Cregis Research: Interpreting the past and present of BRC-20
first level title
1. BRC-20 background and development history
With the rapid development of blockchain technology, various cryptocurrencies and token protocols are emerging. While Ethereum’s ERC-20 token protocol became the industry standard, the Bitcoin community welcomed the experimental BRC-20 token standard. The BRC-20 standard adopts a simple and safe design concept to realize the deployment, minting and transfer of tokens. Based on the Bitcoin network, BRC-20 realizes the issuance and management of tokens by recording data on Satoshis. This article will introduce the principles and applications of BRC-20, as well as its advantages and disadvantages, in order to provide readers with a comprehensive and in-depth understanding.
For a long time, people have felt that the Bitcoin ecosystem is not scalable compared to Ethereum, because except for transfer transactions, almost no data can be stored on the block. The reason why BRC-20 has exploded recently is that it is a Bitcoin-based token standard that introduces NFT and other tokens into the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Important milestones:
In January 2020, Bitcoin Core developer Pieter Wuille released BIP 341 and BIP 342 Bitcoin Improvement Proposals, bringing possibilities to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
In June 2022, Casey Rodarmor made a technical extension and expansion of Tapscript in BIP 342, and proposed new Bitcoin improvement solutions ordinal (serial number) and inscription (inscription), which mainly realized the function of storing data on the Bitcoin chain.
Domodata (author of BRC-20) believes that the BRC-20 standard is just an interesting experiment, showing us that it is possible to prove the state of off-chain token balances by creating on-chain inscriptions. He feels that this is just an attempt, and the BRC-20 standard should not be considered the only standard. At the same time, he encourages people in the Bitcoin community to work together to patch and optimize the standard, and the author of BRC-20 also believes that issuing assets on Bitcoin currently exists. with a better plan.
first level title
2. Pre-knowledge of BRC-20
The principle of BRC-20 is relatively complicated, and it is necessary to understand some concepts on the Bitcoin network, such as Satoshis, Ordinal, Inscription, and Taproot upgrades. Among them, Satoshi is the smallest unit of the Bitcoin network, Ordinal theory numbers each Satoshi, Inscription is to engrave data on each Satoshi, and the technology related to Taproot upgrade is the mechanism to control these Inscriptions. Together, these concepts form the operating logic of the BRC-20 standard.
secondary title
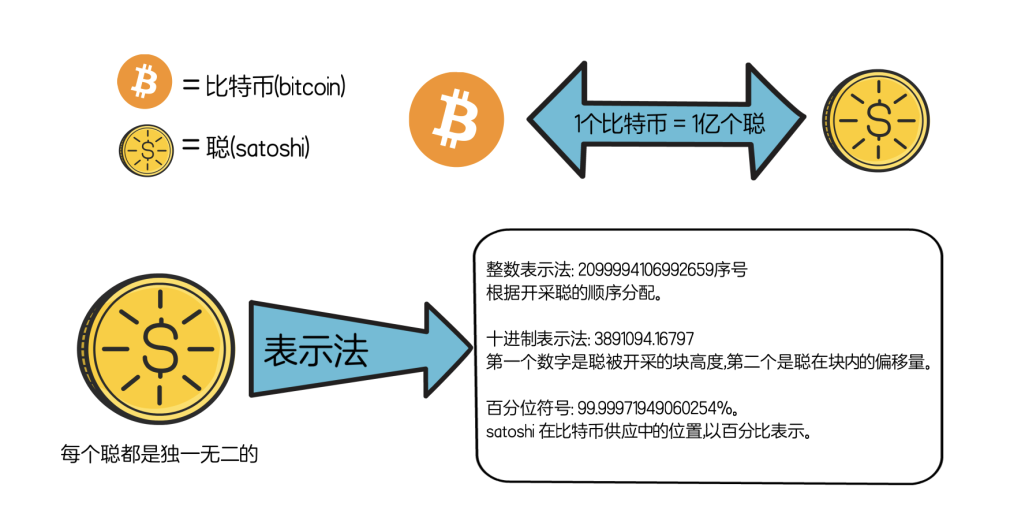
Satoshis (Satoshi) is not Bitcoin, but the smallest unit of Bitcoin. 1 Bitcoin can be divided into 100 million Satoshi.
secondary title
(2) Ordinal (ordinal number)
Ordinal number theory is a protocol for assigning serial numbers to satoshis (bitcoin's smallest subdivision) and tracking those satoshis as transactions are spent. These serial numbers are very large numbers, such as this 804766073970493. Each satoshi, which is ¹⁄₁₀₀₀₀₀₀₀₀ of one Bitcoin, has a serial number.https://github.com/casey/ord). The project consists of several parts. One is the ordinal proposal to improve Bitcoin, and the other is the ord tool developed with rust, which integrates the functions of index, block explorer and command line wallet. Later we will explain how to burn your own inscriptions through the ord toolkit.
secondary title
(3) inscription (inscription)
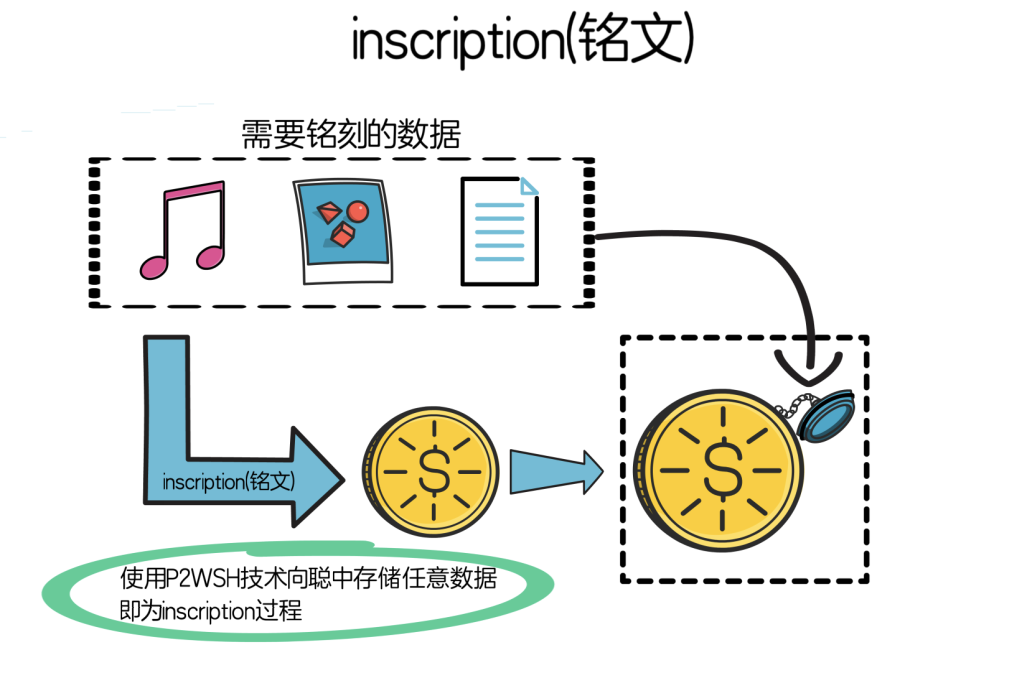
The Ordinal protocol achieves extended functionality by assigning a unique number to each satoshi and adding notes. This process is called inscription, which is to give derivative meaning to Satoshi. Comments, or inscriptions, are written in transaction witnesses, allowing Satoshi to write any type of content. It is safer to limit the size of the inscription content to less than 3.9 M, because the content of the inscription is included in the transaction, so the larger the content, the higher the transaction fee for the inscription transaction.
We can create our own Inscriptions by downloading Bitcoin Core and ord.
curl --proto '=https' --tls v1.2 -fsLS https://ordinals.com/install.sh | bash -s
# install ord
ord --version
#print ord version number
ord wallet create
# Create bitcoin core wallet
ord wallet receive
# Get wallet address
ord wallet transactions
#View pending transactions
ord wallet inscribe --fee-rate FEE_RATE FILE
#Create Inscriptions (inscriptions)
ord wallet send --fee-rate
(4) BIP 341 and BIP 342
BIP 341 and BIP 342 are two proposals related to Bitcoin improvements. The full name of BIP is Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (Bitcoin Improvement Proposal), which is used to describe new features, processes or specifications of the Bitcoin protocol, client or environment. BIP 341 and BIP 342 are related to the Taproot upgrade, the main purpose is to improve the privacy and scalability of Bitcoin, rather than directly used to write data to the blockchain, but the Taproot upgrade can use Bitcoin scripts and transactions to block The chain writes data at low cost, paving the way for the brc-20 standard.
BIP 341: Segregated Witness (isolated witness) output, this proposal defines a new output type that implements Taproot functionality. This allows Taproot-enabled transactions to coexist in a block with other types of transactions while maintaining backwards compatibility. BIP 341 provides detailed descriptions and specifications for new output types.
BIP 342: Tapscript, this proposal describes the scripting language inside Taproot, called Tapscript. Tapscript is based on Bitcoin's existing scripting language, extended and optimized. BIP 342 defines the syntax, runtime environment and execution rules of Tapscript. These improvements make it more efficient and private to execute complex smart contracts on the Bitcoin network.
Normally we can append a small piece of data (up to 80 bytes) to the transaction output using the OP_RETURN opcode, thus permanently writing the data to the Bitcoin blockchain. If we need to store more data, we need to use data splitting, create multiple transactions containing OP_RETURN, and write a piece of data to each small block. This method will greatly increase transaction costs.
When BIP 341 and 342 came out, we could use P 2 WSH (Pay-to-Witness-Script-Hash), P 2 WSH is part of Segregated Witness, which allows you to create a Bitcoin address that Represents the hash value of the Witness-Script (witness script). To spend funds from this address, an input that satisfies the unlocking conditions of the script must be provided. The specific process is as follows:
1. Create a witness script that contains the data you want to store. You can embed data in scripts using the OP_PUSHDATA opcode.
2. Calculate the hash value (SHA-256) of the witness script.
3. Create a P2 WSH address using the hash value. 4. Create a Bitcoin transaction to send funds to the P 2 WSH address.
When we conduct a transaction, the unlocking script is separated from the transaction body and stored in the Witness (witness data). With this technique we can store up to 4 MB of arbitrary data in the Witness portion of any bitblock. This constitutes the upper limit of 4 MB for any Bitcoin Inscriptions.
first level title
3. The technical principle of BRC-20
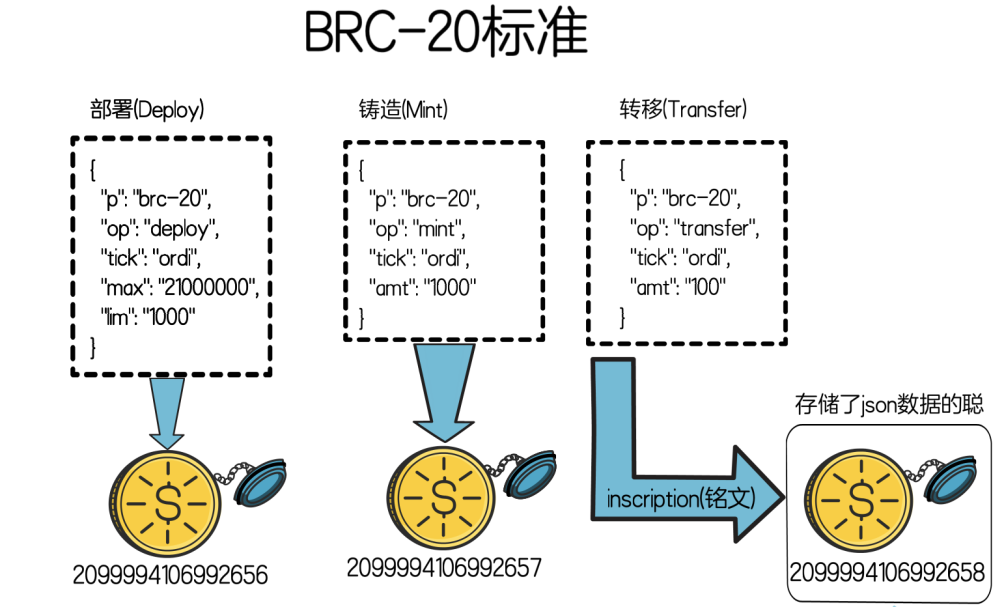
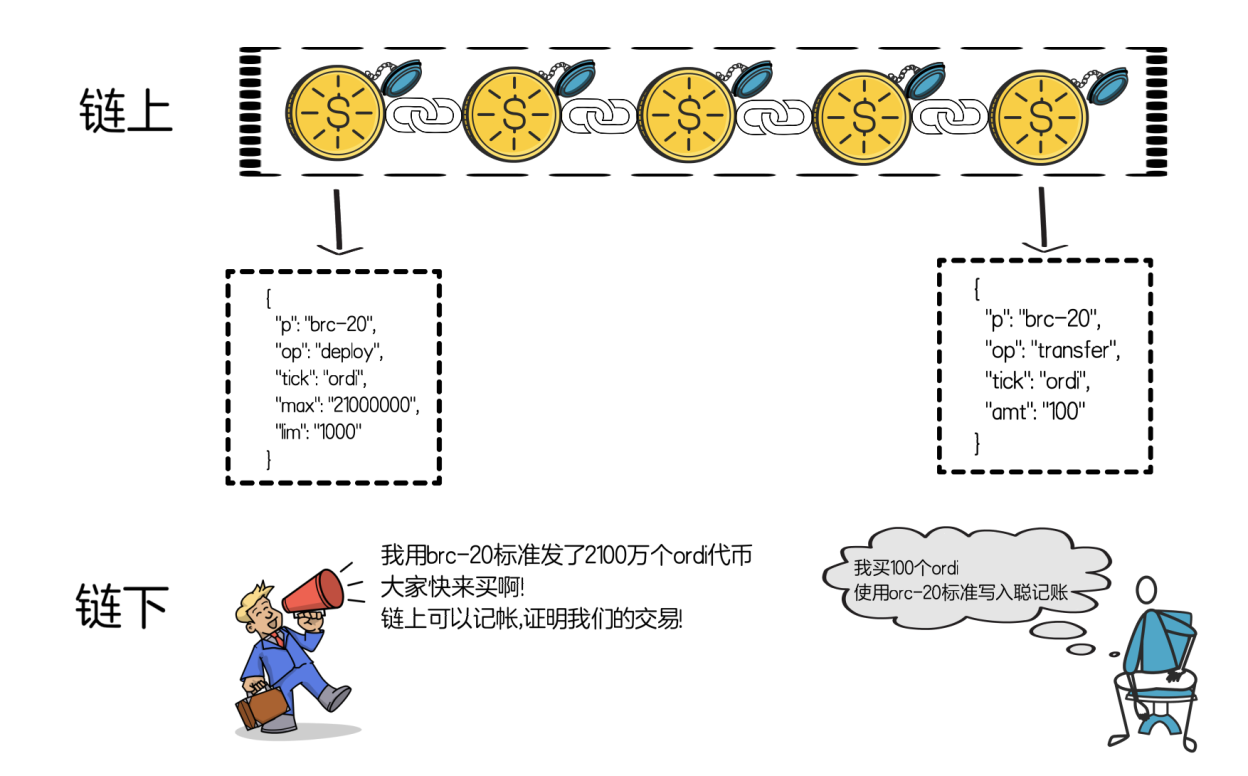
Based on the BRC-20 standard of ordinal inscriptions, Satoshis (Satoshi) is used to store and manage various information of tokens, such as token name, symbol, total amount, etc., and the information is encoded in JSON format and written to Satoshis (Satoshi) Among them, inscriptions are formed one by one. Finally, by summarizing the activities of all inscriptions, the balance status of the BRC-20 pass can be found, thereby realizing the deployment, minting and transfer of tokens.
BRC-20 is an experimental token standard based on Bitcoin. The core idea is to create, mint and transfer BRC-20 tokens through ordinal theory to realize asset management on the Bitcoin blockchain. The experiment mainly includes the following aspects:
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "deploy",
"tick": "ordi",
"max": "21000000",
"lim": "1000"
}
Deploy: To create a BRC-20 pass, you need to set pass parameters, such as token symbol, maximum supply and minting limit, etc. The deployment process is only used to initialize the BRC-20 and does not affect the state.
"p": "brc-20"***************Note****************
"op": "deploy": Specifies the protocol as BRC-20, which helps other systems to identify and process BRC-20 events.
"tick": "ordi": Specifies that the operation type is deployment."ordi": Specify the 4-letter identifier of the token, here use
"max": "21000000"As an example in the demo document, its maximum supply has been reached.
"lim": "1000": Set the maximum supply of tokens to 21,000,000.
: Sets the minting limit per ordinal to 1000 .
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "mint",
"tick": "ordi",
"amt": "1000"
}
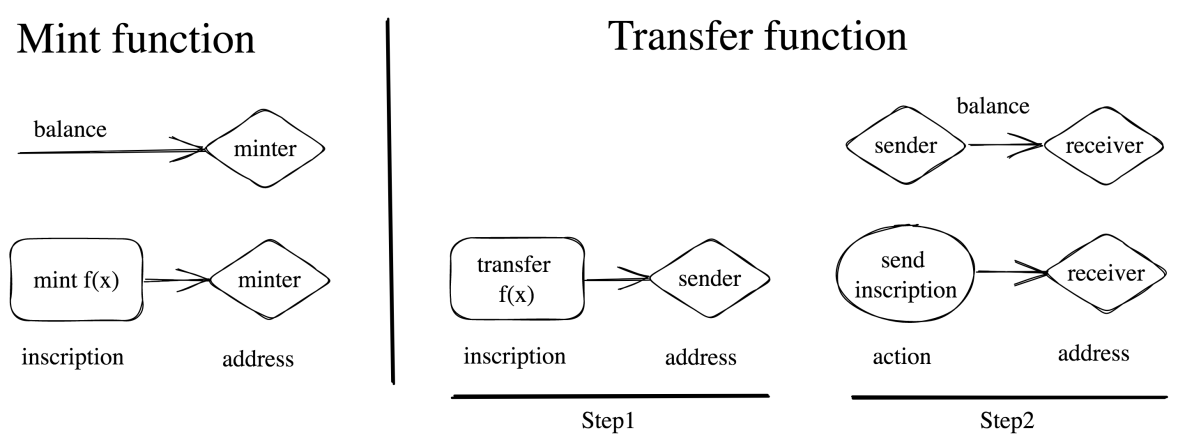
Minting (Mint): Use the minting function to mint a certain number of BRC-20 tokens. The minting operation provides the corresponding balance to the original owner of the minting function. If the token has a minting limit, please make sure that the limit is not exceeded.
"p": "brc-20"***************Note****************
"op": "mint": Specifies the protocol as BRC-20, which helps other systems to identify and process BRC-20 events.
"tick": "ordi": Specifies that the operation type is casting."ordi": Specify the 4-letter identifier of the token, here use
"amt": "1000"as an example.
: Set the number of minted tokens to 1000.
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "transfer",
"tick": "ordi",
"amt": "100"
}
Transfer: Transfer a certain amount of BRC-20 tokens through the transfer function. A transfer operation deducts tokens from the sender's balance and adds them to the receiver's balance. The transfer function only takes effect on the first transfer.
"p": "brc-20"***************Note****************
"op": "transfer": Specifies the protocol as BRC-20, which helps other systems to identify and process BRC-20 events.
"tick": "ordi": Specifies that the operation type is transfer."ordi": Specify the 4-letter identifier of the token, here use
"amt": "100"as an example.
State Tracking: The way we create on-chain inscriptions and store BRC-20 compliant json data in it can prove the status of off-chain token deployment, minting, and transfer. The balance status of BRC-20 tokens can be found by summarizing the activity of all inscriptions on the chain.
4. Application and operation of BRC-20
secondary title
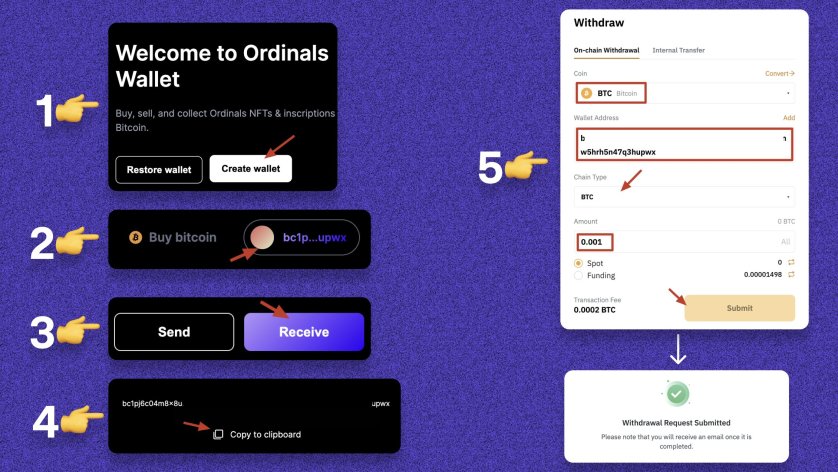
1. Download and create a wallet: ordinalswallet.com 2. Click on your wallet profile. 3. Click "Receive". 4. Copy the wallet address. 5. Go to any exchange that supports taproot and withdraw some BTC to this address. (Binance, Bybit, etc.)
secondary title
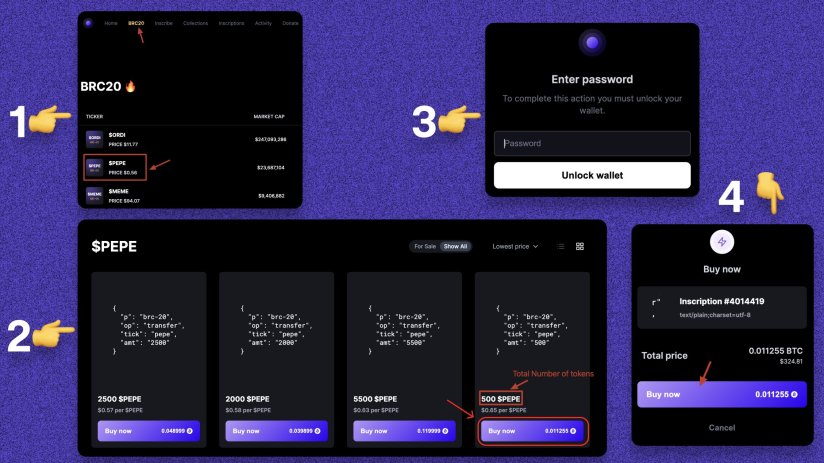
1. Click on the BRC 20 tab and select any token from the list. (Take $PEPE as an example) 2. Now check the number of tokens, the price of each token. Click "Buy Now". 3. Confirm the password. 4. Click "Buy Now" and confirm the transaction.
secondary title
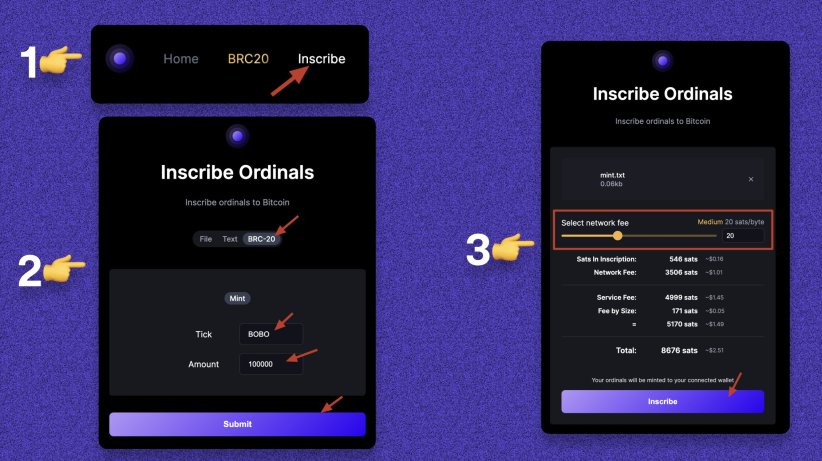
1. Go to the "Inscriptions" section. 2. Select "BRC-20", enter the token abbreviation (4 letters) and quantity, and click "Submit". 3. Select the network fee and click "Inscription".
secondary title
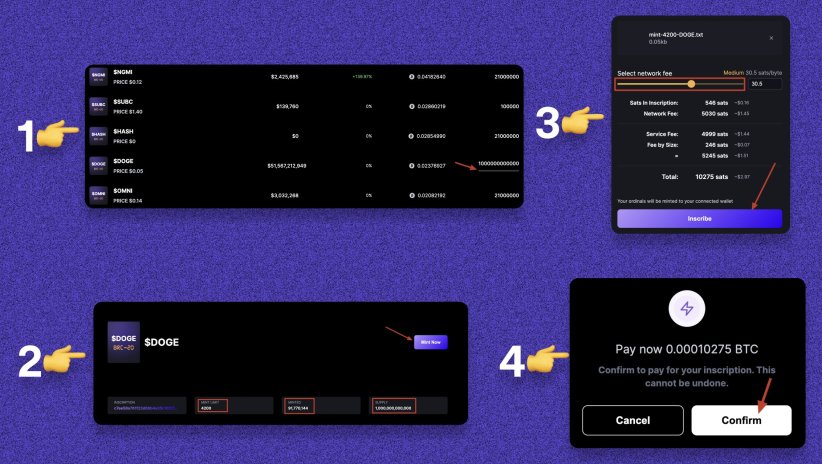
1. Go to the BRC-20 list and see the progress bars under each token supply. (If the progress bar is not 100% then you can mint the token). 2. Click Token >> Check Details >> Mint. 3. Set Fee >> Inscription. 4. Confirm the transaction.
5. Risks of BRC-20
secondary title
The issuance and usage mechanism of BRC-20 tokens results in a certain degree of centralization. This is because BRC-20 tokens need to rely on specific platforms and exchanges for issuance, trading and management, and these platforms and exchanges often have more resources and power. This is contrary to the core spirit of Bitcoin decentralization, because the goal of Bitcoin is to achieve a decentralized, fair and open currency system.
secondary title
Inscriptions on BRC-20 tokens may lead to unfairness on a first-come, first-served basis. This is because on the Bitcoin network, miners can choose to process the transactions they want to process, and the first-come, first-served mechanism of the inscription of BRC-20 tokens makes miners more inclined to process transactions that pay higher fees, and ignore other transactions. This may result in some users being excluded because they cannot afford high transaction fees. In addition, BRC-20 tokens are less secure than the Bitcoin network itself, as it relies on second-layer technology on top of the Bitcoin network, which may have security loopholes and risks.
secondary title
BRC-20 tokens may trigger MEV strategic attacks called time-bandit attacks. This is because the transaction and application of BRC-20 tokens on the Bitcoin network may give miners the opportunity to exploit the MEV (Miner Extractable Value) strategic attack to seek benefits by manipulating the order of transactions. This negatively affects the overall security and reliability of the network. In addition, BRC-20 tokens may also pose the risk of a regulatory crackdown on Bitcoin. This is because the issuance and trading of BRC-20 tokens may involve some illegal activities, such as money laundering, financial fraud, etc., causing governments and regulators to worry about the entire Bitcoin network and take measures to suppress it.
first level title
6. BRC-20 Investment Proposals
Although the BRC-20 protocol is currently in the experimental stage, the BRC-20 protocol provides a new token implementation method for the Bitcoin community. The emergence of the BRC-20 protocol will help promote the innovation of the Bitcoin ecosystem and attract more Developers and users join the Bitcoin community. In the future, as the Bitcoin community optimizes and improves the BRC-20 protocol, it will play a greater role in the cryptocurrency field.
It is an asset management collaboration platform in the web3.0 era, providing users with MPC wallet + enterprise-level financial SaaS tools, and has been in safe operation for 6 years.
About Cregis Research
CregisIt is an asset management collaboration platform in the web3.0 era, providing users with MPC wallet + enterprise-level financial SaaS tools, and has been in safe operation for 6 years.
Cregis Research is its knowledge sharing platform, hoping to provide web3.0 enthusiasts with 0 moisture, 0 misleading, and 0 business-oriented popular science content about blockchain and the underlying technology of cryptography.



