Messari Report: Comprehensive Analysis of Lido Liquidity Staking
Original source: Messari
secondary title
important point
Lido allows users to delegate any amount of assets to professional node operators, eliminating the challenges and risks of maintaining a staking infrastructure.
Stakers receive liquid, tokenized staking derivatives (st assets, such as stETH) to represent their claim to the underlying staking pool and its earnings.
St assets effectively release liquidity and eliminate the opportunity cost of staking, because st assets can be used on some DeFi protocols and obtain additional benefits.
first level title
1. The development status of Lido
PoS networks still have high entry barriers and opportunity costs for potential users (such as Ethereum requires a minimum of 32 ETH), including huge capital investment, technical complexity of the verification process, and long lock-up periods (locked until after the merger). The "staking-as-a-service" track was thus born, and these platforms provide holders with simple, flexible and capital-efficient staking services. The leader in this industry is Lido.
Lido is a non-custodial liquidity staking protocol for Ethereum, Solana, Kusama, Polygon, and Polkadot. Lido can not only make the access conditions of Pos more democratic, but also realize a more secure decentralized PoS network with the gradual realization of Lido's roadmap. Lido currently ranks fourth among all protocols in TVL and accounts for nearly one-third of all staked ETH.
first level title
2. How Lido works
image description
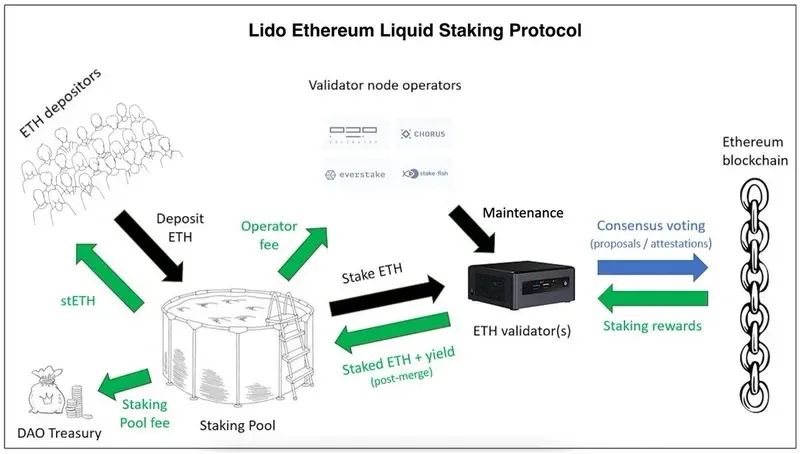
Source: @Leo_Glisic, Messari
The two main parties involved are users (stakers) and node operators (validators).
node operator
node operator
The first key component of the Liquidity Staking Protocol is the Node Operators, who do the actual staking. As of now, node operators are added and removed through the Lido DAO.
Lido's onboarding mechanism is initiated by the Node Operators Subordinate Governance Group (LNOSG), which currently consists of representatives from Lido's 21 Ethereum node operators. Node operator applications are opened when Lido is launched on a new network, or when the group feels it can tackle a network and benefit from additional node operators. The panel evaluates applicants based on several factors, including reputation, past performance, and the security, reliability, and novelty (irrelevant nature) of their setup. Once the group has evaluated a pool of applications, it submits a list of recommendations to the Lido DAO for token holders to vote on. A good set of validators is critical to Lido, as staking rewards and slashing penalties affect all stakers through the liquid staking protocol.
secondary title
pledge contract
Users entrust their pledge rights to node operators through Lido's smart contracts. The 3 main smart contracts are:
1. Node Operators Registry
image description
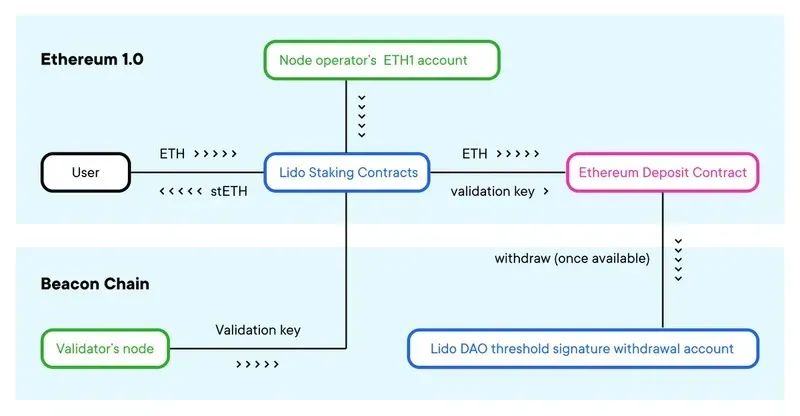
image description
Source: Lido Blog
2. The staking pool
The pledge pool is the most important smart contract in the protocol. Users can access encrypted assets, mint or burn st assets by interacting with the contract. The pledge pool uses the node operator's address and verification key to uniformly distribute the deposits to the node operator in turn. The staking pool contract is also responsible for distributing fees to the Lido DAO treasury and node operators.
3、LidoOracle
image description
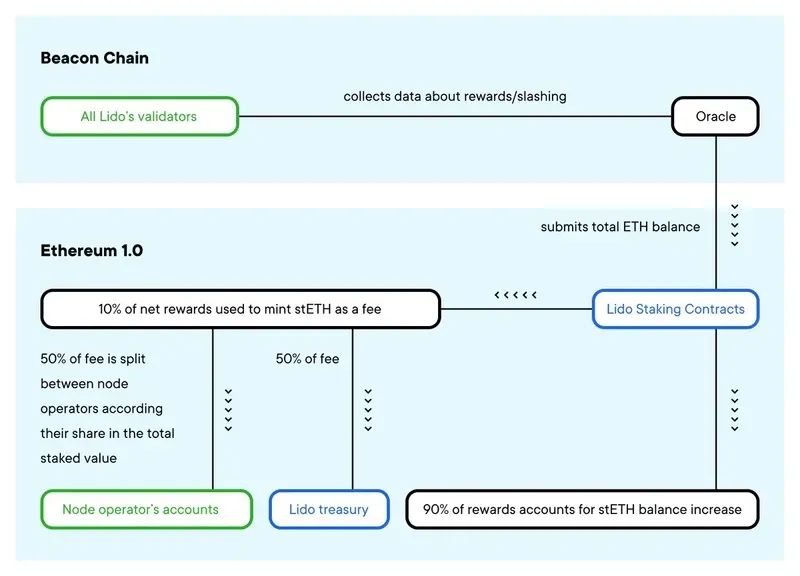
image description
first level title
3. St assets on Lido
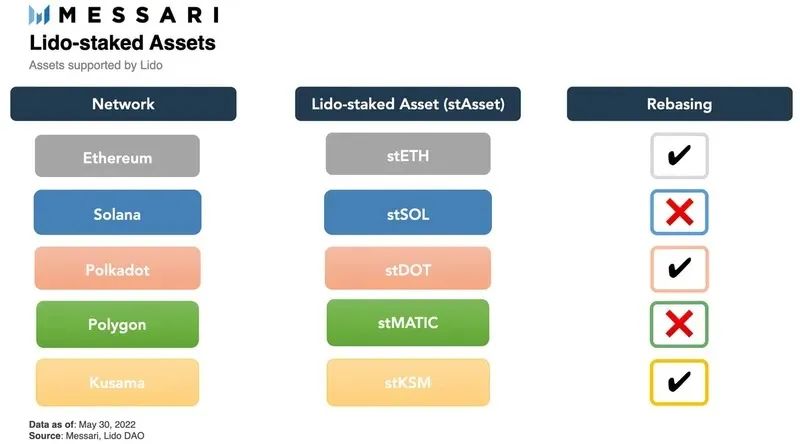
Users who deposit assets into the Lido Liquidity Pledge Agreement will receive corresponding pledge derivatives (for example, pledge ETH and receive stETH). Lido's tokenization of the pledge pool effectively unlocks the liquidity of user assets, and st assets exist in two forms: elastic supply (rebase) and shares (shares).
Elastic supply forms (such as stETH, stKSM, stDOT) mean that st assets are minted 1:1 based on deposited assets. To match the underlying asset, the anchor token balance changes daily with accumulated staking rewards. Regardless of whether st assets are obtained from Lido pledges, purchased from decentralized exchanges, or transferred from other holders, the daily balance of st assets will change according to the accumulated rewards.
The form of shares (stSOL, stMATIC) means that st assets capture pledge rewards through appreciation, and the rewards are reflected in the increase in the exchange rate between st assets and pledged assets (for example, stSOL: the exchange rate of SOL is 1.1, which means that the pledge reward of SOL is 10%). (Anchor tokens can be packaged as share tokens.)
first level title
secondary title
Integration of Lido and DEX
In order to maintain the liquidity of stETH, Lido DAO incentivizes Curve's stETH: ETH pool, which is currently the deepest AMM pool in DeFi. The measures to incentivize Lido DAO tokens (LDO) and CRV by increasing the APY (annualized rate of return) of the pool attract corresponding liquidity. Curve's pools, as well as Uniswap and Balancer, give stETH holders the ability to exit before their staked ETH is unlocked.
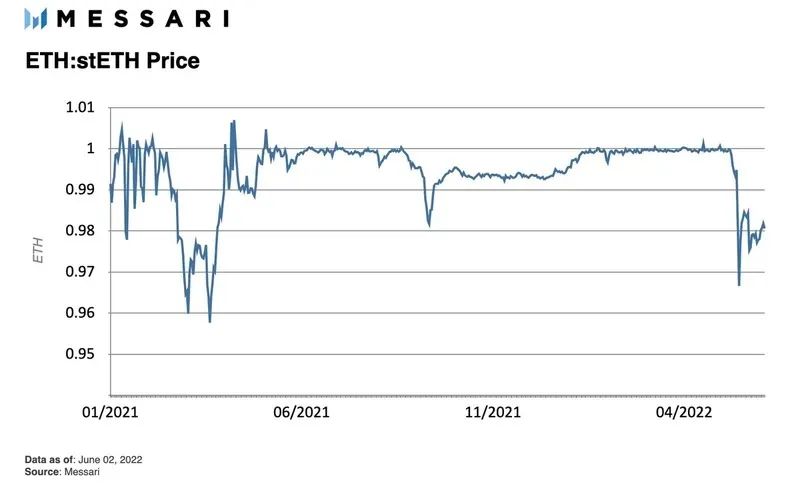
The price of 1 stETH should not really exceed 1 ETH. This cap exists because 1 ETH can always be minted into stETH via the Lido staking protocol. However, the arbitrage mechanism of stETH is not as clear-cut as other arbitrage methods.
Since stETH cannot be burned on the Lido protocol in exchange for pledged ETH, the exchange rate currently relies on market price discovery within the cap. stETH has less liquidity, less practicality (eg, cannot be used to pay gas fees), and more technical (smart contract) risks than ETH. However, the price of stETH is usually not much lower than the 1:1 conversion ratio of ETH, because the low price will attract arbitrageurs to buy and hold, and wait for the merger to unlock to obtain the interest rate difference.
Translator's note: This situation has changed. With the decline of ETH, holders' demand for converting encrypted assets into stable coins has increased. Combined with the impact of the events on the Celsius platform, the ratio of stETH/ETH pool assets has tilted, resulting in The ratio of stETH to ETH has dropped significantly. As of press time, the conversion ratio is about stETH:ETH = 0.95.
secondary title
Integration of Lido and Lending
image description
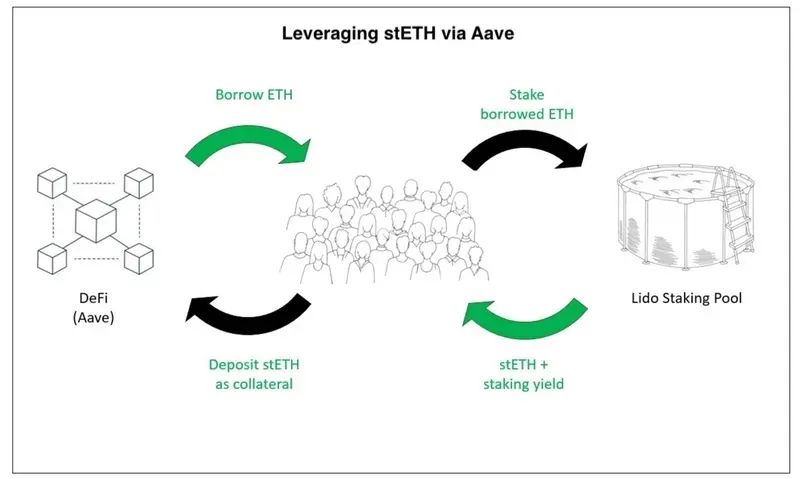
Source @Leo_Glisic, Messari
More recent structured products, such as Index Coop's icETH, have begun offering stETH leverage through Aava, while mitigating some of the risk associated with managing collateralized debt. Nonetheless, events such as hacks, governance attacks, staking cuts by multiple node operators, or a liquidity squeeze across the market could lead to serial liquidations and huge skews for the stETH/ETH trading pair. However, using leverage to borrow assets is the core capability of capital efficiency, and it is also the method Lido uses to try to solve the problem of insufficient liquidity and pledged lock-ups.
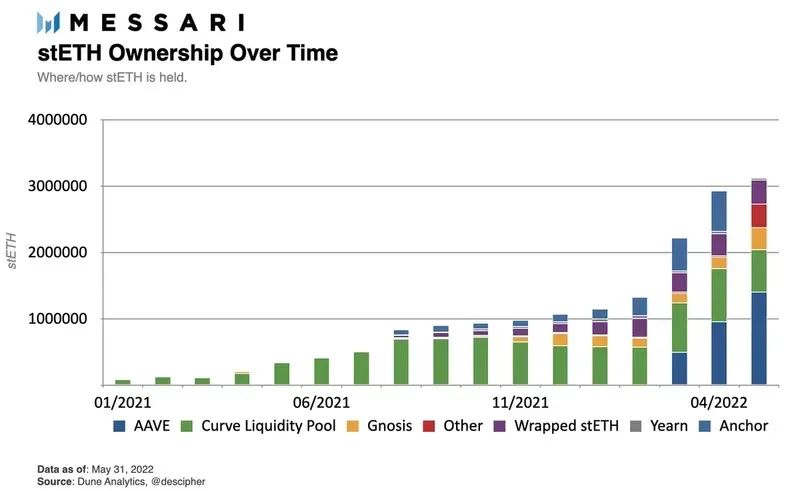
first level title
5. The competitive landscape of the pledge market
In early May, Lido briefly surpassed Curve as the DeFi protocol with the largest amount of TVL. Lido's overall TVL ranking has been around No. 4 since the UST decoupling.
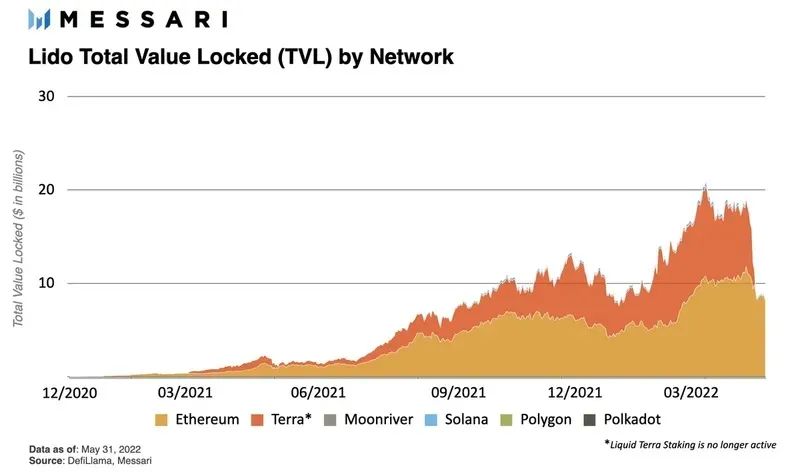
After entering May 2022, about 70% of the new ETH 2 pledged deposits come from Lido. In general, the Lido pledge ratio accounts for 32.5% of the total ETH pledge on the entire network.
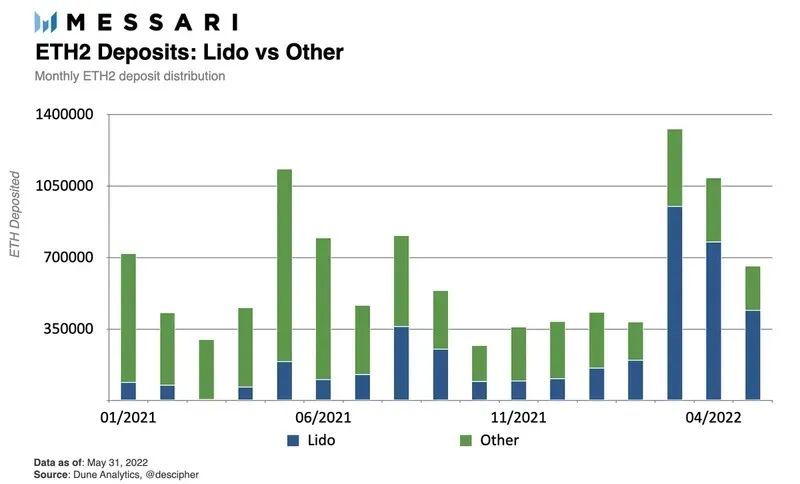
Lido has over 90% market share in the non-custodial, decentralized liquid staking arena.
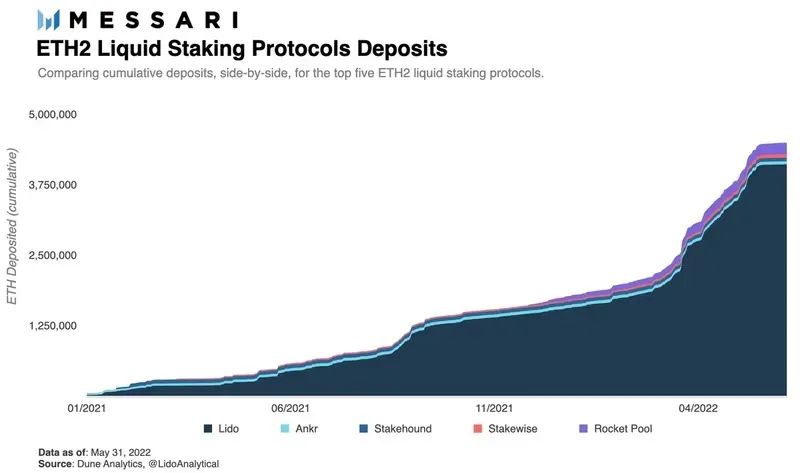
Lido's first competitor in the market, Rocket pool, has gained some market presence and publicity since its launch in November 2021. Although the ETH pledged on Rocket Pool has increased by 3 times, the market share in this segment is still less than 4%.
2 differences between Rocket Pool and Lido:
1. The biggest difference is the difference in the validator settings.While Lido's approach is to centralize validators among professional, hand-picked node operators, Rocket Pool aims to build an approval-free validator set that secures validators through economic incentives rather than validator reputation/past performance Pledge security. While Rocket Pool's system does enable broader participation in the validation process, it also introduces capital inefficiencies (such as requiring node operators to provide 16/32 ETH per validator) that make scaling difficult.
2. The second major difference is the liquidity aspect.Lido DAO currently spends more than 4 million LDO per month to stimulate the liquidity of each chain and DEX on each chain, most of which are spent on the stETH:ETH transaction pair. Rocket Pool has no liquidity incentive payouts. Lido's incentive system promotes demand for stETH by reducing slippage and creating intrinsic fundamental benefits for stETH holders.
Rocket Pool's late start, relatively poor liquidity, and low rETH prices (assets obtained after staking on Rocket Pool), make it difficult for Pocket Pool to catch up with Lido. Therefore, stETH has become the subconscious choice of users in the non-custodial liquid mortgage ETH market.
Another major player in liquidity staking ETH is Binance
The custodial nature of Binance makes it not a direct competitor to Lido. Moreover, although Binance does issue liquidity tokenized derivatives (bETH), the token does not generate additional value outside of the staker's Binance wallet, which is much worse than stETH and rETH.
Taken together, the three largest custodial staking solutions (Kraken, Coinbase, and Binance) collectively deposited close to 2.7 million ETH, roughly 60% of Lido's stake. Going forward, this gap will only grow, as Lido's recent new staking accounts for the vast majority (70%) of ETH 2's new staking.
ETH staking rewards are undoubtedly Lido's main source of income, and Solana staking embodies the aspect of Lido's multi-chain expansion. First of all, Lido is not the winner of the liquid staking segment on Solana, where Marinade is the ruler. The SOL stake on Marinade is currently about 2.5 times that of Lido. However, from a broader perspective, liquid staking is just a small market that is easily overlooked on Solana, and the two largest protocols in this track only account for 2.5% of the total staking amount. In ETH 2, the two largest liquidity staking protocols, Lido and Rocket Pool, accounted for 36% of the total staked amount.
first level title
6. Risk
Given Lido DAO's heavy reliance on Ethereum, any setback in the timeline for the merger or its implementation could have disastrous consequences. Although this article does not discuss Ethereum 2.0 in depth, adverse events during the merger process will hit the ETH:stETH conversion ratio, such as further extension of the transition period, or a crisis of trust surrounding the transition itself.
Given the rehypothecation of stETH, continuous liquidations may put further downward pressure on the price of stETH. However, if the merger goes well, Lido will play a central role in the largest PoS chain.
The choice of progressive decentralization allows Lido to optimize for speed and scalability. While Lido has a first-mover advantage over rivals such as Rocket Pool, Lido's smaller set of node operators has raised concerns about centralization on ethereum.
The LNOSG is a committee of insiders that controls the initial planning process for node operator selection. Even though the finalized list will be voted on by the Lido DAO, the LDO token centralizes insider ownership. This also resulted in 21 professional node operators controlling all of Lido's ETH shares on the Ethereum Beacon Chain, accounting for 32.5% of the total ETH staked. In addition, the withdrawal certificate of ETH pledged before July 15, 2021 is controlled by an 11-person multi-signature, and it can be passed as long as there are 6 signatures. About 600,000 ETH (roughly 15% of the total Lido ETH 2 stake currently) could be locked if more than 5 signers lose their keys or act roguely. The Lido DAO team plans to migrate this part of the pledged assets to the 0x01 (upgradable smart contract) withdrawal certificate as soon as possible, as soon as possible.
In addition, Lido has related plans in place. Part of the plan involves adding permissionless authentication. Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) will allow Lido to onboard new, unknown, untrusted node operators by simply pairing them with trusted whitelisted node providers. These new validator groups will work together to propose and attest blocks while maintaining mutual checks.
epilogue
epilogue
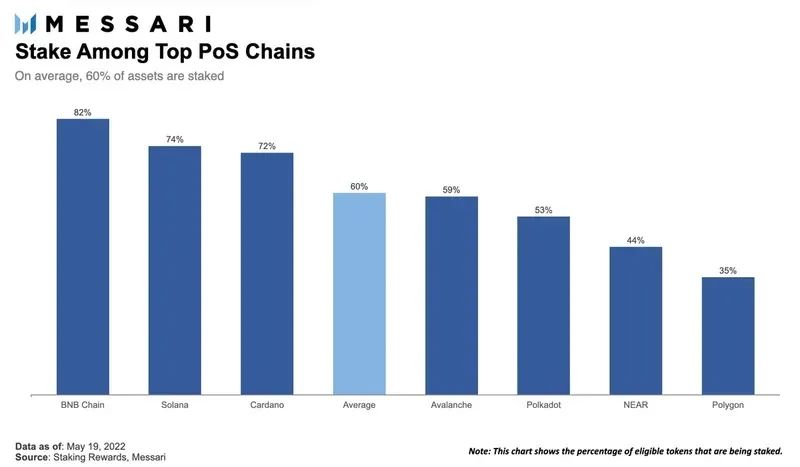
Currently, only about 10% of all ETH in circulation is staked. After the merger, stakers can choose to withdraw funds, and the staking reward may also be doubled. If the ratio of ETH pledged reaches the average level of the current top PoS public chains, then the overall pledge of ETH may also increase by six times. In addition to benefiting from the uptrend, Lido will allow stakers to avoid potentially months-long validator activation queues and start earning staking income immediately. Whether it’s offering lower yields, or using some of its treasury holdings to fill the gap, Lido has another huge opportunity that it could use to solidify itself as the market leader in Ethereum’s liquidity staking track.
Original link



