform also own their share of the liquidity pool and can earn transaction fees.
Dotswap has developed a completely permissionless and non-custodial AMM trading platform for traders/exchangers to use. Liquidity providers are the ones who bear the trust assumption. To date, Dotswap has seen over $40 million in trading volume. If Dotswap succeeds in attracting more liquidity into their pools (through favorable trading fees, liquidity mining, etc.), trading volume should increase.
5. Ordiswap
Website: https://app.ordiswap.fi/
Twitter: https://x.com/OrdiswapLabs
Ordiswap is an AMM that performs BRC 20 or Runes Token swaps on-chain. Users can swap, provide liquidity, remove liquidity, and create new liquidity pools on Bitcoin Layer 1. Last year, Ordiswap was the first AMM to appear in the BRC 20 space.
When a user initiates a swap on Ordiswap (for example, BTC for ORDI), they create a transaction that sends their BTC to an Ordiswap liquidity provider. This transaction also includes a script with the details of the swap. The Ordiswap backend indexer reads this script and sends the user the corresponding amount of ORDI in a subsequent transaction. This means that users must trust the Ordiswap API when signing a transaction to initiate a swap.
Ordiswap uses a set of off-chain servers, oracles, indexers, and Bitcoin nodes to create AMM functionality. Ordiswaps servers update the off-chain balances of participating users and perform periodic settlements on-chain. Currently all swaps are handled by the Ordiswap API. This is slightly less elegant than the solution of using PSBT for atomic swaps, which can complete the entire swap in the same transaction. However, atomic swaps are already on the roadmap.
The liquidity pool is once again custodial and is currently in discussions with custodial partners to upgrade security. Their V2 BRC 20 swap has been live for two months with a total trading volume of around $500,000.
Ordiswap also has the potential to become the main AMM on Bitcoin if it can achieve everything they set out to do. It is an ambitious, modular implementation of a Bitcoin swap. They are currently in the V3 mainnet closed beta. According to reports, testing is going well and they are finalizing the details of the swap mechanism.
6. RunesDex

Website: https://www.runesdex.com/
Twitter: https://x.com/RUNES_DEX
Runes Dex is another recently launched AMM on Bitcoin Layer 1 for Runes-BTC trading. They are well funded, have a large team, and are growing rapidly. They are currently in Alpha testing on the mainnet. Users can test swapping their local Runes IS•THIS•WORKING. Similar to the aforementioned AMMs, trading on Runes Dex is completely non-custodial and permissionless, but the liquidity pools are custodial. Currently Runes Dex has full control over private keys, which are stored in a vault using AWS. Custody partnerships are in the works.
They are also building a launchpad similar to pump.fun, a Runes tracker that takes into account pending transactions in the memory pool, and a Runes bridge to bridge memecoins from other chains such as Solana to Runes. They use Sighash All in the Dex exchange PSBTs, which means that every exchange is sniper resistant. They plan to let liquidity providers charge fees in Bitcoin. They also created an automatic UTXO splitter on the liquidity provision side to ensure a smooth experience when swapping. The AMM for Runes Dex will be fully live in the next few weeks. Another AMM with potential.
7. Runeswap — Swapsats
Website: https://rune-testnet.swapsats.io/
Twitter: https://x.com/Swapsats_io
Runeswap is a Runes-BTC AMM-style exchange developed by the Swapsats team, the team behind the OG sub 10k Ordinals collection Ordinal Eggs. This exchange will operate similarly to the above mentioned exchanges; providing a permissionless exchange experience, but the liquidity pool is custodial.
As a group of collectors, their philosophy is to build a decentralized exchange for their community. Holders of their collectibles will receive various benefits on the exchange, such as reduced transaction fees and revenue sharing from the exchanges revenue. They prioritize smooth user interfaces and good user experiences to further foster their community. Currently, the exchange is in the alpha testnet stage, with the mainnet scheduled to go live in the coming weeks.
8. RunesFi
Website: https://runesfi.io/
Twitter: https://x.com/Runes_Fi
RunesFi aims to be a one-stop infrastructure hub for Bitcoin assets. They plan to build a Runes block explorer, a launchpad and incubator, a Runes carver, and most importantly, a decentralized exchange for Runes and BRC 20. They are currently in the testnet phase of their exchange and expect their mainnet product to be live before the end of 2024.
There are a few other DEXs in development that promise more decentralization than those listed above, such as Omnisats and Motoswap (OPNet). I can analyze them when they get closer to launch and more information is available. Unisat recently announced their new BRC 20 swap module, which will include liquidity pools, etc. It is currently in development and expected to be available within 6 months. Magic Eden is also hinting at an upcoming swap feature, although the timeline is not clear yet.
9. Conclusion and Outlook
Building on Bitcoin is challenging, especially if trying to directly replicate the functionality of the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM). Bitcoins UTXO model is different from the EVMs account-based model, and teams that can take advantage of Bitcoins unique mechanisms (such as PSBTs, Sighashes, etc.) are more likely to succeed in the long run than teams that simply try to recreate the EVM stack.
Teams currently creating innovative solutions are making tradeoffs in different ways. For example, in terms of order book decentralized exchanges, Saturn prioritized ultra-smooth user experience and functionality at the expense of fully permissionless trading. Fluid takes a different approach, prioritizing fully decentralized and non-custodial trading, albeit with some friction in the trading experience. It will be interesting to see which philosophy the market values more.
In the automated market maker (AMM) space, most teams are creating a system that allows traders to trade completely permissionlessly, but with liquidity pools that use some form of vault, multi-sig, or semi-custodial solution. This may be an acceptable tradeoff, as most traders don’t care how the liquidity pool is set up, as long as they can swap quickly and permissionlessly. Additionally, considering how many bridges and contracts have been hacked on Ethereum, providing liquidity to well-known custodians may even be a more attractive solution. Currently, Dotswap has an advantage in this regard, as they are the furthest along in development, product offerings, and custody solutions for liquidity providers. However, other teams such as RunesDex and Ordiswap are catching up, with their products coming soon.
I am sure there are other teams building this that I am not aware of at the time of writing.











