Original post by Todd, Partner at Ebunker

Today, with the news of Kraken suspending Staking, I want to do a popular science analysis of Staking:
-Essentially, the most important thing about Staking is to look at the ownership of the two private keys
-Due to the different ownership of the two private keys, four types of Staking schemes were born
I believe that with this super long thread, you can have a deeper understanding of Lido, Rocket, Coinbase, Kraken, SSV and Ebunker.
If Ethereum is regarded as a company, the validators responsible for staking are employees. Its job is to verify the legitimacy of the transaction, and then package the block on the chain (although the work of building blocks has now been slowly outsourced to MEV service providers).
First of all, as a verifier, you need to prove your employee identity. After all, not everyone can come to verify casually. After paying the 32 ETH deposit, you need to work with a certificate (ie: [verification key]).
In theory, the first step in staking is to create a verification key. Then, you take your verification key, which is your work permit, to stamp each transaction.
Second, Ethereum thoughtfully designed a second private key to receive the deposit (32 ETH) just mentioned.
When you become a verifier, you will need to fill in a withdrawal address. It is the address where you will withdraw your principal and salary in the future, and the private key of that address should theoretically be in your hands (ie: [withdrawal key]).
Let me use an analogy, this is your salary card.
I think everyone understands the purpose of these two private keys: ① verification key (work permit), ② cash withdrawal key (salary card).
Next, according to the different ownership of the two private keys,Four staking solutions were born:
-CEX class
-Pooled Staking
-SaaS class (Staking as a Service)
first level title

Option 1, CEX class/full hosting
If you use an exchange staking solution, such as Binance, Coinbase or Kraken that just announced the cessation of staking services today. You will find that you have never created a [verification key], nor filled in a [withdrawal key], then this is the standard full custody.
Where are the two keys?
- Verify that the key is in Binance Pool or Coinbase Pool
-The withdrawal key is in the cold wallet of Binance and CB
You dont have to go to work at all (participate in verification), and the salary card is also kept by the exchange for you. This solution is the most worry-free and guaranteed.
But it is not suitable for those who pursue decentralization. After all, there are FUD every three days, and now the United States does not even allow you to do this.
Solution 2: Pooled Staking (Pooled Staking)
This is the staking solution of Lido and Rocket Pool. You still dont need to create two Keys, which are managed by Lido and Rocket, so whats the difference between it and an exchange?
Let’s talk about the verification key first:
Exchange: Obviously, it operates only 1 under its umbrella, which is itself.
Lido: There are 29 professional operators under Lido 1.0, and Lido entrusts them with the management of ETH, so the verification key is relatively scattered, and each of the 29 operators gets a part. It is equivalent to saying that Lido is a group, and there are 29 strong migrant workers under it. You don’t need to work yourself, let the professionals of the migrant workers help you to work. Therefore, the operator takes 5% and Lido takes another 5%.
Rocket Pool: Rocket Pool can have countless operators, and anyone with a machine/cloud server + 16 ETH can be an operator. It is equivalent to saying that Rocket Pool is a crowdsourcing platform. It has a bunch of Meituan riders with its own electric vehicles (machines/cloud servers) and computer rooms to help you run nodes.
Of course, they also have to take a commission.
Let’s talk about the cash withdrawal key:
It is necessary to add another principle here: what is the process of staking withdrawal?
In my previous post, I briefly introduced Shanghai upgrades, cash withdrawals, and portals→
https://twitter.com/0x_Todd/status/1619950421124206593
As we all know, Ethereum has two chains: Ethereum 1.0 (execution layer) and Beacon Chain (consensus layer). When you go to Stake, the first step is to remit ETH to the Ethereum 1.0 Beacon vault address (https://etherscan.io/address/0x00000000219ab540356cbb839cbe05303d7705fa…) to lock the position, and then Beacon Chain will generate the corresponding eth for you in the consensus layer.
Note that these ETHs are locked, not destroyed on 1.0, or cross-chained to the beacon chain, it is just locked-mapped.
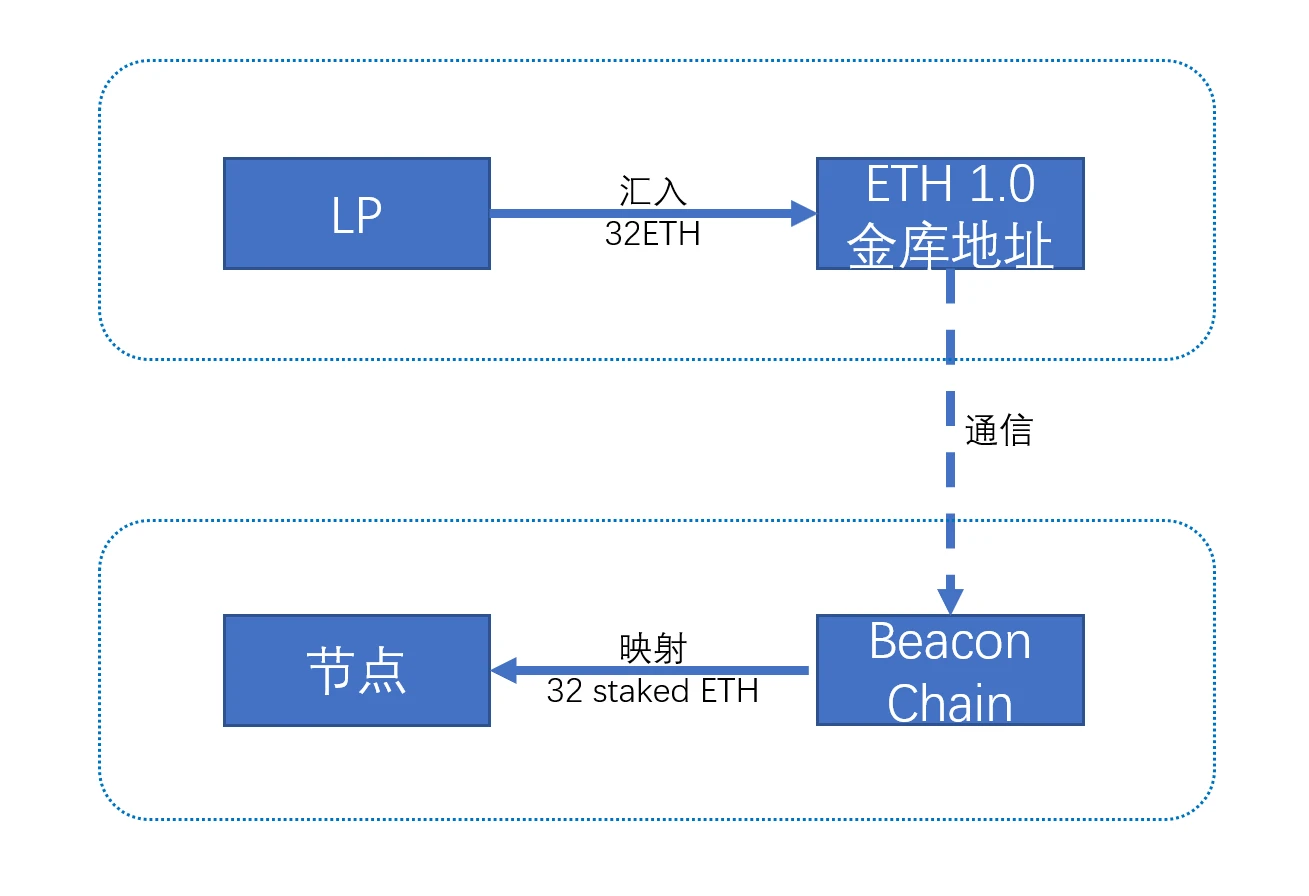
After the Shanghai upgrade, cash withdrawal will be a new type of transaction. When you withdraw:
1. Your node notifies Beacon Chain and sends out a withdrawal signal
2. queue
3. After queuing up to you, Beacon Chain will notify the Ethereum 1.0 treasury
4. The vault address of Ethereum 1.0 remits money to the address you specify, such as 0x Todd.eth
Therefore, the so-called [withdrawal key] is essentially the private key of the address 0x Todd.eth.
The withdrawal key of Lido Rocket is to help you pack 3 more layers:
1. You inform Lido\RPL that I want to withdraw cash
2. Lido\RPL notifies the operator that a certain node wants to withdraw cash
3. The operator notifies Beacon Chain that a certain node wants to withdraw cash
4. Queue
5. Beacon Chain notifies Ethereum 1.0 treasury
6. Ethereum 1.0 vault address to Lido\RPL withdrawal cash vault remittance
7. You destroy stETH\rETH, Lido\RPL smart contract sends money to your address.
PS: If you switch to an exchange, the seventh step is to add balance directly to your Binance\Coinbase central account by CZ\Armstrong.
For the large pool subclass scheme,
Steps 1, 4, 5, 6, and 7 are flawless ✅ and are purely on-chain operations.
And the weak link is in steps 2 and 3 ⚠️.
Theoretically, the Dachi subcategory scheme can reject your withdrawal. For example, if you are sanctioned by the OAFC of the United States for using a tornado, then steps 2 and 3 can be done without sending you a letter.
Why do I call it the big pool scheme, because the withdrawal addresses of all its nodes are filled with the same address, which is the smart contract address of Lido\RPLs withdrawal cash library.
Of course, as far as CEX is concerned, they still have great progress.
However, due to the existence of the operation space in steps 2 and 3, this type of solution has also become a solution that is very close to full hosting. After all, the withdrawal key is theoretically still owned by Dachizi, and what you hold is only the withdrawal address of the withdrawal address.
Therefore, I tend to classify as full trusteeship all schemes that do not control the final whereabouts of funds.
Some Rocket Pool supporters often claim that it is completely decentralized, and this slogan is deeply rooted in the hearts of the people.
But when you read this thread, you will know that it is verifying the key part, which is decentralized, and anyone can be a verifier (Lido V2 is also working hard to achieve it).
As for the withdrawal key part, as a user, you still cannot participate, and your assets are still quietly lying in the third-party wallet.
Of course, Lido and Rocket are only one or two steps more than exchanges, but they are more decentralized, which is still a good compromise. Especially for Lido, the liquidity of stETH is very good (currently far surpassing all other LSD schemes), which is an important plus item.
Solution 3. SaaS (Staking as a Service) category/Koike subcategory
By the third step, staking is even more fundamentalist. I personally have a certain degree of decentralization and cleanliness, especially after a series of CEX thunderstorms.
I made a metaphor just now, the verification key is a work permit; the cash withdrawal key is a salary card.
Then, people will naturally think, is there a way to let others work for me, and at the same time I get paid by myself?
There is no such beauty in real life, but the Ethereum network has it, which is SaaS or VaaS (Validator as a Service). Lets use the non-custodial mining pool @ebunker_eth as an example.
The first thing we need to do is to make the verification key into a keystore and give it to Ebunker Pool. Next, a professional mining pool will maintain the block generation of this node. At the same time, fill in my own withdrawal address, that is, I have the final withdrawal right of Ethereum.
To sum up:
[Verification key], one for me and one for the mining pool;
[Withdrawal key], only I have it.
That is: work in the mining pool/I get the money/the mining pool gets a commission.
What is the difference between this scheme and the big pool subclass? The difference is:
For the Pooled category, the withdrawal address is unified (that is, Lido\RPL vault), so it is a big pool.
For SaaS, the withdrawal address is filled by everyone, so it is a small pool.
PS: The idea of Dachizi and Xiaochizi was made by me. I think this is very vivid and easy to understand.
Then you may ask, it’s like SaaS, if the mining pool doesn’t help you broadcast on the Beacon chain, you still can’t withdraw cash?
Here comes the key, because you have your [verification key] in your hand, if the worst happens, such as the mining pool rug, you can still run this node and broadcast in person.
At the same time, you still have the [withdrawal key] in your hand, so you can withdraw the cash yourself and get back the principal intact.
In the big pool subclass scheme, after the worst case occurs, you do not have this ability, because you have neither the verification key nor the withdrawal key.
Then you may ask the second question, in the SaaS solution, can the small pool mining pool take my money and run away? This is the ingenious design of Ethereum Staking, because when you create a node, you will fill in your withdrawal address, and the mining pool cannot tamper with it. Therefore, even if the mining pool is rug, your principal cannot be taken away by the mining pool, because the difficulty of stealing it ≈ attacking Ethereum itself.
In the big pool plan, after the worst case happens, it can theoretically run away with the money. Quite simply, it just needs to upgrade its vault contract, transferring its ownership to the attacker. Of course, this is the worst case, and the probability of it happening is very small.
In order to counter this, Lido introduced multi-signatures to manage smart contract upgrades; and Rocker Pool seems to be secretive about this matter, and it has not found relevant content discussing contract upgrades for the time being.
Therefore, for those who do not want to work (after all, 7*24 operation and maintenance nodes are not an easy job), and have security requirements (do not manage funds for third parties), choosing SaaS services is a good choice. In addition to @ebunker_eth, there are some mining pools that provide similar non-custodial services, which can be checked on Rated.
Of course, there are also disadvantages. All unmanaged SaaS types do not have LSD solutions. The reason is also very simple, how dare someone send you a passbook (LSD) if they dont know your private key? Of course, some SaaS mining pools will also provide a large pool plan, and the large pool plan can be given to LSD.
In more concise words: Whoever holds the private key determines whether LSD can be obtained. Both CEX and large pool solutions are acceptable, but small pools and Solo solutions are not acceptable.
After the upgrade in Shanghai, the withdrawal of Ethereum can take up to 1-2 months, and the liquidity of the SaaS small pool solution has also been guaranteed to a certain extent. Therefore, this is also my personal favorite solution. Giving someone else the key/APR is fine.
Solution 4, Solo class
Finally, I would like to introduce you to the ultimate holy grail, Solo Staking.
Solo, as the name suggests, plays by itself, does not introduce any third parties, and is a solution that is full of stars for decentralization and security.
Solo miners own the verification key and withdrawal key by themselves. The advantages are obvious, safe, no one takes a commission, adds diversity to Ethereum, and...meet the needs of the spiritual world!
The disadvantages are also obvious: working by yourself requires cost: time cost (maintaining it), capital cost (renting server/building a physical computer room). Without 24-hour maintenance, your APR will be slightly lower because of the penalty.
For example, the current effective rate of block generation in the entire network is 97%. Vitalik may be a Solo miner. As professional as him, he can only achieve 96% effective rate. Rocket Pool is even lower. It is crowdsourced, and the effective rate is only 95%. .
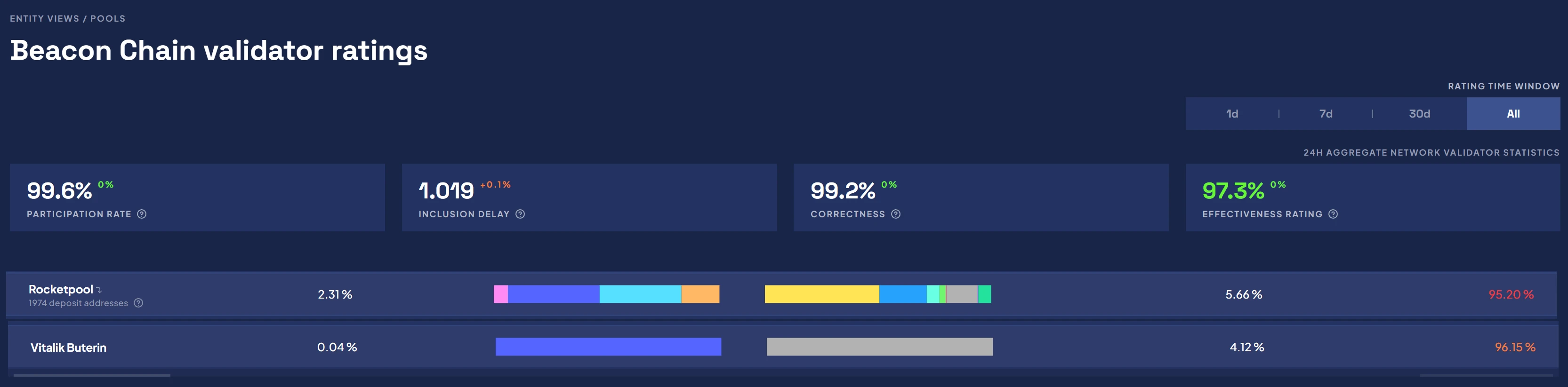
I think the threshold for Solo is at least 10K Ethereum, that is, more than 30 groups of nodes. On the one hand, it is to consider the stability of block generation (it is also very uncomfortable not to grab MEV blocks). On the one hand, the income does not equal the cost.
However, if you have enough ether, even more than 30 K, 50 K, then you can consider hiring some people to run it. After all, paying wages is cheaper than being commissioned by a large pool/small pool, and there must be more surplus.
And, Solo is the holy grail of eternity. If the number is large enough, I strongly recommend looking into Solo. For quantities below 100K, it is recommended to revisit classes 2 and 3.
Also, insert a spur.
What is SSV for? SSV is actually a researcher of DVT technology. For the time being, it is not a competitor with the above four types of solutions, but a cooperative relationship. DTV is used to split verification keys.
When your verification key is split into 4 parts, the beauty is:
① If one operator drops the line, other operators can make up immediately;
② At the same time, each operator does not know the complete verification key, which makes the verification process more decentralized, and it can make Lido, SaaS and Solo solutions stronger.
Finally finished this article! Although it is very long, I hope this analysis can help you thoroughly understand the relationship and similarities and differences between all staking schemes. Everyone is welcome to mark and review at any time. If you have any questions about Ethereum or Staking, please DM the author @0x_todd on Twitter.
last of the last! Everyone is welcome to be a validator! Make your contribution to the security of the Ethereum network.










