One of the biggest obstacles to the widespread adoption of Ethereum is that users have to pay high gas fees for transactions or interactions. As on-chain activities increase, gas fees also significantly increase, thereby raising the user threshold.
In order to improve the performance of Ethereum L1+L2 and address the gas fee issue, the Ethereum Foundation proposes to reduce gas fees and increase throughput with EIP-4844 as a mid-term transitional solution. This article will provide a detailed introduction to EIP-4844 and why it is crucial for the implementation of Ethereum's roadmap.

Introduction to EIP-4844
Ethereum EIP-4844 is a core component of the Cancun upgrade, which introduces a new transaction type (blob-carrying transactions) to reduce Ethereum transaction fees. Blob-carrying transactions are similar to regular Ethereum transactions, but with some additional data called blobs. Compared to the current calldata storage where transaction data is immutable and memory is read-only, blobs have much larger storage capacity and are cheaper.
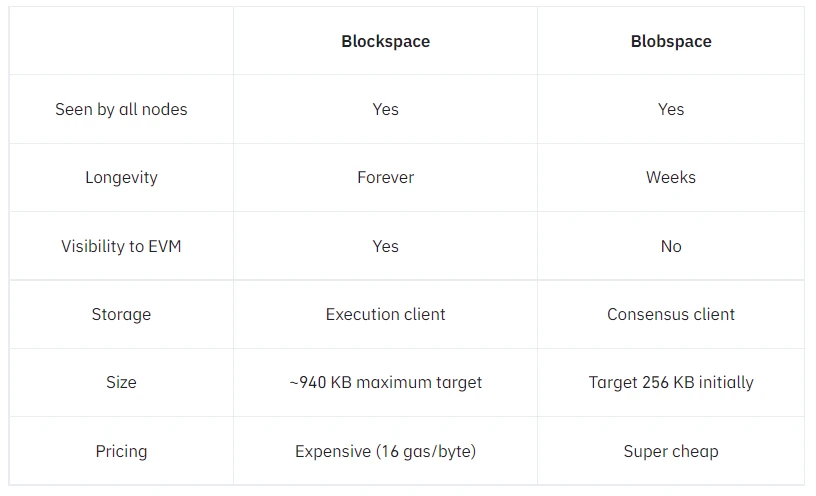
From the difference between blockspace and blobspace in the figure above, blobs are different from blocks visible to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), and blobs are only available for a short period of time, while they are not visible to the EVM. In addition, blobs are located on the Ethereum consensus layer, rather than the execution layer that focuses on computation. Most importantly, blobspace is much cheaper than blockspace.
EIP-4844, also known as Proto-Danksharding, will implement the framework and logic of Danksharding with the same new transaction format and validation rules.
EIP-4844 Development Timeline
Over the past 3 years, Ethereum has undergone a series of upgrades, transitioning from PoW to PoS consensus and making its blockchain more scalable.
On December 1, 2020, the PoS-driven Beacon Chain went live, allowing Ethereum users to stake their ETH on a separate Beacon Chain to validate transactions.
In September 2022, the Beacon Chain will merge with the Ethereum mainnet, combining the network's execution layer and consensus layer.
On April 13, 2023, the Shanghai Upgrade (EIP-4895) goes live, enabling Ethereum validators to withdraw staked ETH.
These upgrades are necessary for Ethereum to improve its scalability, but they do not directly improve the transaction speed or gas prices of the blockchain. Future upgrades such as shardchains and Danksharding will actually achieve scalability for Ethereum.
What is Sharding?
Another innovation of Danksharding is to merge the fee market, where only one proposer selects the transactions for all shards instead of each shard having its own proposer. To make this merged fee market work efficiently and mitigate the problem of Maximum Extractable Value (MEV), a method called proposer and builder separation will be implemented (proposer refers to the Ethereum protocol validator that selects which transactions to include in the next block).
However, implementing full Danksharding on Ethereum is not an immediate process, but requires several upgrades to be implemented gradually, such as EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding).
What is Proto-Danksharding?
Proto-Danksharding, named after Ethereum researchers Proto Lambda and Dankrad Feist, will increase Ethereum's TPS to approximately 1,000. It is a simpler step that is required before achieving full Danksharding. Most importantly, it will introduce a new transaction type that accepts blob data, which is a crucial component for enabling full Danksharding.
Vitalik Buterin believes that Proto-Danksharding implements most of the logic and framework of Danksharding, but it has not yet implemented any actual sharding. In other words, Proto-Danksharding is a prototype of Danksharding that provides a framework for implementing other shard upgrades in the future.
How does EIP-4844 reduce gas fees?
The main purpose of EIP-4844 (Proto-Danksharding) is to reduce Ethereum gas fees by using blobs to carry transactions. Blob data is cheaper and cannot be accessed by the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), it can only view the commitment to the blob. Additionally, the data bandwidth in Proto-Danksharding is fixed at 1 MB per slot.

Since simply making CallData cheaper could lead to a mismatch in average or worst-case scenarios, Ethereum developers are attempting to reduce gas fees by establishing a new type of blob to carry transactions (focusing on transactions from L2 Rollup).
The average Ethereum block size is about 90 KB, but theoretically, the maximum block size is approximately 1.8 MB. This means that Ethereum blocks can accommodate more transactions during periods of network activity, but at a very high gas fee. If calldata is 10 times cheaper, the transaction volume will increase by 10 times, and in extreme cases, the block size will increase by 10 times (18 MB). It is apparent that Ethereum cannot accommodate such large blocks within its network.
Solution
ProtoDanksharding solves the gas pricing crisis through a multi-dimensional EIP-1559 fee market.
Proto-Danksharding creates a separate transaction type that stores data from L2 Rollup in a large blob, and there is a limit on the number of blobs per block, which significantly reduces L2 fees. The blobs are stored on the consensus layer rather than the execution layer, so the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) cannot access them.
Even after Proto-Danksharding, sharding remains a complex task, but the complexity will be limited to the consensus layer. Therefore, the execution layer client teams and rollup developers will not need to do any additional work to transition from Proto-Danksharding to full sharding.
EIP-4844 also separates blob data from calldata, making it easier to store blob data within shorter time periods.
Data Storage Options for EIP-4844
Proto-Danksharding produces approximately 1 MB of data per slot (12 seconds), resulting in 2.5 TB of data per year. The storage of this data is performed within the Proto-Danksharding system on the consensus layer.The layer of knowledge can be addressed by the Historically Preserved Period (EIP-4444) to tackle data storage challenges and automatically remove blob data after a certain period of time. Regarding the issue of accessing old blob data, there are various methods to store historical data on decentralized protocols. For example, rollup, BitTorrent, Ethereum gateway networks, blockchain explorers, API providers, and third-party indexing protocols (such as The Graph) can store complete historical records for specific applications. What are the upgrades before and after EIP-4844? Before EIP-4844, Ethereum developers proposed several upgrades to reduce gas fees. For example, EIP-3651 reduced gas fees for block producers to interact with Ethereum block building software (Coinbase), EIP-3855 reduced gas fees for developers by pushing 0, and EIP-3860 reduced gas fees for specific use cases. EIP-4844 is a step towards full sharding, expanding the Ethereum network and reducing gas fees. Developers are planning a "Verge" after EIP-4844, which will introduce Verkle trees for scalability.
Impact of EIP-4844
The main goal of EIP-4844 is to reduce the L2 gas fees for Ethereum by 10-100 times by using a new type of blob to carry transactions, making the transition to full sharding easier as all future upgrades will be done only at the consensus layer.
At the architectural level, EIP-4844 introduces the use of a blob to carry transactions, which is the first time Ethereum has built a separate data layer for L2, laying the foundation for future fully Danksharding.
At the economic model level, EIP-4844 will introduce a new fee market for blobs, which will also be the first step for Ethereum towards a multi-dimensional market.
At the user experience level, the most significant perception for users will be the significant reduction in L2 fees. This underlying improvement will provide a crucial foundation for the explosion of L2 and its application layer.










