Encrypted digital assets, based on a decentralized consensus mechanism, are issued on the public chain and shuttle between decentralized applications. They are indispensable value certificates in the blockchain world. However, different public chain systems are independent of each other, and the assets on different chains are also isolated from each other like isolated islands. The interoperability of multi-chain assets is more conducive to the cross-chain combination of high-quality assets and accelerates the development of the industry. With the increase of high-quality public chains, the original solutions that focus on two-two cross-chains are stretched. The two-two cross-chains of N public chains require N^2 cross-chain bridges, and the workload is huge. The development of chain asset interoperability technology. As a hub for asset interoperability, the use threshold, transaction performance and use cost of the transit chain will be the key indicators that must be considered.The cost and efficiency of asset interoperability should not become the threshold for ecological development. In order to further empower multi-chain mutual integration and win-win results, the ShuttleFlow asset cross-chain protocol came out at the historic moment, and is committed to providing decentralized application developers with a low-cost decentralized multi-chain homogeneous asset fusion governance solution. The performance public chain Conflux serves as a transit chain to build a cross-chain bridge infrastructure, allowing DApps developers and users to complete asset cross-chains with zero perception.
In order to better describe ShuttleFlows multi-chain homogenous asset fusion governance solution, lets define the terms first:1. Homologous assets: assets issued on only one chain, but released to different chains through cross-chain2. Homogeneous assets: assets that are issued on multiple chains, but are essentially the same token3. Issuance chain: the public chain where the assets are issued4. Source chain: the public chain where the asset is to be crossed5. Transit chain: the public chain for asset exchange, this article refers to ConfluxTaking a simple cross-chain scenario of homologous assets on the source chain to the destination chain as an example, you can refer to the following diagram to clarify the relationship between the various terms in this scenario:1. Background introduction
1. Background introductionThe explosion of the DeFi ecosystem on Ethereum in 2020 has greatly stimulated the migration of digital assets from various centralized services to decentralized services. As the main position of decentralized services, the public chain has once again sparked competition among heroes. According to statistics, as of March 2021, the amount locked on the Ethereum chain has exceeded 38 billion U.S. dollars, and the total locked-up mainstream assets of BSC have exceeded 10 billion U.S. dollars. During the same period, projects on the Heco chain are on the rise, and the ecology of OEC is also growing. ready to go. The increase of high-quality public chains, on the one hand, has created the wealth myth of the ecological dividend period, but on the other hand, it has also caused various project parties to disperse their energy to issue homogeneous assets on multiple chains, but the circulation of homogeneous assets between chains is blocked. How to achieve low-cost multi-chain homogeneous asset fusion governance becomes imminent.
At present, BTC is the digital currency with the highest market value, and there are many services for transferring BTC assets to other public chains, such as wBTC, tBTC and renBTC. In addition, Ethereum, as the smart contract public chain with the highest market capitalization, supports cross-chain services of ETH and ERC20 assets, such as Near’s Rainbow Bridge, Binance’s Binance Bridge and RenProject’s RenEVM, etc. These cross-chain solutions generally focus on two-two cross-chains and are not open enough. Ecological project parties cannot add cross-chains of new currencies without permission, and with the increase of high-quality public chains, we are facing cross-chain needs It is no longer a dual-chain intercommunication, but an N-chain intercommunication. Using the dual-chain interoperability solution to deal with N-chain interoperability is extremely costly. N-chain interoperability needs to support N^2 double-chain cross-chain bridges. As N increases, maintenance costs will continue to increase. Therefore, the N-chain interoperability scheme with the transit chain as the hub is more suitable for the development trend of the industry.Due to the dominance of the Ethereum ecosystem, there is a certain degree of interoperability between various public chains and Ethereum, and Ethereum has become the choice of the transfer chain for various project parties to open up assets in disguise. However, if Ethereum is used as a transfer chain, all homogeneous assets including Ethereum and other public chains will be opened up, and Ethereum will be required to carry the high-frequency circulation needs of token transfers in and out. However, the limitations of Ethereums underlying performance lead to frequent transaction congestion and a surge in transaction fees, making it difficult to become a high-frequency hub.
Shuttle,first level title
It means shuttle, Flow, which means flowing water, entrusts the beautiful vision of allowing cross-chain assets to flow freely between various public chains through asset cross-chain bridges. In order to meet the needs of cross-chain hubs for high performance and transaction costs, ShuttleFlow chose the high-performance public chain Conflux as the transit chain to build a decentralized multi-chain homogeneous asset fusion governance service.On the premise of not sacrificing security, Conflux has optimized the performance of the PoW consensus algorithm to 3000+ TPS. Transactions are uploaded to the chain in seconds and confirmed in minutes, which is sufficient to meet the performance requirements of the transit chain. Moreover, the Conflux Foundation currently provides gas fee payment subsidies for all smart contracts on the chain. Users can use the contract services on the Conflux chain for free without holding any CFX, which can also meet the needs of transit chain transaction costs.
secondary title
According to the same asset, whether it is issued in the form of homogeneous assets on multiple chains, and whether the issuance chain and the transit chain are the same, we divide the fusion governance of multi-chain homogeneous assets into the following two typical types.3.1.1 Same-origin asset cross-chain when the issuance chain and transfer chain are the sameCross-chain in this scenario is the most convenient and recommended. If the project party originally issues tokens on the transfer chain, they can directly map and cross-chain to other public chains through the ShuttleFlow protocol. Taking Conflux as the transfer chain as an example, the specific process is shown in the following figure:Taking the native asset FC on the Conflux chain as an example, FC can be transferred to Ethereum with one click through ShuttleFlow under the alliances escrow acceptance, displayed in the form of mapped asset eFC and seamlessly participates in Ethereum ecological projects. On the contrary, if the cross-over eFC needs to cross back to the Conflux chain for fast and free transactions, it can also cross back to the Conflux chain with one click through ShuttleFlow, and participate in projects on the Conflux chain in the form of native assets.For the project side, since the tokens are originally issued on the Conflux chain and belong to the same source assets, the mapped assets across the chain to other public chains correspond to the original assets on the Conflux chain 1:1, and the project side does not need to worry about tokens Liquidity and acceptance risks on other public chains. At the same time, the cross-chain application of tokens does not require entry threshold. For newly launched projects, the project party can directly apply to become the cross-chain service provider of its project tokens, and formulate the rules for the entry and exit fees of the tokens. For details, please refer to 3.4 Application for cross-chain without permission in this article.3.1.2 Cross-chain homogeneous assets when the issuance chain and the transfer chain are differentThe cross-chain in this scenario needs to consider the exchange of homogeneous assets mapped to assets on the transit chain, which is more complicated. The project party may issue homogeneous assets on the same chain or simultaneously issue homogeneous assets on multiple chains. At this time, in order to realize interoperability of multi-chain homogeneous assets, it is necessary to map the mapped assets on each chain to the transit chain (such Conflux), and then use the Curve-like StableSwap exchange service to carry out asset cross-chain, the specific process is shown in the following figure:Assuming that there is a natively issued asset DOT on the Ethereum chain, and then DOT is also crossed over to the Heco and BSC chains, becoming hDOT and bDOT. At this time, if the hDOT on Heco is to be cross-chained to BSC to become bDOT, we first need to establish the mapping assets of the respective DOTs on Heco and BSC on the transit chain Conflux, such as Hecos chDOT and BSCs cbDOT. Then inject the liquidity of chDOT and cbDOT trading pairs into the StableSwap service of Conflux Curve, so that users can complete hDOT -> (ShuttleFlow) -> chDOT -> (Conflux Curve) -> cbDOT -> (ShuttleFlow) -> In the bDOT exchange process, the user does not need to perceive the intermediate process during the whole process, and only needs to pay the transfer fee of hDOT and bDOT to complete the cross-chain from Heco to BSC.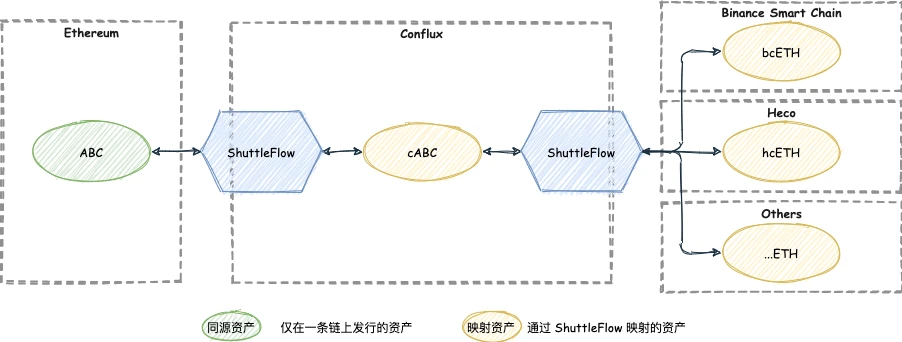 ShuttleFlow adheres to the principle of no permission, and anyone can become a cross-chain service provider of any currency on the ShuttleFlow integrated public chain. Consider the following scenario. After Ethereum issues ABC, a project party hopes to transfer ABC to other chains such as Heco and BSC. However, the cross-chain gateways of some public chains have access thresholds, which prevents ABC from logging into other chains immediately. At this point, with the help of ShuttleFlows license-free transit chain service, the ABC multi-chain interoperability requirements can be directly completed. The specific process is shown in the following figure:
ShuttleFlow adheres to the principle of no permission, and anyone can become a cross-chain service provider of any currency on the ShuttleFlow integrated public chain. Consider the following scenario. After Ethereum issues ABC, a project party hopes to transfer ABC to other chains such as Heco and BSC. However, the cross-chain gateways of some public chains have access thresholds, which prevents ABC from logging into other chains immediately. At this point, with the help of ShuttleFlows license-free transit chain service, the ABC multi-chain interoperability requirements can be directly completed. The specific process is shown in the following figure:ABC can first complete the mapping in the form of cABC through ShuttleFlow on the Conflux chain. cABC can be mapped in the form of bcABC by stepping across the chain to the BSC chain. ShuttleFlow does not require admission, and can provide services for all tokens with cross-chain needs in a decentralized manner, so that the circulation of tokens will no longer be an obstacle to the development and innovation of project parties.
secondary title
3.2 Basic principles of cross-chain
ShuttleFlow conducts asset custody based on 2/3 multi-signatures of cross-chain alliance nodes. The core operation of cross-chain alliances can be divided into two links: coinage and acceptance. Taking BTC as an example, alliance members issue 1:1 tokens on Conflux through multi-signatures. Anchoring BTCs cBTC, and providing minting and acceptance services.
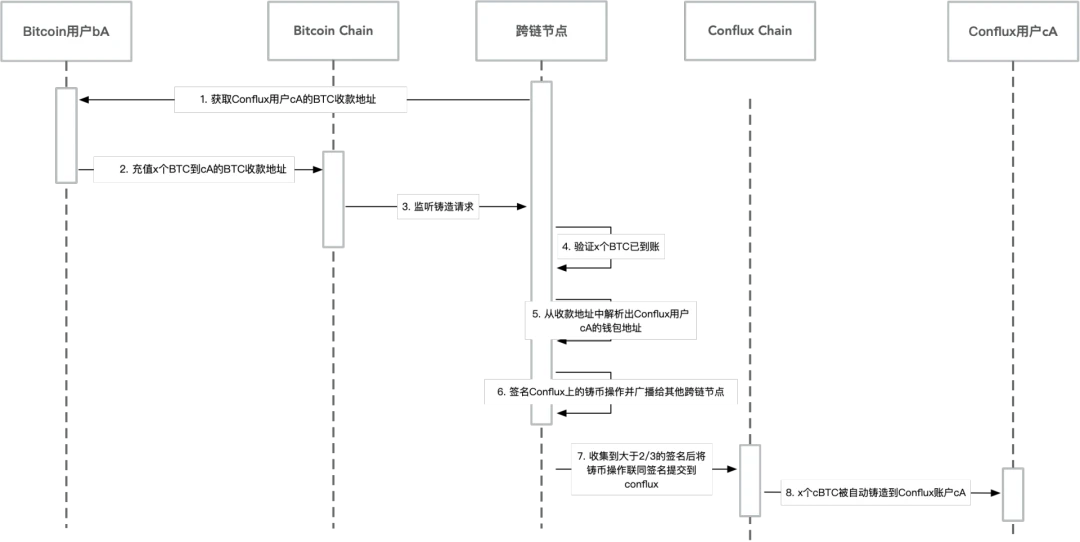 The specific operation is as follows. Create a multi-signature account on Bitcoin to lock the BTC required to mint cBTC. On Conflux, a smart contract is deployed to manage and record the minting and acceptance of cBTC. Both the multi-signature BTC account and the cBTC smart contract are jointly managed by members of the aforementioned alliance. The alliance will adopt an admission mechanism, and the joining of new members will be jointly decided by members already in the alliance offline. Each member runs a managed node. This node is responsible for monitoring and verifying the events on the Bitcoin and Conflux chains, and submitting the corresponding transaction operations after the event occurs.1. The cross-chain node obtains the receiving address of the Conflux account cA from the application scenario.2. User A deposits x BTC from Bitcoin account bA to the BTC receiving address of cA.3. The alliance node listens to the minting request in the multi-signature account on Bitcoin.4. After the alliance node listens to the request, it verifies the request: wait for the corresponding transaction to be confirmed on Bitcoin and reach Finality, and x BTCs are confirmed to arrive at the account.5. The alliance node resolves the wallet address of the Conflux account cA from the receiving address.
The specific operation is as follows. Create a multi-signature account on Bitcoin to lock the BTC required to mint cBTC. On Conflux, a smart contract is deployed to manage and record the minting and acceptance of cBTC. Both the multi-signature BTC account and the cBTC smart contract are jointly managed by members of the aforementioned alliance. The alliance will adopt an admission mechanism, and the joining of new members will be jointly decided by members already in the alliance offline. Each member runs a managed node. This node is responsible for monitoring and verifying the events on the Bitcoin and Conflux chains, and submitting the corresponding transaction operations after the event occurs.1. The cross-chain node obtains the receiving address of the Conflux account cA from the application scenario.2. User A deposits x BTC from Bitcoin account bA to the BTC receiving address of cA.3. The alliance node listens to the minting request in the multi-signature account on Bitcoin.4. After the alliance node listens to the request, it verifies the request: wait for the corresponding transaction to be confirmed on Bitcoin and reach Finality, and x BTCs are confirmed to arrive at the account.5. The alliance node resolves the wallet address of the Conflux account cA from the receiving address.6. The alliance node signs the minting operation minting x cBTC to Conflux account cA on Conflux and broadcasts it to other alliance nodes.
7. When a custodian node receives more than 2/3 of the nodes signatures for the operation, it submits the operation and the received signature to the cBTC smart contract on Conflux to perform the minting operation. Repeated submissions are ignored.
8. After the contract executes the minting operation, x cBTC will be automatically issued to the Conflux account cA.1. Conflux account cA of a consortium member submits a transaction to the cBTC smart contract and proposes an acceptance request accept x BTC to Bitcoin account bA. In this transaction, cA needs to actually transfer x cBTC to the smart contract. x cBTC will be destroyed directly. Among them, the information of Bitcoin account bA is specified in the request parameter.2. The escrow nodes in the alliance listen to the acceptance request in the cBTC contract on Conflux3. After the hosting node listens to the request, it waits for the corresponding transaction to be confirmed on Conflux to reach Finality, and x cBTCs are confirmed to be destroyed4. If the acceptance request is verified to be correct, the escrow node signs the acceptance operation accept x BTC to Bitcoin account bA on Bitcoin and broadcasts it to other custodian nodes.
5.1 When a custodian node receives more than 2/3 of the nodes signatures for the operation, it submits the operation and the received signature to the multi-signature account on Bitcoin to perform the acceptance operation, and the repeated submission is ignored
5.2 After the multi-signature account performs the acceptance operation, x BTC will be automatically accepted to the Bitcoin account bA
secondary title
3.3 No need to apply for permission to cross-chain assetsAsset cross-chain application does not require admission. Anyone or a project party can submit an asset cross-chain application to ShuttleFlow by adding the contract address of the token. It supports cross-chain tokens on Conflux and any chain, and becomes the owner of the token. Cross-chain service provider. There is only one service provider per token.Service providers rights: Service providers can set the transaction fee charged to users for each cross-chain and benefit from it. The users cross-chain handling fee parameters can be defined by the service provider, such as the amount of handling fees for crossing in and out, the minimum number of crossing in and out, and the amount of handling fees for creating new addresses. The on-chain processing cost of each cross-chain is deducted from the tokens mortgaged by the service provider, and the handling fee and new address fee paid by the user across the chain will eventually be settled to the wallet address of the token service provider.
Service provider election: If there are multiple project parties with the same token who want to become cross-chain service providers, they can campaign through the amount of pledged tokens. The person who pledges the most tokens can become the cross-chain service provider of the token.
secondary title
3.4 Alliance Governance
When a new member needs to join the alliance, all existing members cooperate to complete a multi-signature transaction, and transfer the BTC in the current multi-signature account to a new multi-signature account including the new member. When an existing member wants to withdraw from the alliance, all other existing members cooperate to complete a multi-signature transaction, transferring the BTC in the current multi-signature account to a new multi-signature account without the exiting member.3.4.2 Alliance member private key management
The small-amount minting acceptance behavior uses the private key in the hot wallet, the alliance node monitors the request in real time, automatically verifies the data on the chain, and automatically executes the signature, and the minting acceptance request can get immediate feedback.
For large-amount coinage acceptance, the private key in the cold wallet is used. After the alliance node automatically monitors the verification request, a second manual review is required. After the manual confirmation is correct, the signature is manually executed. The coinage acceptance request needs to wait for the manual review to be completed.
In Q1 of 2020, ShuttleFlow V1.0 was officially launched, and it has been running smoothly for one year, supporting 49 assets worth a total of $25 million from mainstream public chains Bitcoin and Ethereum to the Conflux chain.
Related Reading










