First Class Warehouse Research Report: A Comprehensive Interpretation of the Public Chain Project Aptos
Original Author: First Class Warehouse
The goal of Aptos is to build a scalable, secure, trustworthy and upgradeable smart contract platform, using BFT consensus mechanism and parallel computing mechanism to achieve better performance. Improve the mechanism of leader rotation, reduce the impact of a single node failure on the network, and improve the security of network operations. The project has received USD 350 million investment from investment institutions such as A16Z, and the team has strong research and development capabilities. It is currently in the testnet stage, ecological construction is in its infancy, and the developer community is active. Follow-up attention will be paid to the launch of the mainnet of the project and the ecological development.
The Aptos token APT was launched on major exchanges on October 19th. We chose to publish the research report, and on the basis of the original text, we supplemented the latest official token economic model (chapter 4), financing news (section 2.2) and The situation of the test network (Table 3-2), the rest will not be changed, hoping to help readers understand its fundamentals.
Investment Summary
The competition on the public chain track is fierce, and there is a lot of room for imagination.Ethereum has significant ecological advantages and a prosperous ecology; new public chains such as Solana have established relatively rich ecology. Among the competitors of Aptos in the same period, there are public chains with a high degree of similarity in the mechanism of the Meta system such as Sui and Linera, as well as other modular and specialized public chains.
Aptos' goal is to build a scalable, secure, trustworthy and upgradeable (scalability, safety, reliability, and upgradeability) smart contract platform that can meet the needs of billions of users in the future.
In terms of team and funds, the Aptos team is strong and has received sufficient funds.The team is recruiting talent, expanding business, and continuing to operate in a bear market environment.
Technically, Aptos focuses on performance scaling and user security issues.
The main innovations of Aptos in terms of technology include: 1) The new smart contract programming language Move, which is a programming language more suitable for digital assets and adapted to the needs of the blockchain. 2) Improve the leader rotation mechanism, increase the node reputation system, and reduce the impact of a single node failure on the network. 3) Developed the Block-STM smart contract parallel execution engine to improve the efficiency of transaction execution. 4) Adopt an appropriate node structure and develop a series of different state synchronization protocols to achieve effective and rapid state synchronization.
The main measures for user security include: 1) Identify the transaction process, including the sender's serial number, transaction expiration time, and the specified chain identifier, so as to make the transaction specific; 2) Realize secret key rotation and Mixed hosting reduces the risk of private key leakage and loss; 3) Authorized signatures are transparent, clarifying possible consequences and reducing the risk of fraud.
Compared with Ethereum, Aptos adopts BFT consensus mechanism and parallel computing to achieve better performance. Compared with Solana, Aptos improves the leader rotation mechanism instead of the leader tree verification mechanism, which reduces the impact of a single node failure on the network and improves the security of network operations. Aptos has chosen a more balanced position.
Ecologically, the ecological construction of Aptos is in its infancy, the team has taken active measures in terms of project marketing and community management. Aptos currently has 160 projects under construction and testing, and the community is active.
The main risks of Aptos include: 1) Insufficient decentralization. Facing the "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain, Aptos tends to be high-performance, and the decentralization of nodes is weak. 2) Technological innovation is limited. Aptos mainly improves the performance of the public chain. The main innovative technologies are smart contract programming language and account types, and no more disruptive technologies are proposed. 3) The innovation of Aptos ecological projects is insufficient, and the advantageous projects have not yet appeared, and many projects come from other ecology such as Solana. Compared with the other two public chains of the Meta series, Aptos has a certain first-mover advantage in ecological construction. However, due to the highly similar technology, it may cause multi-chain deployment and similarity of ecological projects. 4) The valuation of VC investment is high. In the financing in July 2022, Aptos' valuation reached 2.75 billion US dollars, while Solana's current market value is 10.8 billion. From the perspective of the bear market, Aptos' valuation is too high. Moreover, there may be new financing in the follow-up before entering the secondary market, which will further increase the valuation. However, Solana's historically high market capitalization is about $76 billion, and if it enters the next round of bull market, the upper limit of the project's market capitalization will also increase. 5) The risk that the main network will fall short of expectations. At present, the main network has not yet landed, and there may be the following risks: first, it cannot be deployed and launched as scheduled; second, the user experience is not good after it goes online; third, it lacks strong projects and cannot drive users and funds into the market.
Continue to pay attention to the implementation of the Aptos main network, including the construction and distribution of nodes and the actual operating efficiency of the network. Pay attention to the ecological construction situation, especially the emergence of advantageous projects. Advantageous projects can bring a lot of attention, funds, and sudden wealth effects, thereby quickly increasing the popularity and TVL of the public chain.
1. Basic overview
1.1 Project Introduction
Aptos is a Layer1 public chain project, and its goal is to build a scalable, safe, trustworthy and upgradeable (scalability, safety, reliability, and upgradeability) smart contract platform.
Aptos is inextricably linked to Facebook (later renamed Meta). Also because of this connection, it has become a blockchain project that has attracted much attention. Facebook once formed a team to develop the stable currency project Libra (later renamed Diem), but due to regulatory issues, it failed to continue. The teams involved in the development of Diem have gradually become independent, established their own teams, and developed new public chain projects. Aptos is one of them.
1.2 Basic information
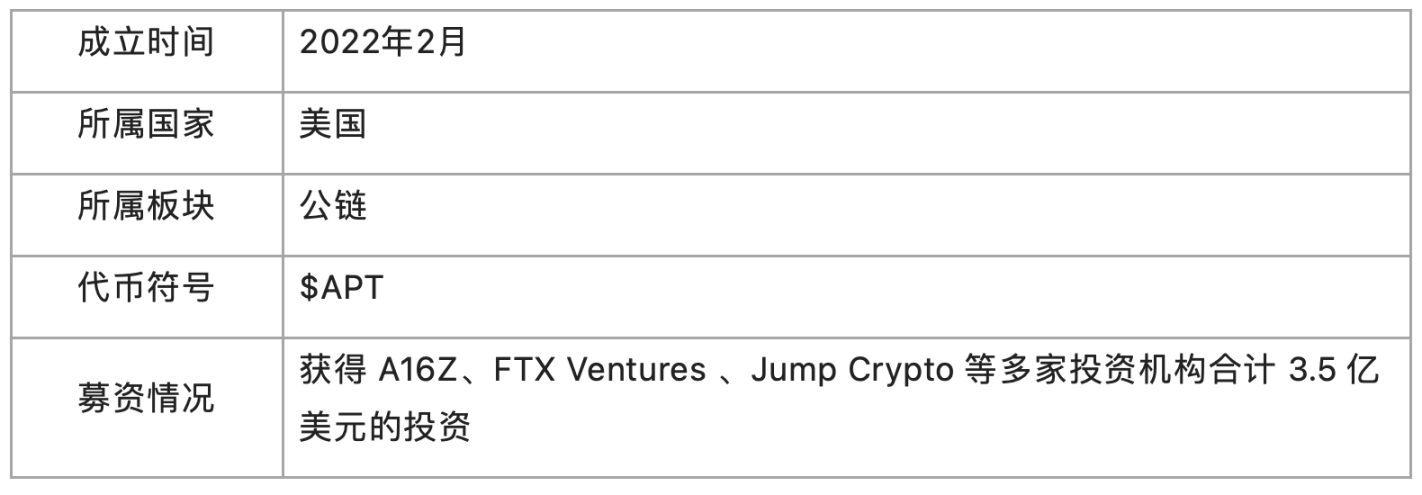
2. Project details
2.1 Team [1]
Aptos Lab is headquartered in California, USA, with decentralized offices and employees all over the world. Its founding members and some core researchers and developers are introduced as follows:

Mo Shaikh, founder and CEO, graduated from Hunter College with a major in accounting, and a Master of Business Administration (MBA) from the Simon Business School at the University of Rochester. From 2007 to 2017, he successively worked in KPMG, Blackstone, Boston Consulting Group and other institutions, engaged in real estate investment analysis and equity investment analysis. From 2017 to 2020, he founded and served as CEO of Meridio, a blockchain-based platform for investing and trading partial real estate with liquidity. Responsible for strategic partnerships in Meta and Novi from May 2020 to December 2021. Since December 2021, he has served as the founder and CEO of Aptos.

Avery Ching, co-founder and CTO, Ph.D. in computer engineering from Northwestern University, has served as the chief software engineer of Yahoo, Facebook and Novi. From September 2011 to December 2021, he served as the chief software engineer at Facebook for more than 10 years, and was the technical director of the Novi team, an encryption platform under the original Meta, focusing on the development of various aspects of blockchain technology. Maintain the Diem blockchain. Since December 2021, he has served as the founder and CTO of Aptos.

Yuxuan Hu, founding team member, software engineer. Master of Computer Science from Harbin Institute of Technology. Since 2009, he has successively worked in Baidu, Instagram, Novi, and Aptos, and his main research direction is distributed storage and system efficiency.

Alin Tomescu, founding team member, cryptography scientist. From 2013 to 2020, he worked as a research assistant at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology for a Ph.D., focusing on cryptography, public key distribution, authenticated data structures, secure communication, and secure network applications. From February 2020 to February 2022, work as a postdoctoral researcher and research scientist at cloud service provider VMware. In February 2022, enter Aptos.

Rati Gelashvili, founding team researcher, Ph.D. from MIT, with expertise in concurrent, parallel and distributed algorithms and data structures, worked as a senior research scientist at Novi from May 2020 to January 2022.

Josh Lind, the founding team engineer, received his Ph.D. from the Large-Scale Data and Systems (LSDS) Group and the Center for Cryptocurrency Research and Engineering (IC3RE) at Imperial College London. The PhD focuses on improving security and privacy in large-scale distributed systems using trusted hardware. He has worked as a research assistant and research scientist in Google, Meta, Navi and other institutions.
visible,Aptos' team has strong research and development capabilities.According to the information disclosed by LinkedIn, the project currently has 64 employees. Aptos' team includes computer experts from leading Internet companies, universities, and research institutions. In addition to the research experts listed above, there are more than 20 engineers, most of whom have Facebook work experience.
The team is expanding rapidly. In the past 6 months, the team has continued to expand, the total number of employees has more than tripled, and the average tenure is now 0.3 years. At present, there are still 34 positions on its official website for external recruitment, accepting telecommuting, and the types of positions involve external cooperation, marketing, data experts, computer engineers, designers, product managers, etc.
2.2 Funding
image description
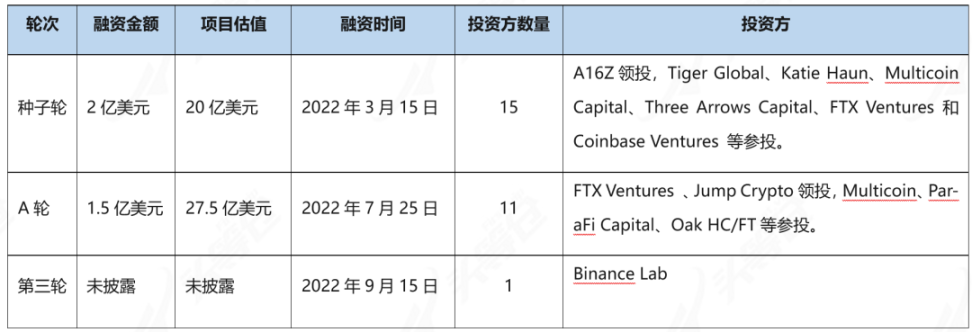
Table 2-1 Aptos Lab's financing situation[2]
In addition, Dragonfly partner Haseeb revealed on Twitter on September 29, 2022 that Dragonfly has made a strategic investment in Aptos. [3]
image description
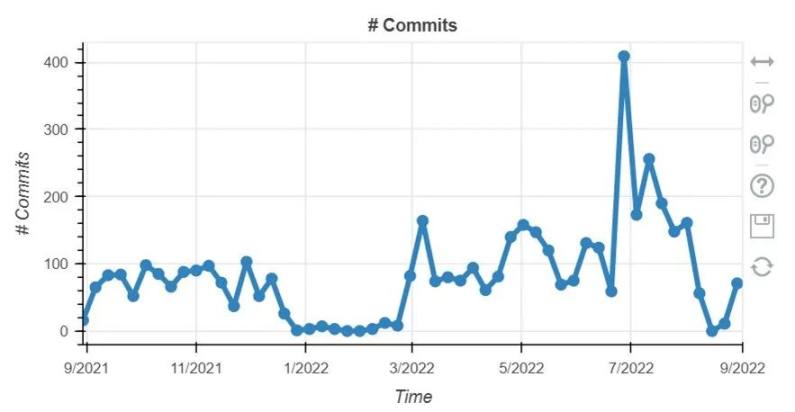
image description
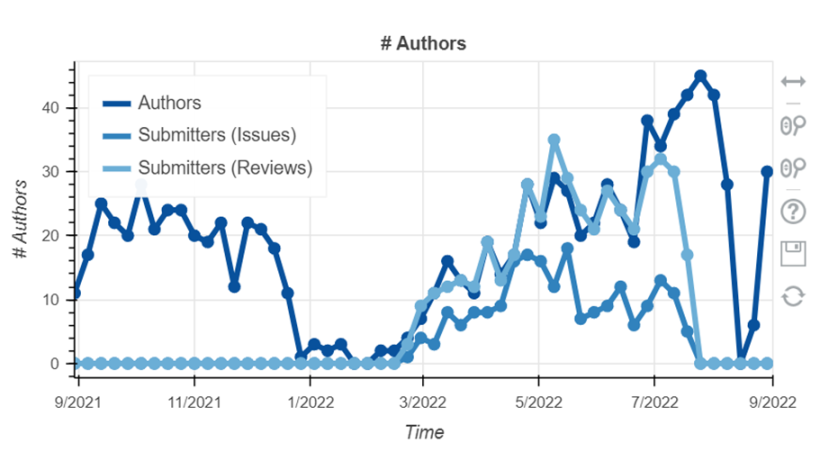
Figure 2-2 Aptos code contributors
The source code of Aptos is open source on Github, and the project code update is active. As can be seen from the above figure, the Aptos code is continuously updated, with more than 14,000 submissions in the past year, and the number of code submissions will reach its peak in July 2022. The number of developers has gradually increased since March 2022, reaching a maximum of more than 40 people. This basically matches the pace of team expansion and the launch time of the testnet.
2.4 Technology [5]
2.4.1 Target Vision and Technical Framework
The goal of Aptos is to build a scalable, secure, trustworthy and upgradeable (scalability, safety, reliability, and upgradeability) smart contract platform. This goal implies the understanding and response to the "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain.
The "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain was proposed by Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum. It refers to the fact that the public chain cannot simultaneously achieve scalability (Scalability), decentralization (Decentralization), and security (Security). Get second.
To put it simply, Ethereum and Bitcoin belong to the pursuit of decentralization and security at the expense of scalability. New public chains such as Solana are pursuing the ultimate scalability, and lack decentralization and security.
image description

Table 2-2 Aptos goals and corresponding technical means [6]
And according to the Aptos white paper,The core principles of its technical framework include:
1) Fast and secure transaction execution through the new smart contract programming language Move.
2) Pipelining and parallelizing applications to achieve high throughput and low latency.
3) Support the processing of arbitrarily complex transactions through the Block-STM parallel engine.
4) Optimize performance, decentralize, and realize reputation tracking through fast equity weight validator rotation.
5) Upgradability and configurability are first-level principles, embracing new technologies and new use cases.
6) Modular design to achieve component-level testing, which can improve safety and operability.
The core technical parts involved in the above are explained below.
2.4.2 Development programming: the new smart contract programming language Move
Move is a new smart contract programming language. Originally developed by Facebook, Inc., it is a next-generation language for secure, sandboxed, and formally verified programming. Its first use case was the Diem blockchain, for which Move provided the basis for its implementation.
The Aptos project mainly emphasizes the security and flexibility of the language. The Move ecosystem includes compilers, virtual machines, and many other development tools. Move is inspired by the Rust programming language, which makes ownership of data clear in the language through concepts such as linear types. Move emphasizes resource scarcity, conservation, and access control. The Move module defines the lifecycle, storage and access modes of each resource.For example, in Solidity, token assets are no different from other numbers, they are a string of data that can be modified at will, so hackers may attack and modify the number of digital tokens issued to unlimited. In Move, the number of digital tokens is fixed as an asset, and it is basically impossible to attack the number of its issuance. Digital tokens cannot be copied, but can only be transferred.
The Move language also allows for secure resource management and verifiable execution on the blockchain. Transaction execution is deterministic, closed and quantifiable. Determinism and closure mean that the output of a transaction execution is completely predictable and based only on the information contained in the transaction and the current ledger state. Scalability prevents denial of service attacks. A denial of service attack refers to a malicious party sending a large amount of useless information to a specific website, causing the server of the website to be overloaded and paralyzed, so that it cannot provide services to normal users. The Move language also supports upgradability and full programmability of modules. This capability also allows it to support upgrades to the Aptos blockchain.
It should be noted that the Move language is a new language, and developers need to learn and be familiar with it. At the same time, if other ecological projects want to migrate, they also need to use the Move language for programming. Ecological creators need to learn cost and time.
2.4.3 Consensus mechanism: Diem BFT version
Consensus mechanism (also known as consensus protocol or consensus algorithm) refers to the mechanism that keeps distributed systems (computer networks) working together and keeping accounts securely. More specifically, the mechanism by which blocks (transactions) are ordered and confirmed among a set of validators.
Different blockchains, based on different goals, may adopt different approaches. Bitcoin adopts a proof-of-work mechanism (PoW). Nodes perform massive calculations, collide with random numbers, and distribute accounting rights. POW has the highest degree of decentralization, the largest resource consumption, and relatively low performance efficiency. Early proof of stake (PoS), according to the proportion and time of tokens held by nodes, reduces the difficulty of mining and speeds up the speed of finding random numbers. The degree of decentralization of PoS is reduced, resource consumption is reduced, and performance efficiency is improved.
Aptos uses the BFT mechanism. Diem BFT is a production-grade, low-latency Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) engine developed by Aptos. This consensus protocol is a derivative version of HotStuff, the underlying consensus protocol that Diem originally used. In order to improve efficiency, the BFT mechanism only needs to reach a threshold number of nodes to participate in consensus and verification. Diem BFT total verification nodes ≥ 3f + 1, and there can be at most f wrong verifiers. In other words, only ≥ 2f + 1 nodes need to be verified to confirm.
In the past three years, Diem BFT has implemented the fourth iteration of the protocol. The main contents of the iteration include:
1)The block submission time is shortened, requiring only two network round trips to commit, achieving sub-second finality.
2)Added node reputation system[7], for checking on-chain data and automatically changing leader rotation. It is possible to analyze and judge the non-response of the verifier without manual intervention.
Under the BFT consensus, the leader rotation mechanism is usually adopted, and the leader proposes the ordering of the blockchain. Most of the rotation mechanisms do not take into account the state of the leader, that is to say, a faulty node may be selected as the leader, and once there are too many faulty nodes, the speed of the blockchain will be affected.
Diem BFT improves the leader rotation mechanism and adds a node reputation system (State-Machine Replication, SMR). The system focuses on the liveness and validity of nodes. Liveness refers to tracking active parties by checking on-chain data and electing leaders from them. When the leader node is attacked or the network is interrupted, it may not be able to perform its tasks, but the reputation system on the chain will quickly find a suitable node to act as the leader node and start working, so as to avoid the large-scale impact of the attack on the network.
Furthermore, Aptos' protocol clearly separates network liveness from security. In the event that the network is unlinkable or the non-secure core is compromised in some way, as long as the honesty guarantee of the BFT mechanism is maintained, there is no need to fork the blockchain. The security of the consensus protocol has been audited and formally verified.
Aptos has begun research and development on the next iteration of the consensus protocol to advance transaction propagation, and plans to use this technology to upgrade the testnet later this year.
2.4.4 Calculation execution: pipeline and parallel processing, using Block‑STM parallel execution engine
When we describe the system performance of a public chain, the two indicators usually used are throughput and finality.Throughput (TPS) refers to the number of transactions processed per second, and finality (Finality) refers to the time required from the client to create and submit a transaction to the other party to confirm the transaction.
image description
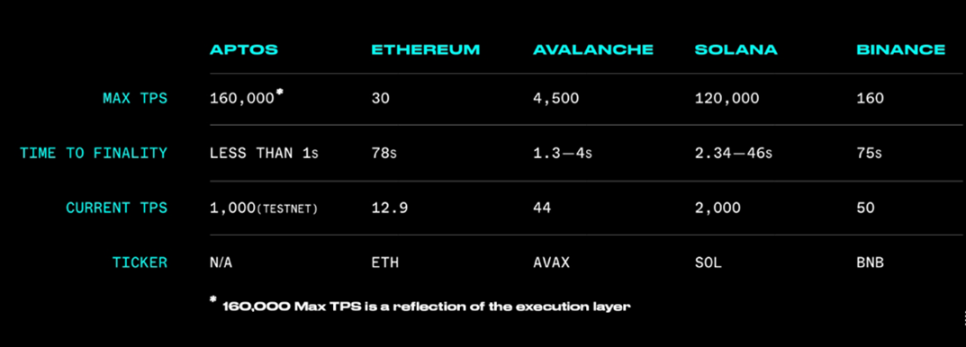
Figure 2-3 Comparison of TPS between Aptos and other major public chains [8]
In order to achieve the described high performance, Aptos intends to implement the following measures:
1) Consensus protocol is completely separated from transaction execution
The consensus protocol accepts the proposed ordering of transactions. Validators execute transactions in different protocols away from the critical path, and agree on the final transaction ordering and execution results. Higher throughput and latency can be achieved by eliminating the co-dependencies that come with combining consensus and execution. Aptos Labs is working on this decoupling for the next iteration of the protocol, which is expected to be integrated into the testnet later this year.
It should be noted that there is no detailed description of the specific method of transaction ordering in the currently disclosed information. In addition, in a distributed system, by giving a reliable global time to determine the time order, the system efficiency can be improved. Solana also uses this approach. However, the premise that this method is applicable is that most of the nodes are good faith nodes. If the nodes are malicious, the system is vulnerable to attack.
2) Block-STM parallel engine [9]
Aptos Labs designed an in-memory smart contract parallel execution engine called Block-STM. STM stands for Software Transactional Memory, a new engineering approach that enables flexible transactional programming of synchronous processes.
In Ethereum, the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is single-threaded, with only one core processing transactions. When there is a transaction peak, because there is only one thread, a large number of transactions accumulate, and it takes a long time to digest these transaction volumes, resulting in transaction delays. In order to solve this problem, new public chains such as Solana try multi-threaded concurrent processing. Aptos has also adopted this approach. According to its current test, the highest is 32 threads. [10]
image description
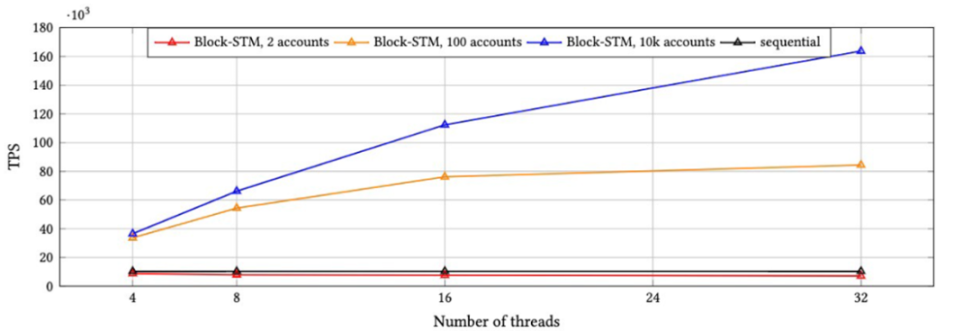
Figure 2-4 Performance of Block-STM under different threads
It can be seen from the above figure that the TPS executed sequentially is not affected by the number of threads, and the TPS is 10,000. When there are 4 threads, the highest TPS of Block STM is 40,000. When there are 16 threads, the highest TPS of Block STM is 110,000. When there are 32 threads, the highest TPS of Block STM is 160,000. It can be seen that the parallel engine improves the transaction speed. When the number of users increases, the advantage of 32 threads becomes more obvious, which can provide higher TPS.
3) Optimize the authentication data structure
To address the scalability issues posed by writing Merkle trees to persistent storage, Aptos is developing an authenticated data structure that aims to be a scalable, database-friendly solution. This will be achieved by evaluating higher branching factors, access pattern optimization caching, and careful versioning.
2.4.5 State synchronization: full nodes, light nodes and verifiers in the network can effectively synchronize the data of the whole network [11]
State synchronization is a protocol that allows non-validating nodes to distribute, verify and persist blockchain data and ensure that all nodes in the ecosystem are in sync.
image description
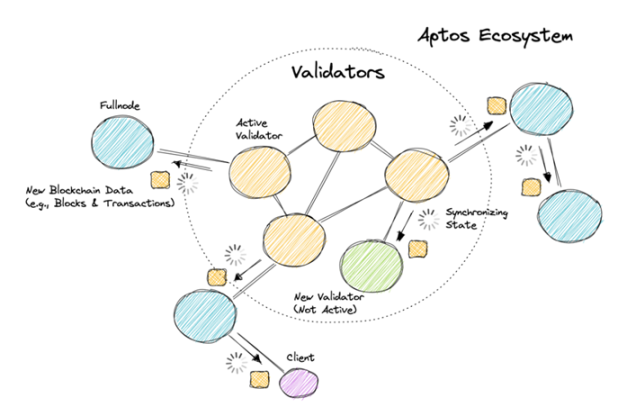
Figure 2-5 Aptos node system
The figure above shows Aptos' node system. Its core nodes are connected to each other, the dotted circles are verifiers, the yellow circles are active verifiers, and the green circles are new verifiers (or inactive verifiers). Outside the circle, there are full nodes, clients and other nodes that do not participate in verification.
How to effectively synchronize is very important to the blockchain, the main reasons are as follows:
1) Data correctness.State synchronization is responsible for verifying the correctness of all blockchain data during the synchronization process. This prevents malicious peers and adversaries in the network from modifying, censoring, or falsifying transaction data and presenting it as valid.
2) Affect user experience.State synchronization is responsible for propagating data to peers and clients when validators execute new transactions. If state synchronization is slow or unreliable, peers will perceive long transaction processing latencies, artificially inflating finality times.
3) Affect consensus reaching.Validators that crash or fall behind other validator sets rely on state synchronization to bring them back up to speed. If state synchronization cannot process transactions as quickly as consensus enforces, a crashed validator will not be able to recover. New validators will not be able to start participating in the consensus, and full nodes will not be able to synchronize to the latest state.
4) Affect the realization of decentralization.Having a fast, efficient, and scalable state synchronization protocol allows for: A. faster rotation of the active validator set, as validators can move in and out of consensus more freely; B. more potential validators in the network to choose from; C. . More full nodes go online quickly without waiting for a long time; D. Reduce resource requirements and increase heterogeneity. All these factors add to the decentralization of the network and help to scale the blockchain both in size and geographically.
To achieve more efficient state synchronization, Aptos has taken the following measures:
1) Support a series of different state synchronization protocols, and match different CPU capacities and network bandwidths between different protocols. Nodes can be selected according to needs, thus encouraging more nodes to participate in the Aptos system.
2) Support low-cost full nodes, which can synchronize transactions and their execution results. Signed by a certain number of validators, allowing nodes to skip calculations and update results directly from the executed ledger state.
3) The client can use the top-level transaction accumulator to obtain the latest submitted transaction without downloading the full ledger like most blockchains to obtain the latest ledger. Also allows for cheap pruning of previous transactions and ledger history if required.
At this stage, Aptos state synchronization throughput has increased by 10 times, latency has been reduced by 3 times, and peers can verify and synchronize more than 10,000 transactions per second.
2.4.6 Safe User Experience
Aptos' goal is to bring Web3 to the general public, thus, emphasizing transaction security for users. At present, blockchain fraud occurs frequently, and measures need to be taken to increase the security of user transactions:
1) Transaction feasibility protection
When the user trades, he needs to sign the authorization. Sometimes users inadvertently sign transactions they didn't intend to complete, or without adequate consideration that transactions could be manipulated. To mitigate this risk, Aptos limits the viability of each transaction, protecting signers from infinite validity. The Aptos blockchain currently offers three different protections: the sender's sequence number, the transaction expiration time, and an enacted chain identifier.
A transaction's sequence number can only be submitted once for each sender's account. If the sender observes that the sequence number of his own account is greater than or equal to the sequence number of a transaction, then either the transaction has already been submitted, or the transaction will never be submitted (because the sequence number used by the transaction has been replaced by another transaction). transaction used).
Blockchain time is recorded with sub-second precision. If the blockchain time exceeds the expiration time of a transaction, then either the transaction has already been committed, or the transaction will never be committed.
Each transaction has a specified chain identifier to prevent malicious parties from duplicating transactions in different blockchain environments.
2) Secret key rotation and hybrid hosting
Aptos accounts support key rotation to help reduce the risk of private key leakage, remote attacks, and future cracking of existing cryptographic algorithms. Users can delegate the ability to rotate account private keys to one or more custodians and other trusted entities, and then define a policy through the Move module that enables these trusted entities to rotate keys under specific circumstances. For example, an entity might be a k-out-of-n multisig key held by many trusted parties, thereby providing key recovery services to prevent loss of user keys. Compared with other key recovery schemes such as cloud backup and social recovery, Aptos' key management scheme is on-chain and more open and transparent.
3) Improve the transparency of pre-signed transactions
The current wallet is not transparent enough for signatures. Many signatures are not in clear text, and users cannot clearly know the consequences behind each signature. This has led to frequent malicious transactions being tricked into signing, resulting in the theft of funds.
Summarize:
Summarize:
The founding team of Aptos is from Facebook, and previously participated in the development of the Diem blockchain. The team members have relevant knowledge reserves such as cryptography, distributed algorithms, data structure and storage, and secure communication, and have strong research and development capabilities. It has received a total of US$350 million in investment from multiple investment institutions such as A16Z, FTX Ventures, and Jump Crypto, and has sufficient development funds.
Aptos' goal is to build a scalable, secure, trustworthy and upgradeable (scalability, safety, reliability, and upgradeability) smart contract platform that can meet the needs of billions of people in the future for the blockchain. Its technical focus is on scalability and security.
The main innovations of Aptos in terms of technology include: 1) The new smart contract programming language Move, which is a programming language more suitable for digital assets and adapted to the needs of the blockchain. 2) Improve the leader rotation mechanism, increase the node reputation system, and reduce the impact of a single node failure on the network. 3) Developed the Block-STM smart contract parallel execution engine to improve the efficiency of transaction execution. 4) Adopt an appropriate node structure and develop a series of different state synchronization protocols to achieve effective and rapid state synchronization.
Aptos' main measures in terms of user security include: 1) Identify the transaction process, including the sender's serial number, transaction expiration time, and the specified chain identifier, so as to make the transaction specific; 2) Implement the secret key on the chain Rotation and mixed hosting reduce the risk of private key leakage and loss; 3) Authorized signatures are transparent, clarifying possible consequences and reducing the risk of fraud.
Many projects are already aware of these security measures. For example, the clear culture of transaction authorization, some wallets and trading markets have been initially realized. However, if we can realize this problem from the public chain level, and systematically standardize account key management, transaction process management, authorization management and other aspects, it should be able to further improve the security of user transactions and improve public security. The ease of use of the chain reduces the learning threshold and cost for users to enter.
From the perspective of the overall structure, 1) Aptos is not sufficiently decentralized. Facing the "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain, Aptos chose high performance, and the degree of decentralization of nodes was insufficient. It is necessary to continuously observe the operation and security of the test network and the main network. 2) Technological innovation is limited. Aptos mainly improves the performance of the public chain and does not propose more disruptive technologies.
3. Development
image description
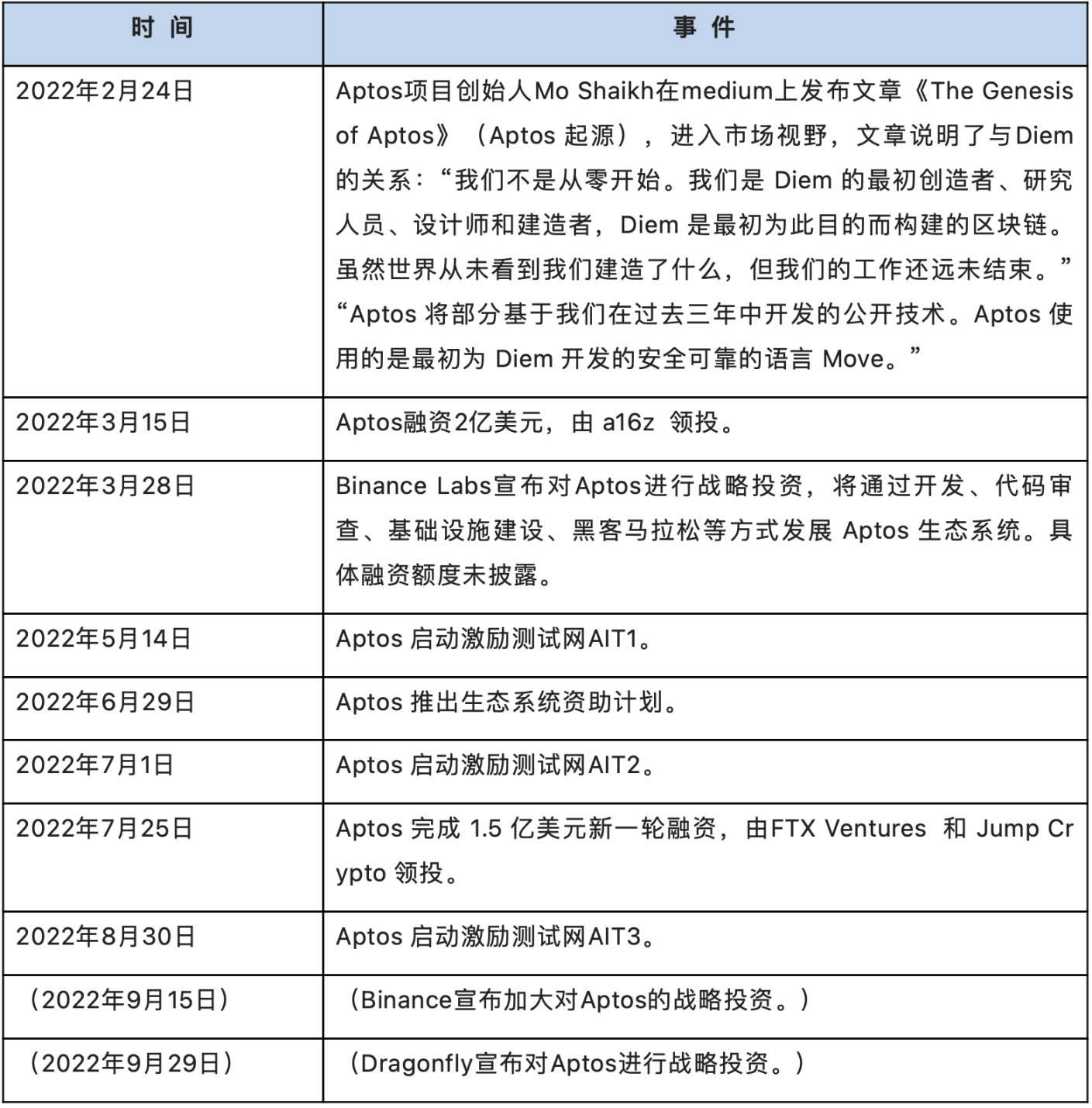
Table 3-1 Major events of Aptos [12]
3.2 Status
Currently, Aptos is undergoing the third round of testing. At the same time, various operational activities are being carried out to attract developers, projects and users to Aptos and build an ecosystem. For the development of the public chain, in addition to technology and performance, ecological construction is crucial. The participation of a large number of developers and the emergence of innovative projects can attract enough users to enter, thus forming a positive cycle and continuously developing and growing.
3.2.1 Testnet
image description
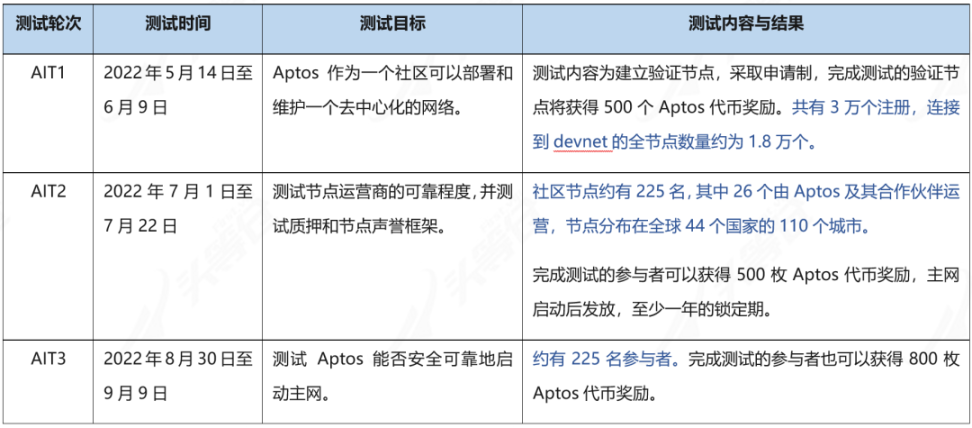
Table 3-2 Aptos test situation [13]
3.2.2 Ecological projects
image description
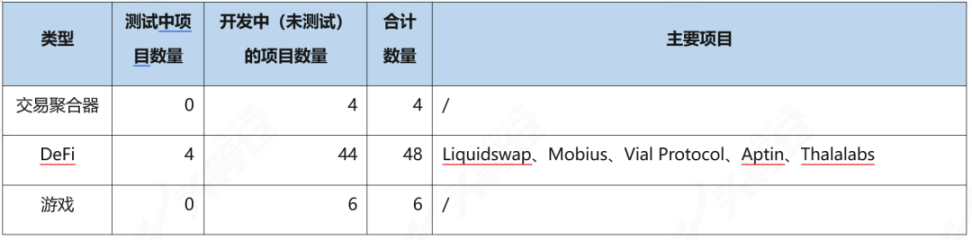
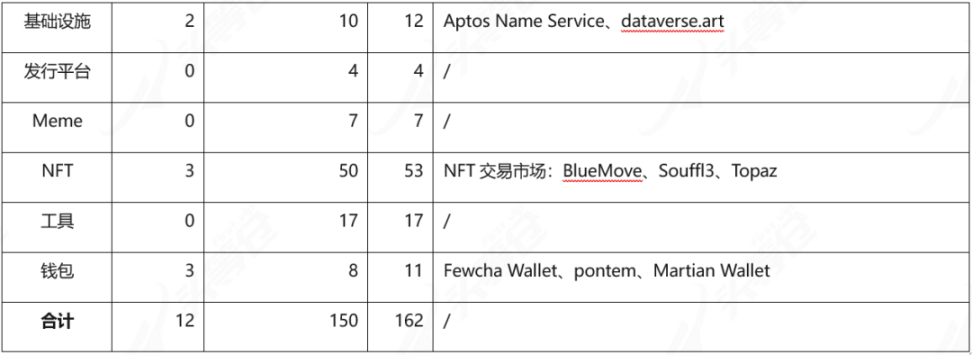
Table 3-3 Aptos project distribution table [14]
From the above statistics, we can see that there are currently 12 projects that have been tested by Aptos; most of the projects are in the development stage and have not entered the test stage; among the projects that have not participated in the test, a small number of projects can already link to Aptos wallets.The largest proportion is NFT, about 34%; followed by DeFi, about 29%; there are as many as 11 wallets.
In addition, some projects were migrated from other ecosystems such as Solana and zkSync. In this regard, many public chain players pointed out on Twitter that some project parties usually deploy on multiple public chains in order to obtain ecological funding for the new public chain. These projects are mainly imitations of classic projects, with single functions and simple codes. They do not focus on operation and development, are less attractive to users, and have limited effects on ecological development. Therefore, when observing ecological development, it is necessary to pay attention to the degree of innovation and user participation of the project.
image description
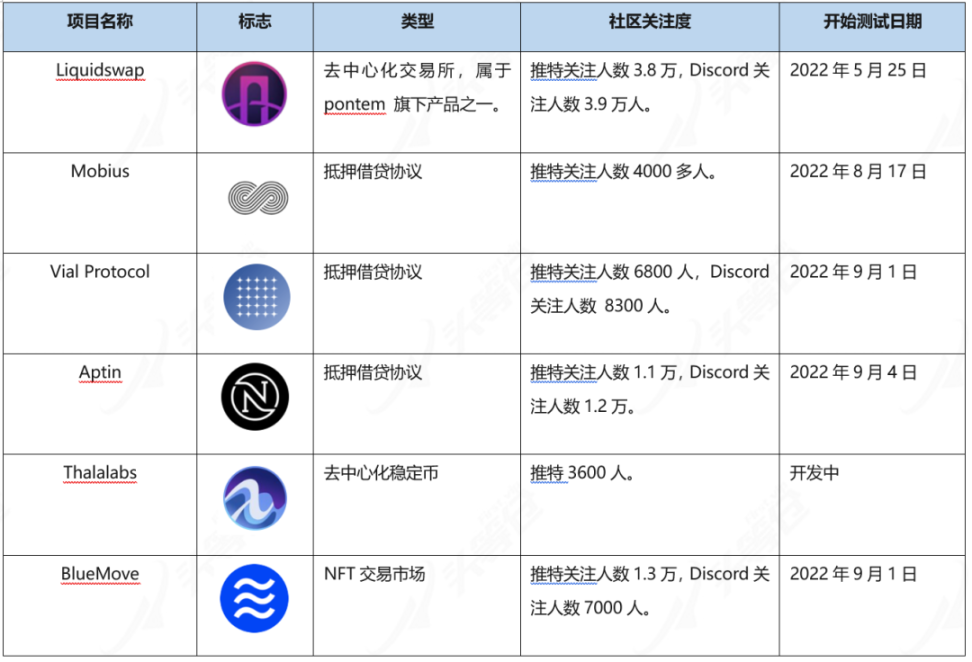
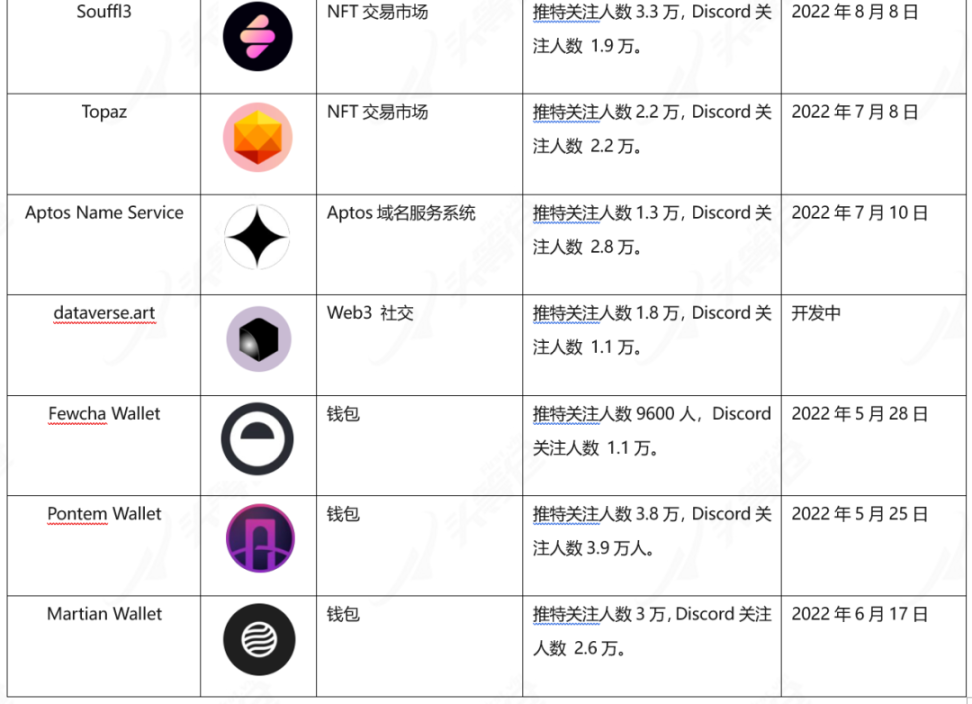
Table 3-4 Introduction to Aptos' main projects
It can be seen that the ecological construction of Aptos has begun to take shape, with basic business forms such as DEX, lending, stable currency, NFT, domain name service, and wallet. However, the mainnet has not yet launched, and the project is still in the early stages of development. Related DAPPs are still relatively limited in terms of completion and participation. From the perspective of completeness, most projects only provide the most basic functions without a data analysis panel. From the perspective of participation, it is still in the testnet stage at this stage, the mainnet has not been launched, and user participation is limited.
In order to promote the development of the ecology, Aptos will launch the Aptos Launch Ecosystem Funding Program at the end of June 2022 to provide funds for teams, individuals and creators. Funding categories include: developer tools, SDKs, libraries, documentation, guides, and tutorials; tools and frameworks for development, governance, DeFi, and NFTs; core protocol contributions: token standards, libraries, protocol upgrades, and more; open source and public products ; educational initiatives; applications. Grant funds will be distributed in U.S. dollars, with the option to distribute tokens in the future to help incentivize long-term ecosystem growth for all parties, Aptos said.Aptos is currently reviewing the first batch of applications and has suspended accepting new applications. [15]
3.2.3 Developer Community
According to the identity selection of Discord, there are 2600 developers, 3500 contributors, and 4800 node operators. [16] However, it should be noted that this is not real-time data. At the same time, there are many people who did not choose the relevant identity and can only be used as a reference.
Aptos has opened a developer channel in Discord to discuss developer issues, including sub-channels such as development discussion, Move language, wallet development, testnet information, and development resources. The test network information mainly releases various precautions and notices of the test network, which can beI saw that the number of likes ranged from about 100 to 300.Development discussion, Move language, wallet development and other sub-channel discussions are more active, and many developers post questions on it, looking for answers.
image description
Table 3-5 A list of Aptos forum activities
It can be seen that the developers of Aptos are relatively active at present, and Aptos also provides a more convenient communication method for developers to learn and discuss. However, currently Aptos does not have relevant statistics on the data of active developers on the chain. It mainly checks the number of ecological projects to confirm the degree of ecological activity.
image description
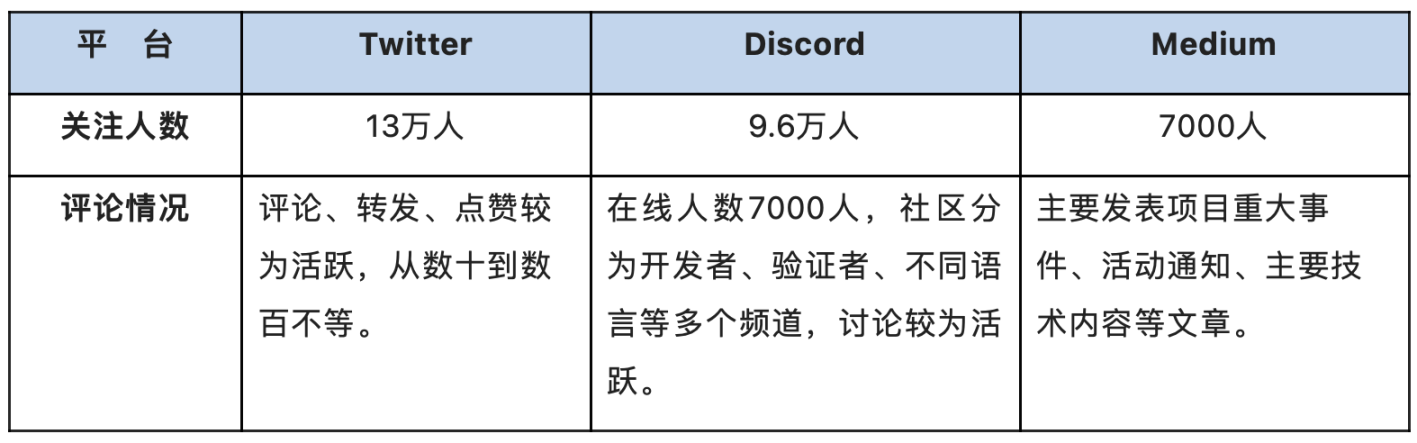
Table 3-6 Aptos social media data [18]
3.3 Future
Summarize:
Summarize:
At present, Aptos is still in the test network stage, and mainly promotes the following items: 1) After multiple test network operations, a safe and reliable decentralized verification node network is established to realize the main network launch. 2) Carry out an ecological funding plan to attract more developers and projects into the Aptos network and activate the ecology. 3) Strengthen community operations, use Twitter, forums, various media, volunteers, etc. to strengthen brand operations and increase brand awareness.
Through the observation of the projects in the ecosystem, it can be seen that they are mainly common DEX, lending, NFT, wallet and other projects, and the advantages are not obvious. Some projects have single functions and simple codes, and do not focus on business development. They mainly want to obtain the ecological fund support of Aptos. This leads to low project innovation and limited help to ecological development. In the follow-up, attention should be paid to the innovation degree and user operation of ecological projects, and the development of advantageous projects.
4. Token economic model [19]
On October 18, 2022, major exchanges such as Binance and FTX announced the listing of Aptos, and tokens will be issued on October 19. A few hours after the listing announcement, the Aptos Foundation officially released the core summary of the token economic model.
According to the abstract, the token issuance scale is 1 billion, and the total number of liquid tokens at the time of listing is 130 million. In addition, this is an inflationary token, and staking APT will be rewarded with newly added tokens.
image description
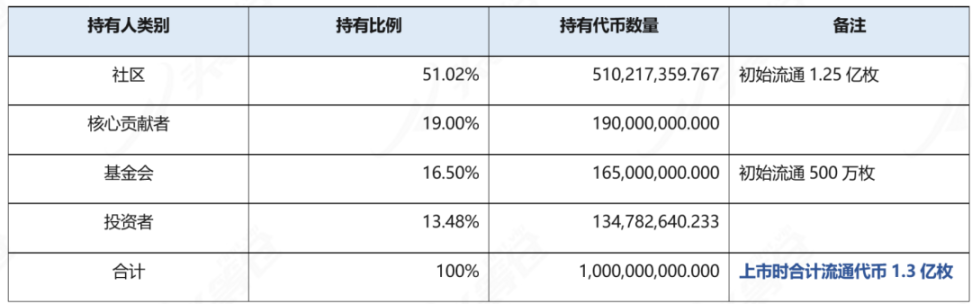
Table 4-1 APT distribution list
Community and Foundation Section
Community (51.02%) and Foundation (16.5%) shares will be earmarked for ecosystem-related projects such as donations, incentives, and other community growth initiatives, some of which tokens have already been allocated to projects developed on the Aptos protocol , will be awarded when the project completes certain milestones. The majority of these tokens (410,217,359.767) are currently held by the Aptos Foundation and a smaller portion (100,000,000) is held by Aptos Labs, which are expected to be distributed over a ten-year period. The specific locking and circulation conditions are as follows:
1) In terms of community shares, 125 million APTs entered circulation at the time of creation, which can be used for ecological support, donations and other community growth plans;
2) In terms of foundation shares, 5 million APTs will also enter circulation at the time of creation, which can initially be used to support the plans initiated by the Aptos Foundation;
3) In the next 10 years, the remaining tokens of the community and the foundation will be unlocked at a rate of 1/120 each month.
Core contributors and investors section
The shares of core contributors (19%) and investors (13.48%) will be fully locked for 1 year and will be distributed in the next 3 years. The specific locking and circulation conditions are as follows:
1) In the first 12 months after creation, no core contributors and investor shares will enter circulation;
2) From the 13th to the 18th month (including the 18th month) after the creation, this part of tokens will be unlocked month by month at a rate of 3/48 each month;
3) From the 19th month after creation, the remaining tokens will be unlocked month by month at a rate of 1/48th of each month.
4.2 Token release
At present, more than 82% of the tokens on the Aptos network have been pledged. These tokens belong to multiple entities. According to the above distribution and unlocking plan, most tokens are currently locked and have not entered circulation. It is important to note that both unlocked (i.e. tokens that have entered circulation) and locked (i.e. not yet entered circulation) tokens can be staked.
image description
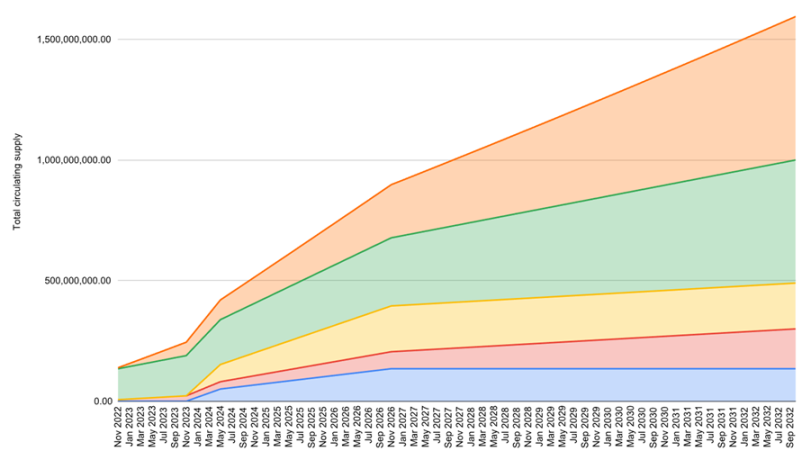
Figure 4-1 APT token release diagram
It is important to note the impact of staking on the total supply of APT tokens.
1) For the purpose of protecting the network and reaching consensus, APT holders can pledge their tokens to verification nodes to obtain pledge rewards, which can be freely distributed between verification nodes and stakeholders.
2) Currently, the highest reward rate (APY) for network staking is 7%, and the reward rate decreases by 1.5% every year until it drops to 3.25%.
3) Staking rewards will increase the total supply of APT, and the increase is related to the total amount of pledged tokens and the overall operation of the verification node.
4) The transaction fees on the mainnet will be burned for the time being, but the future use of these tokens may change with the decision of on-chain governance.
5) All reward mechanisms can be modified through on-chain governance.
5. Competition
5.1 Industry Overview
Aptos belongs to the public chain track.
The first stage
The first stagesecond stage
second stageFrom 2014 to 2017, the addition of Turing's completeness made Ethereum a turning point in the development of the public chain. The concept of smart contracts appeared in the blockchain for the first time, and made the public chain have the programmability of carrying applications; at the same time, With the advent of applications such as CryptoKitties, people began to truly experience the application display of blockchain technology. Ethereum also established its own ecological barriers in the public chain with its first-mover advantage. The public chains produced during this period include ETH, NEO, QTUM, EOS, etc.
The third stage is from 2018 to the present. The iteration of various consensus mechanisms and verification transaction layer technologies has created a batch of high-performance and low-cost public chains, including BSC, Solana, Avax, etc.
The development of the public chain in the next stage has the following three trends: one is the development of Ethereum as the base layer and various second layers; the other is the development of single-chip chains using new technologies, such as Aptos and Sui; the third is professional The development of specialized and characteristic public chains, such as modular public chains, privacy public chains, etc.
For the development of the public chain, we mainly examine three aspects:
First, from the perspective of the consensus mechanism, the degree of decentralization of the project is recognized by the public chain community.This involves the psychological security of the public chain. Users tend to put their core assets on the blockchain they think is the safest, such as BTC and Ethereum, rather than BCH or LTC. This is the most difficult situation for the public chain to break through, and it is also the core competitiveness. For a while, EOS was on par with Ethereum in popularity, but in the end it was short-lived because of the serious centralization of its own nodes.
The second is from the perspective of technical mechanism, whether it has innovation and advantages, and whether it can achieve performance optimization.This mainly involves the "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain. The "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain was proposed by Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum. It refers to the fact that the public chain cannot simultaneously achieve scalability (Scalability), decentralization (Decentralization), and security (Security). Get second. To put it simply, Ethereum and Bitcoin belong to the pursuit of decentralization and security at the expense of scalability. New public chains such as Solana are pursuing the ultimate scalability, and lack decentralization and security.
The third is from the perspective of ecological construction, whether it can attract developers and projects, thereby gaining more user participation and forming a virtuous circle.The public chain itself is only an infrastructure, and it needs developers, projects, and users to be active on it in order to continuously capture value. The more developers, the stronger the innovation, the more prosperous the ecology, and the more active users, the marginal income will increase significantly.
5.2 Comparison of competing products
Aptos faces stiff competition. The trend of Ethereum has been established, and both ETH2.0 and the second layer are working hard in the direction of improving efficiency and expanding capacity. In the new public chain, Solana, BSC, etc. have also attracted specific projects and users by virtue of their respective advantages. Among the next-generation new public chains, there are currently multiple teams and multiple public chains in research and development. Only the public chains developed by Meta-related teams include Sui and Linera.
Ethereum
Ethereum, a decentralized, open source, public blockchain platform with smart contract deployment and development functions. It was developed in 2014 and proposed concepts such as Turing completeness and smart contracts, bringing programmability to the blockchain, bringing the possibility of application development and ecological development, and currently has the largest number of developers and the most prosperous ecology. It is difficult for most public chains to surpass Ethereum in the short term.Taking Ethereum as a comparison helps to clearly understand the positioning of Aptos.
Solana, a high-performance new public chain that focuses on solving the scalability problem of the public chain, with a maximum TPS of 100,000. It was developed in 2017 and proposed concepts such as POH (Proof of History), validator tree propagation, pipeline mode, and multi-threaded virtual machine, which greatly improved performance. Its ecological development has advantages in the new public chain.This is a direct competitor of Aptos, both focused on performance scaling.
Sui、Linera, two Meta public chains, the founders are both from Meta, the team members used to be the main creators and core developers of Diem and the encrypted wallet Novi, and a16z participated in the investment. The goal is to develop a new public chain with high performance and low latency. Aptos and Sui use the smart contract programming language as Move, and Linera uses Rust.If the technical similarities of these three projects are relatively high, then whoever makes the first effort in ecological construction will be more likely to have an advantage.
The following is a comparison of the development of different public chains from the five aspects of team funds, consensus mechanism, transaction execution, node structure and number, and ecological construction. Ethereum and Solana have been in operation for a long time, and the information and data are relatively sufficient; Aptos and Sui are in the process of testing, with more test data; Linera is still in the early stage of development, and has not published white papers and detailed technical documents, mainly brief introduction.
5.3 Comparison of elements of competing products
image description
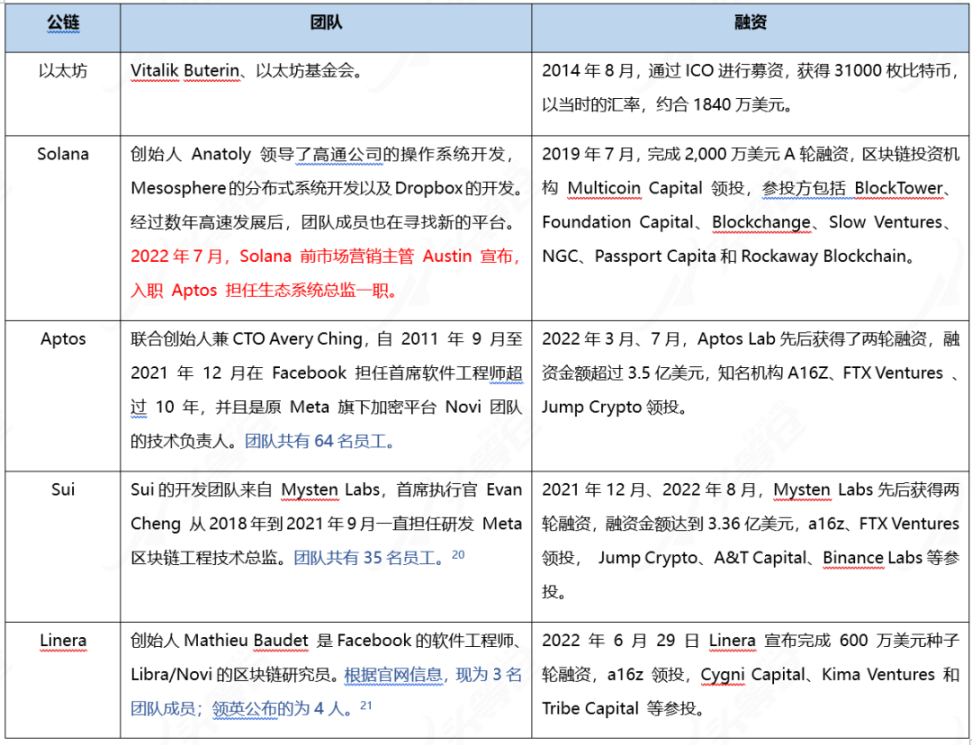
Table 5-1 Aptos Competing Product Team and Funding Comparison
Overall, Solana has completed phased development, and the period of explosive development is over. The Aptos public chain is still in the early stages of development and has a large room for future development. Therefore, it has attracted Solana team members to join. This phenomenon can also be seen in the developer community, where developers and projects migrate from public chains such as Solana to Aptos. This migration of people can show that Aptos has strong appeal at this stage.
Aptos, Sui, and Linera are in the development stage. From the perspective of the technical director's resume and the number of teams, Aptos has the strongest technical ability, followed by Sui, and Linera is the weakest.
From the perspective of financing, A16Z has participated in the investment of these three projects, and the financing amount of Aptos and Suinear.
Ethereum:
Ethereum:At the beginning of its establishment, Ethereum adopted the proof-of-work mechanism (PoW), and the bookkeeping rights were determined according to the computing power. In mid-September 2022, Ethereum will undergo an upgrade, completely switching from a proof-of-work mechanism to a proof-of-stake (PoS). In the proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, nodes pledge ETH tokens to Ethereum. If a node exhibits dishonesty or laziness, its staked ETH tokens face fines. Nodes are responsible for checking that new blocks propagated on the network are valid.
Under proof-of-stake, Ethereum manages the finality of transactions through "checkpoint" blocks.Briefly understand related concepts such as Slot, Epoch, Checkpoint, and Pair of Checkpoint. Slots are time intervals at which blocks are added to Ethereum. Each time slot on Ethereum is 12 seconds, and each epoch is 32 time slots, or 6.4 minutes. A checkpoint is the first block of an epoch. Checkpoint pairs are checkpoints of two adjacent epochs.
Nodes vote on which "checkpoint pairs" they consider valid. If a pair of checkpoints receives a vote of at least two-thirds of the total ETH tokens staked, then both checkpoints are upgraded. The newer of the two checkpoints becomes the "reasonable" state. An older checkpoint is already a reasonable state, since it was the "target" in the previous epoch. Now, this checkpoint will be promoted to "confirmed" state.
To roll back the confirmed blocks, the attacker will incur a loss equivalent to at least one-third of the total number of staked ETH tokens.Because finality requires a two-thirds majority of votes, an attacker can vote with one-third of the total number of staked ETH tokens to prevent the network from achieving finality. For this kind of attack behavior, the defense mechanism that can be adopted is: laziness punishment. This mechanism is triggered when the chain cannot be finalized for more than four periods. The laziness penalty gradually consumes the ETH tokens staked by nodes that voted against the majority, allowing the majority to regain a two-thirds majority and finalize the chain.
Solana:The Tower BFT consensus algorithm is adopted. In the Tower BFT consensus algorithm, there are two roles involved, one is the leader (block producer), responsible for recording transaction data. The other is the verifier, which is responsible for verifying the transaction data. Divide each working epoch of the network into several time slots, and at the same time, arrange a schedule for the leader, so that each leader can work within the specified time slot, instead of waiting for the previous block to be generated to start operation, but Define the working hours of each leader and work on time. Simply put, the leaders line up to produce blocks in turn, and at this time the verifiers confirm the block information. If more than 2/3 of the verifiers pass the verification, the information of the block can be confirmed.
Aptos:The Diem BFT consensus algorithm is adopted. In the Diem BFT consensus algorithm, the total validator nodes ≥ 3f + 1, there can be at most f wrong validators. In other words, only ≥ 2f + 1 nodes need to be verified to confirm. The fourth iteration of Diem BFT has been completed. The current main innovations include: 1) The block submission time is shortened, and it only needs two network round trips to submit, achieving sub-second finality. 2) Improvements have been made to the node reputation system, by checking the data on the chain, the leader rotation can be changed automatically. The system analyzes and judges the non-response of the verifier by itself, and does not require manual intervention to reduce the impact of faulty nodes on network efficiency.
Sui:A new peer-reviewed consensus protocol based on Narwhal and Bullshark is adopted to provide a DAG-based memory pool and efficient Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus. Narwhal and Bullshark represent the latest variants working on a high-throughput consensus algorithm reaching throughputs of over 130,000 transactions per second over the WAN, with production encryption, persistent storage, and a scale-out master-slave architecture. [twenty two]
Linera:The BFT consensus algorithm is also adopted.
visible,Both Solana and Meta new public chains adopt the BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerant) mechanism.
5.3.3 Transaction Execution
1) Ethereum
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is single-threaded - the EVM can only utilize one CPU core to process transactions sequentially.When a project is very popular and there are many participants, a large number of transactions are backlogged in the transaction pool, and the gas fee is therefore very alarming. On May 1, 2022, the Otherdeeds land under Yuga Lab was released, with a total of 55,000 pieces of land. The transaction took 2 hours, burned more than 70,000 ETH, and the average gas fee per transaction exceeded 1.2 ETH.The current TPS of Ethereum is 30, and the block time is 15 seconds.
2)Solana
Solana uses Sealevel multi-threaded virtual machine, which uses Nvidia GPU with 4096 cores, and can run multiple smart contracts at the same time.Combined with technologies such as Proof of History, Pipeline, and Gulf Stream, it can significantly increase transaction speed and reduce transaction costs.Solana's current TPS is close to 65,000, the block time is 0.4 seconds, and the transaction fee can be as low as $0.0001.
However, NFT mint and IEO transactions often lead to outages on the Solana network. The reason: these transactions cannot be performed concurrently on 4096 cores. When Minting NFTs, it is not known which ones have already been mint, which will lead to duplication and BUG. All mint transactions in the same collection must be processed sequentially. At this point, Solana's parallel processing fails.
3)Aptos
Aptos uses the Block-STM parallel execution engine. According to the current test network situation, it uses up to 32 cores, and the maximum TPS reaches 160,000.Note that this is test data. In a more complex actual production environment, if there are more nodes, TPS will decrease. The TPS that Aptos actually runs is likely to be close to Solana's.
Regarding the issue of minting NFTs, Aptos published an article in its Medium "Aptos NFTs: Solving NFT Minting at Scale——How we minted millions of NFTs in under an hour on the Aptos Blockchain (Aptos NFTs: Solving the problem of large-scale NFT casting—— How we minted a million NFTs in an hour)". However, this article also does not explain the details of the processing when the same series of NFTs are minted.
4)Sui
Sui employs parallel transaction execution.For transactions that have a causal relationship, they are sorted according to causality. Transactions that have no causality can be processed by validators in any order. At the same time, each validator can use more CPU to improve performance. This enables massive parallel execution of transactions. [twenty three]
5)Linera
The Linera project will develop a new execution model suitable for linear scaling.The project founders studied FastPay and Zef, two protocols that they believe can revolutionize blockchain scalability. Simple operations like payments can be sped up by removing the mempool entirely and minimizing interactions between validators. In this series of protocols, blockchain clients communicate directly with validators to submit and confirm new account operations.
In such a model, by default, operations on different user accounts will run concurrently—that is, in different threads of execution. In this way, execution can be scaled by adding new processing units to each validator. This will enable most account-based actions to be confirmed within a fraction of a second. [twenty four]
It can be seen that from the perspective of transaction execution, Ethereum uses single-threaded execution, while other public chains use multi-threaded parallel execution. In comparison, Ethereum and Solana are two extremes, and Aptos is in between.Sui and Linera have not released many details so far, mainly conceptual statements.
5.3.4 Node structure and quantity
In a centralized platform, calculations happen only once, and users trust the platform to be correct. The blockchain itself is a decentralized ledger. We don't trust anyone, and all data needs to be calculated and verified by different nodes. The extra number of times an identical computation is done is redundancy. To discuss decentralization, it is necessary to examine the redundancy of the system structure. In addition, the policies of various countries on cryptocurrencies have an important impact on the industry, and it is also necessary to pay attention to the degree of anti-censorship of nodes.
image description
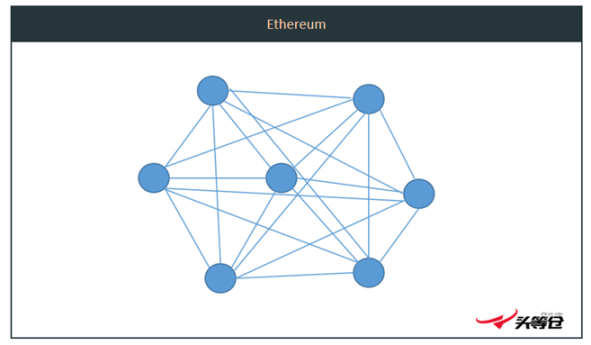
Figure 5-1 Ethereum node structure
Ethereum's validating nodes, each node must transmit, check and compare the work of every other node. this means,Redundancy of Ethereum = N2. As the number of network nodes (N) grows, the redundancy increases exponentially.
image description
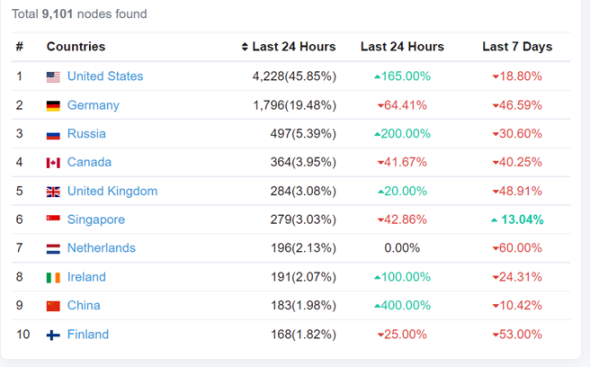
image description
2)Solana
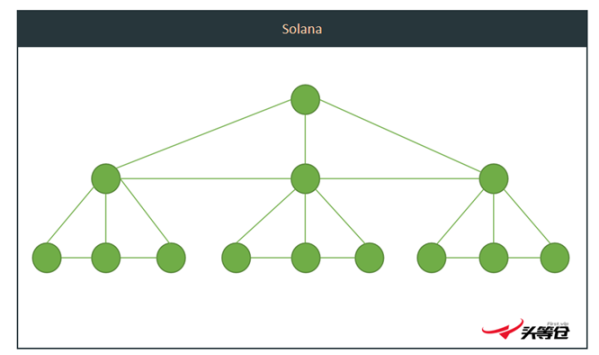
Figure 5-3 Solana node structure
Solana designed the Turbine tree propagation mechanism. Using this mechanism, when the verifier propagates the information to be verified, it is divided into several steps: 1) Divide the information to be verified into several small blocks, and the largest data block is 64 KB; 2) The leader sends these small data blocks to some verifiers; 3) the verifier then transmits the data to more verifiers according to the tree structure.
This numerical structure is a randomly generated path. In this way, during the verification, the leader does not need to interact with all the verifiers, and the verifiers do not need to complete 1-to-1 verification, which improves the efficiency of block information verification. Theoretically, if each verifier transmits data to 200 verifiers in the lower layer, then from the root leader to the final 3-layer network can reach 40,000 verifiers, and each layer transfer takes 100 milliseconds, then the entire transfer is about It only takes 200 milliseconds. The Turbine propagation mechanism greatly accelerates the communication speed of the network. In the best case, network redundancy = log n.
A major problem with this design is the collapse of the leader node. Since no other node has the same transaction data or network role as the current leader node, once a leader node crashes, the entire Solana network will be affected.
Currently, Solana has about 2,000 validator nodes, of which there are 30 leader nodes. It can be seen that the leader node is highly centralized. Once the leader node crashes or is regulated, it will affect the entire network, and the degree of decentralization and resistance to censorship are relatively weak.
3)Aptos
Aptos employs leader rotation and does not try to split and validate blocks like Solana does, because splits would create extra work in case of errors. To improve the efficiency of the leader rotation mechanism, a node reputation system has also been added.The system focuses on the liveness and validity of nodes. Liveness refers to tracking active parties by checking on-chain data and electing leaders from them. When the leader node is attacked or the network is interrupted, it may not be able to perform its tasks, but the reputation system on the chain will quickly find a suitable node to act as the leader node and start working, so as to avoid the large-scale impact of the attack on the network.image description
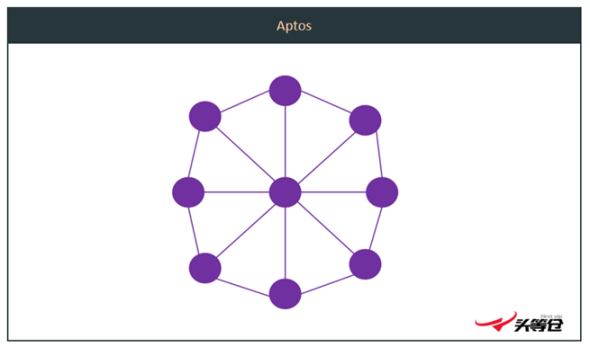
Figure 5-4 Aptos node structure
image description
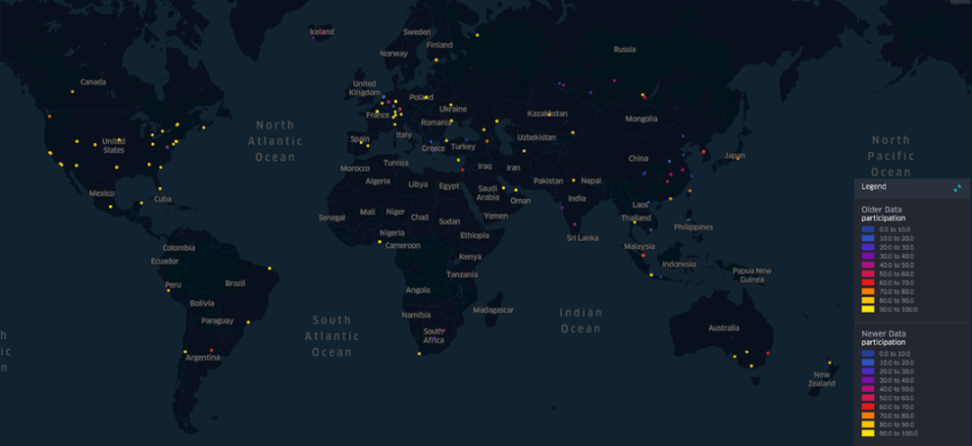
Figure 5-5 Schematic diagram of node distribution in Aptos community[26]
From the figure above, we can see the distribution of nodes, and the degree of dispersion is acceptable. It is mainly concentrated in the United States, Europe, and East Asia, but it is also distributed in other places.
4)Sui
According to the project documentation states,Sui uses a leaderless protocol to process transactions, defective nodes do not have a major impact on network performance, however, they can cause slight performance degradation. [27]
The Sui test network will be launched in August 2022, and there are currently more than 5,000 full nodes running in 271 cities in 65 countries. [28] Sui has not disclosed more detailed node information.
5)Linera
Linera did not disclose the specific verifier node structure model. It has not yet entered the testing phase, and there is no validator data.
It can be seen that from the perspective of node structure, Ethereum has the most reserved redundancy; however, since the nodes are concentrated in the United States and Germany, and most nodes are maintained and managed by node operators such as Lido, regulatory risks may arise. Solana emphasizes performance expansion and adopts a leader tree propagation structure. There are only 30 leader nodes, with a high degree of centralization, the lowest redundancy reservation, and weak anti-censorship. Aptos adopts a more flexible design, and its best performance is not as good as Solana. However, when faced with extreme situations, its node structure is more resilient and has a higher degree of security. It will not collapse as easily as Solana; at the same time, the nodes are also scattered. Reduce the impact of regulatory policies.
5.3.5 Ecological construction
image description
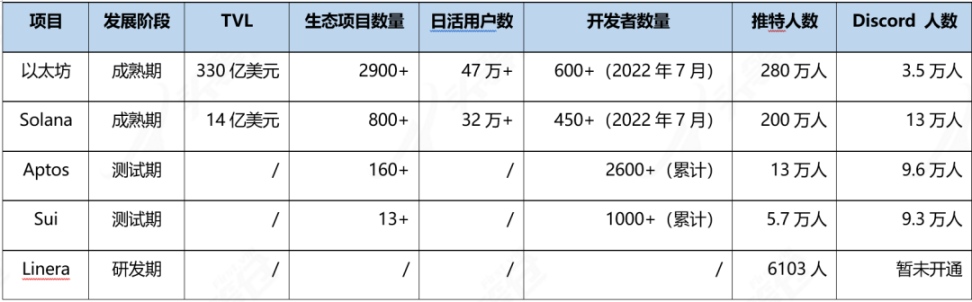
Table 5-2 Comparison of ecological construction of Aptos competing products [29]
Summarize:
Summarize:
The competition on the public chain track is fierce. Ethereum has significant ecological advantages and a prosperous ecology; new public chains such as Solana have established relatively rich ecology. Among the competitors of Aptos in the same period, there are public chains with a high degree of similarity in the mechanism of the Meta system such as Sui and Linera, as well as other modular and specialized public chains.
In terms of team and funds, the Aptos team is strong and has received sufficient funds. The team is recruiting talents, expanding business, and continuing to operate in a bear market environment. In the financing in July 2022, Aptos' valuation reached 2.75 billion US dollars, while Solana's current market value is 10.8 billion. It can be seen that in the bear market, the valuation of Aptos is high. Moreover, there may be new financing in the follow-up before entering the secondary market, which will further increase the valuation. However, Solana's historically high market capitalization is about $76 billion, and if it enters the next round of bull market, the upper limit of the project's market capitalization will also increase.
In terms of system architecture, the degree of decentralization of Aptos is insufficient. Facing the "impossible triangle" problem of the public chain, Aptos tends to be high-performance, and the degree of decentralization of nodes is relatively weak. However, the degree of dispersion of its node distribution is acceptable. Solana puts performance expansion first.
Technically, Aptos focuses on scaling performance and wants to better balance security concerns. Ethereum is a public chain that focuses on decentralization and security, while Solana expands performance to the extreme. Aptos tries to find a more balanced position between the two. The main technological innovation of Aptos lies in the account type and programming language. The technology it adopts is basically involved in public chains such as Solana. However, it tries to optimize the system architecture to achieve a network with better performance and higher security.
Aptos uses a consensus mechanism and parallel computing similar to Solana to achieve better performance; however, it does not use a leader tree verification mechanism similar to Solana, but uses a leader rotation mechanism to reduce the impact of a single node failure on the network. The influence of the network improves the security of the network. This positioning choice is more likely to achieve large-scale use.
In terms of ecological construction, the ecological construction of Aptos is in its infancy, and the team has taken active measures in marketing and community management. At present, the innovation of Aptos ecological projects is insufficient, and advantageous projects have not yet appeared, and many projects come from other ecology such as Solana. Compared with the other two public chains of the Meta series, Aptos has a certain first-mover advantage in ecological construction. However, due to the highly similar technology, it may cause multi-chain deployment and similarity of ecological projects.
Continue to pay attention to the implementation of the Aptos main network, including the construction and distribution of nodes and the actual operating efficiency of the network. Pay attention to the ecological construction situation, especially the emergence of advantageous projects. Advantageous projects can bring a lot of attention, funds, and sudden wealth effects, thereby quickly increasing the popularity and TVL of the public chain.
6. Risk
1) The mechanism of the Meta system is similar, and the competition of the same type is fierce
Meta projects Aptos, Sui, and Linera are highly similar in background, technology, and capital. In particular, Aptos and Sui have similar development stages and fierce competition in the same category.
2) High valuation
In the financing in July 2022, Aptos' valuation reached 2.75 billion US dollars, while Solana's current market value is 10.8 billion. Therefore, in terms of bear market conditions, Aptos is overvalued. Moreover, there may be new financing in the follow-up before entering the secondary market, which will further increase the valuation. However, Solana's all-time high market capitalization is about $76 billion, and if it enters the next round



