E2MResearch: Shawn (December 2023)
The popularity of this round of BRC-20 has directly led to a sharp increase in gas fees on the Bitcoin chain. Correspondingly, various solutions have been used to expand the Bitcoin ecosystem and projects to improve efficiency have emerged in endlessly. Here are a few related projects.
1. Map Protocol
Introduction
On December 7, 2023, the Bitcoin Layer 2 MAP protocol announced that it had received strategic investment from Waterdrip Capital.
MAP Protocol was founded in 2019 and began as a full-chain network focused on cross-chain interoperability.
There are three main current cross-chain communication solutions:
Multi-Party Secure Computation MPC, or Secure Multi-Party Computation, is a privacy-preserving distributed computing technology in the field of cryptography. The main representatives that adopt this cross-chain verification method include Axelar, Celer (cBridge), Multichain, Wormhole, and Thorchain. In the MPC cross-chain solution, fixed or regularly rotating witnesses composed of several roles designated by the project party serve as the final confirmer of cross-chain validity. Since the existence of privileged roles cannot be eliminated, the entire verification process cannot completely avoid the risk of evildoers.
A quasi-centralized solution, the oracle is an off-chain infrastructure that links off-chain data to the blockchain. In quasi-centralized cross-chain solutions, oracles are widely used, and the most representative one is LayerZero: LayerZero uses relayers and Oracle oracles for cross-chain transmission and validity confirmation. However, this solution also has the risk of relays and oracles working together to cause harm.
The light node is the light client, which is the SPV simple payment verification technology (Simplified Payment Verification) discussed in the Bitcoin white paper. It can quickly verify the legality of a transaction in the entire ledger in a lightweight manner. It has the characteristics of independent self-verification and does not rely on any privileged third party or authorized third party for legality verification. =Projects currently using light clients for cross-chain include MAP Protocol, Cosmos, Polkadot and Aurora (Rainbow Bridge).
MAP Protocol adopts a light node solution. Different from Cosmos, Polkadot and Aurora (Rainbow Bridge), MAP Protocol can cover all L1, not just ecological isomorphic chains.
It hopes to use Map Protocol to enable developers to easily build full-chain Dapps, thereby truly solving the problems of liquidity and ecological fragmentation in the multi-chain era. The official document lists some possible full-chain Dapps, such as full-chain Swap, full-chain lending, full-chain DID, etc.
Relationship with Bitcoin Ecosystem
Recently, Map Protocol announced that the protocol has been upgraded to become a layer 2 solution for Bitcoin. It mainly uses the Bitcoin network to improve the network security of the Map protocol.
PoS chains can take advantage of the features of Bitcoin’s timestamp service to enhance their security and solve long-range attacks. The MAPO platform periodically (every epoch) submits the hash and signature of the last block of each epoch as a checkpoint for the Bitcoin network. Therefore, the MAPO client can determine the final canonical chain of the MAPO platform PoS chain by retrieving checkpoints from the Bitcoin network, thus preventing long-range attacks by malicious validators on the MAPO network.

Image Source:https://mapo.gitbook.io/docs-en/base/index_en-2
This solution should be based on the relevant architecture of Babylon. At the same time, from the recent announcement of a strategic alliance between Map Protocol and Babylon, it can be seen that the two will cooperate to release the potential of the Bitcoin ecosystem in the future.
BRC-201
Another innovation of the Map protocol is the proposal of the BRC-201 standard. This standard is backward compatible with the BRC-20 standard, through which BRC-20 tokens can be easily bridged to chains that support smart contracts such as Ethereum, thereby expanding the application scenarios of BRC-20 tokens.
The following is the BRC-201 token standard. Compared with the BRC-20 protocol, three fields are added: chain (target chain), ext (extended operation type), and ref (reference content such as target address).
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "transfer",
"tick": "ordi",
"amt": "100",
"chain": "eth",
"ext": "bridge-out/in",
"ref": "address/txhash"}
An example of bridging:
{
"p": "brc-20",
"op": "transfer",
"tick": "ordi",
"amt": "100",
"ext": "bridge-in",
"chain": "eth",
"ref": "0x 857 ab 26790 d5 926 de 3a a 3972230 dd 8 b 926 b 1 e 6 d5 7 c 6 b 7 a 077 d 649 ae 3 bea 393 bc"}
Token
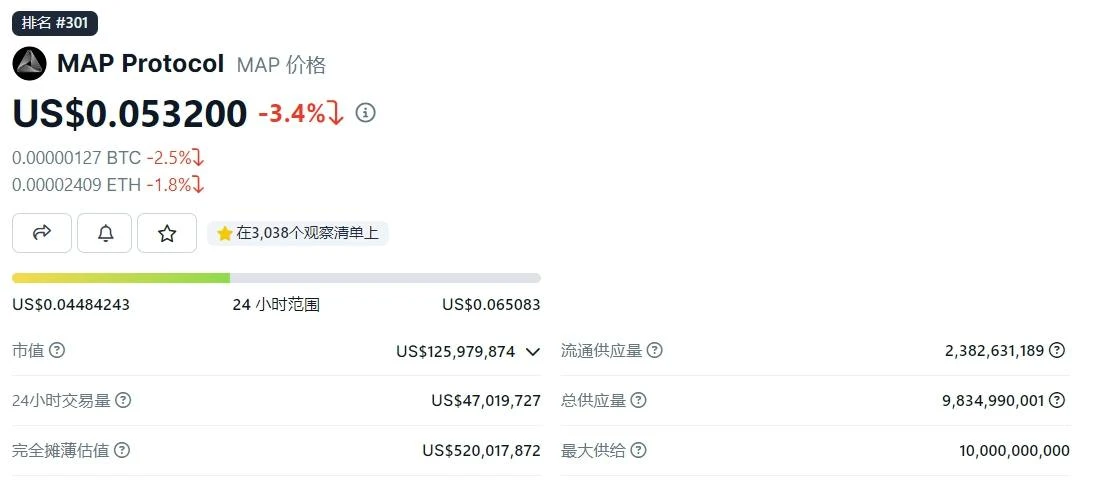
Data Sources:https://www.coingecko.com/en/digital currency/map-protocol
evaluate
The Map protocol only uses the Bitcoin network to enhance its own network security. It also proposes the BRC-201 standard that extends BRC-20 to the smart contract chain, but it is not a Bitcoin second-layer network in the true sense. More (from this perspective, after the Babylon mainnet is launched, all Cosmos chains that obtain Bitcoin security through the Babylon chain can be regarded as the second-layer Bitcoin network). At the same time, the BRC-201 standard also introduces the risk of cross-chain bridges, which requires relevant indexers and project parties to support the standard to achieve it.
2. Roup
Roup is a protocol that uses the BRC-201 standard to cross BRC-20 assets to Bitcoin Layer 2. The implementation process is as follows:
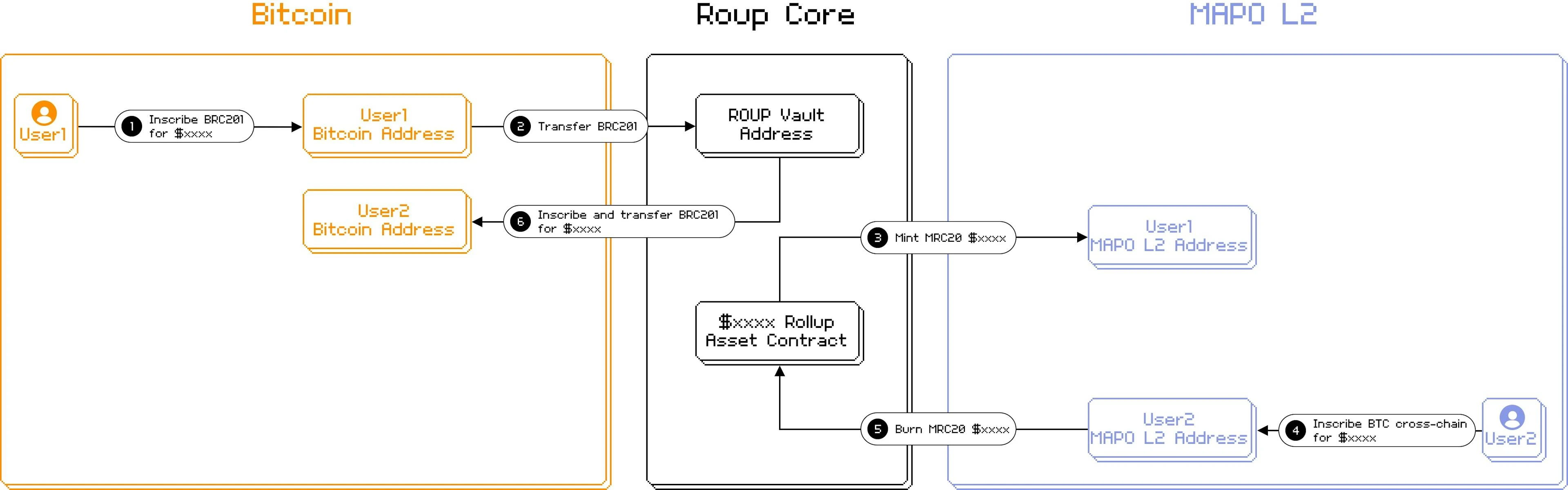
source:https://docs.rolluper.xyz/how-does-roup-work/tech-workflow
From Bitcoin to Mapo L2:
The user will launch the new BRC 201 inscription. BRC 201 token parameters need to be entered, including target chain, target address, token code, token amount, and rate.
After the new BRC 201 is inscribed, it needs to be transferred to the official ROUP Vault address.
After the transfer is confirmed, the token asset contract will mint the corresponding number of tokens on MAPO L2 to the users designated address.
From Mapo L2 to Bitcoin:
Users initiate cross-chain transactions by specifying the target chain, target address, token code, and token amount.
The token asset contract will destroy user tokens at MAPO L2.
Cross-chain transactions are verified.
New BRC 201 will be credited and transferred to the user-specified Bitcoin address.
Currently, only one-way transfer from BTC to MAPO is supported, and only whitelisted token operations are supported.
Features: The project token ROUP is distributed using BRC-20 fair casting. The handling fees generated by ROUP will be returned to the community through destruction, repurchase, etc. The specific proportion will be determined by user voting.
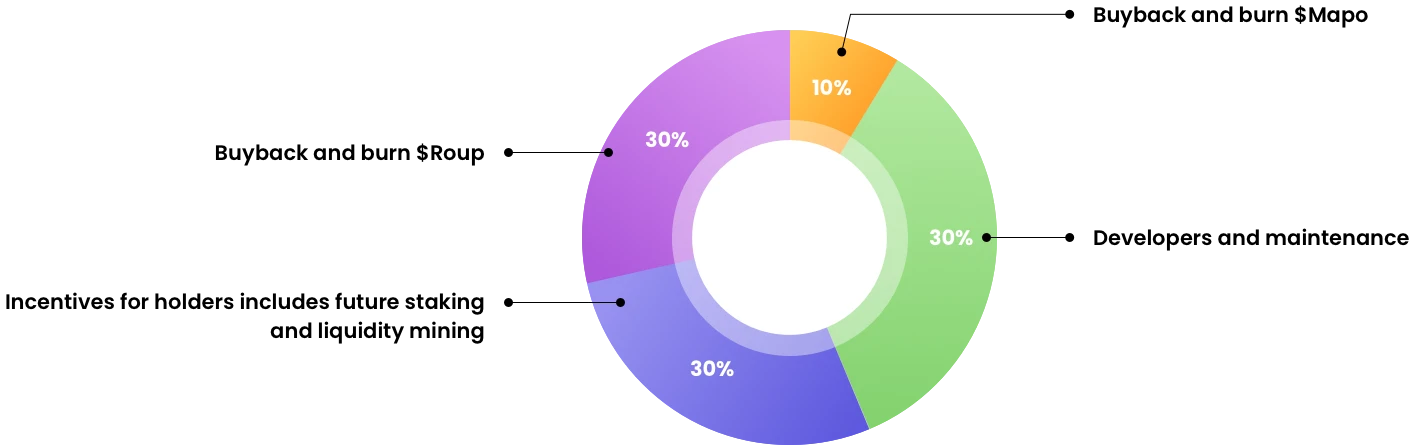
30% of the revenue will be distributed to developers, etc., and part of it will be used to repurchase Roup and Mapo.
The token has experienced significant growth recently, with its full-circulation market value approaching $40 million.
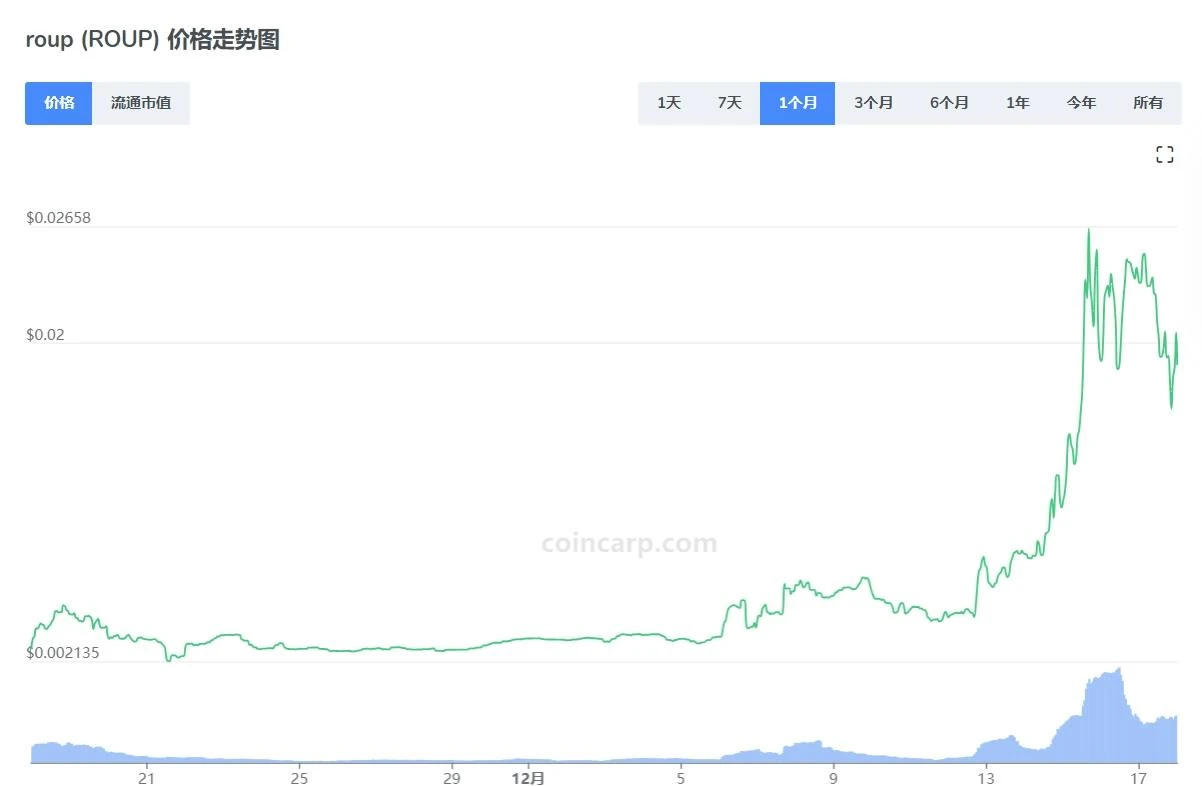
source:https://www.coincarp.com/zh/currencies/roup/
evaluate
The cross-chain solution developed based on the Map protocol and the BRC 201 protocol is somewhat innovative, but it relies on the ecological support of the BRC 201 token on the Map chain, and the standard has great limitations. The project party began to empower the BRC-20 token, which separated the BRC 20 token from the nature of a meme currency. At the same time, a fixed proportion of income was distributed to developers, which solved the problem of the project party not receiving incentives when launching BRC-20 fairly. The problem.
3. MultiBit
MultiBit is the first two-way cross-chain bridge between BRC-20 and ERC-20 tokens.
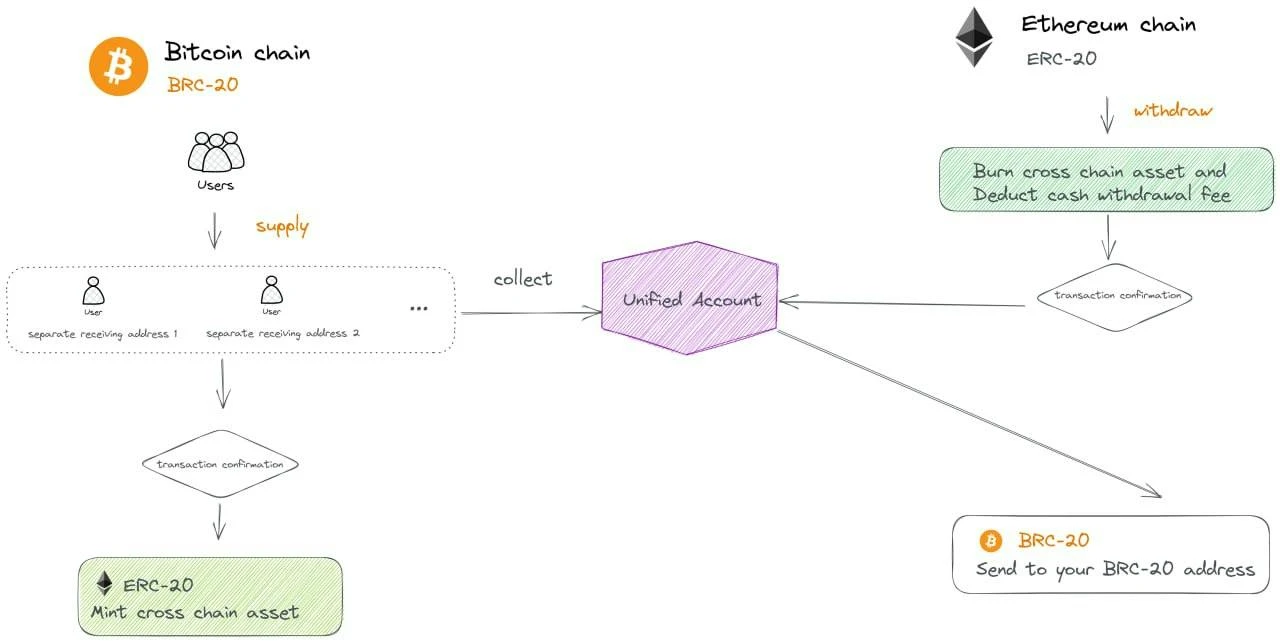
source:https://docs.multibit.exchange/multibit
The following is the cross-chain process:
BTC network to ETH/BNB network:
After connecting the wallet, the Multibit platform will assign each user a dedicated BRC-20 address.
Users need to transfer BRC 20 tokens to their dedicated BRC-20 address for cross-chain transfers.
After a block is confirmed, users can see the tokens available for minting in the order book. The user has minting permissions and needs to manually mint the transferred tokens.
When minted, the transaction requests the signers signature from the backend and provides it to the contract. Once the contract verifies the signature, users can mint tokens on the ETH/BNB chain.
The project hopes to realize AMM, Farm, mortgage stablecoins, etc. of BRC-20 tokens by cross-chaining BRC-20 to the ETH/BNB network.
Because it involves the BRC-20 cross-chain concept, the project tokens have grown significantly recently:
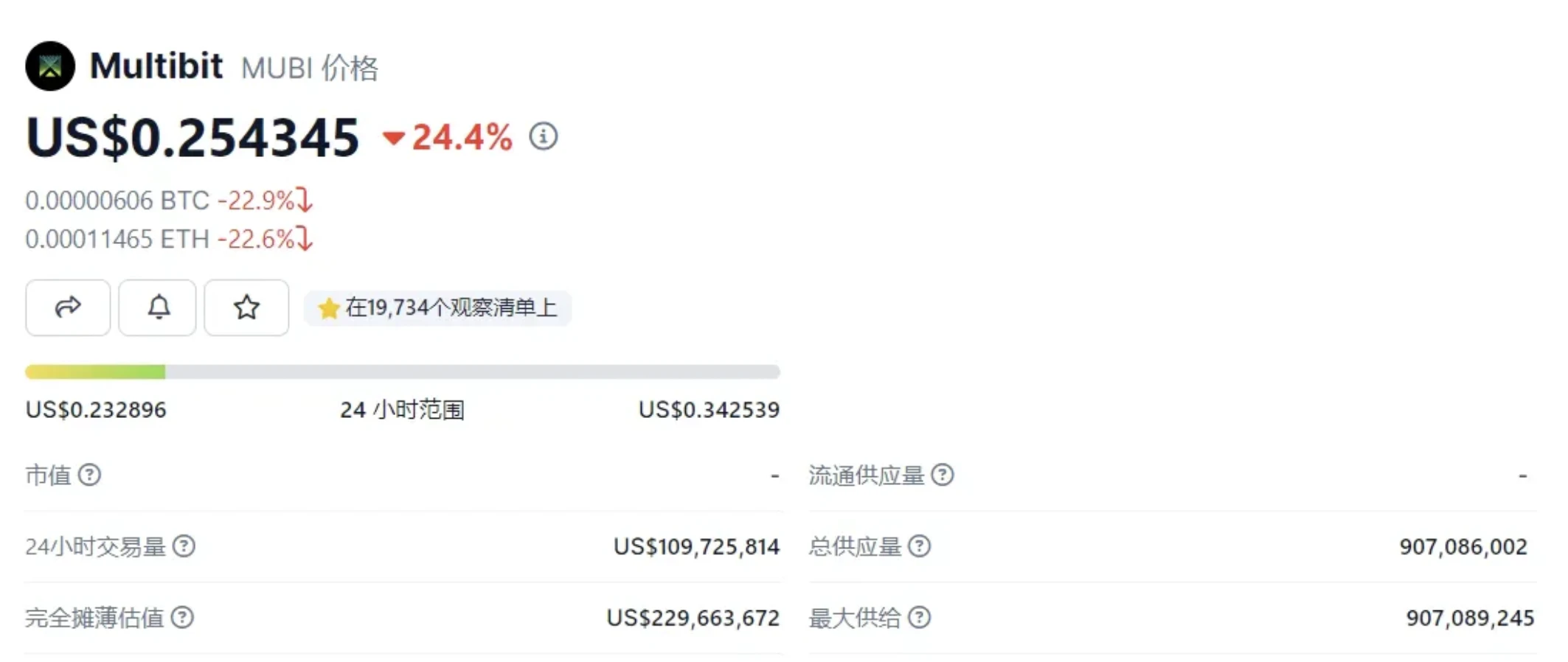
Source: https://www.coingecko.com/zh/%E6%95%B0%E5%AD%97%E8%B4%A7%E5%B8%81/multibit
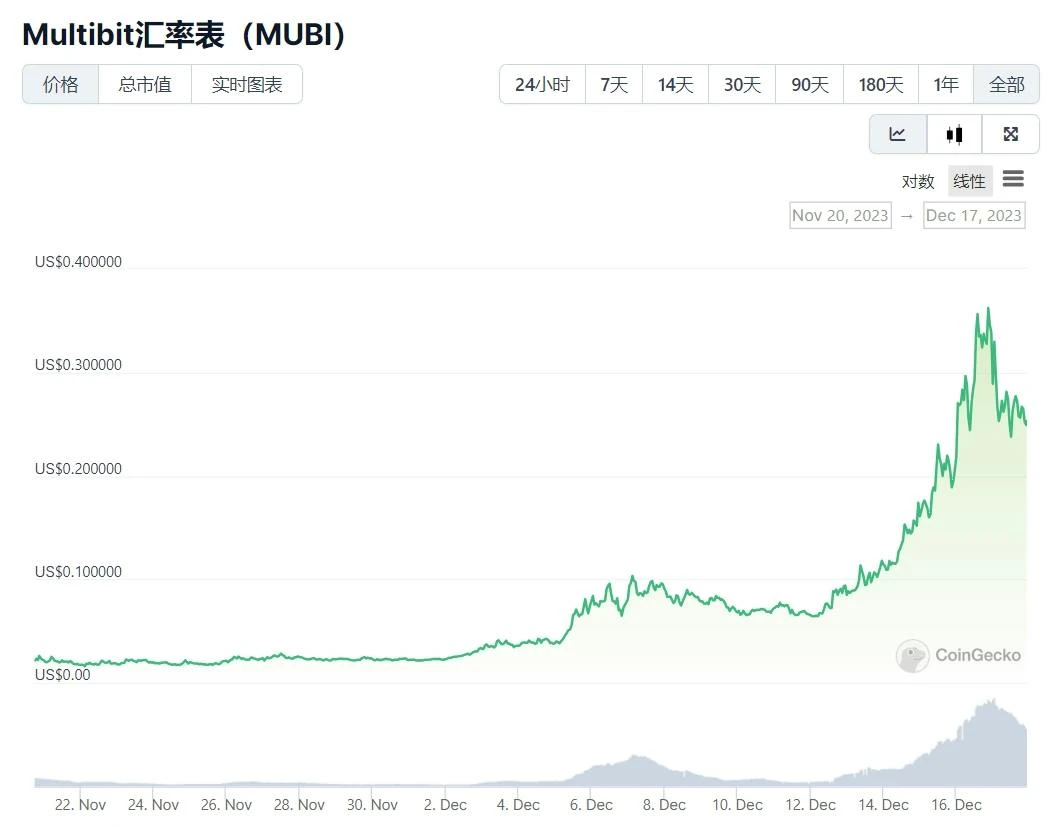
source:https://www.coingecko.com/zh/%E6%95%B0%E5%AD%97%E8%B4%A7%E5%B8%81/multibit
evaluate
It can be seen that the project still uses a similar traditional cross-chain bridge solution, but has made some improvements for the BRC-20 token, but there is still a risk of centralization. At the same time, the solution of cross-chaining BRC-20 to the existing smart contract chain to implement BRCFi is exactly the same as the implementation of AMM, Farm, and collateralized stablecoins in the ERC-20 ecosystem, without much innovation.
4. Stacks
Introduction
Stacks is a smart contract layer for Bitcoin, but has a different relationship to the Ethereum mainnet and Layer 2. Stacks has its own chain, compiler, and programming language called Clarity. It runs in sync with Bitcoin. Essentially, a new chain is built outside the Bitcoin chain, with an independent governance structure and transaction model.
The first feature of Stacks is the adoption of the PoX consensus model.
The Stacks layer relies on STX and BTC for its novel consensus mechanism called Proof of Transfer (PoX), which leverages both the Stacks and Bitcoin layers. PoX is similar in spirit to Bitcoin’s Proof of Work (PoW) consensus: just like Bitcoin PoW miners spend electricity and are rewarded with BTC, Stacks PoX miners spend (mined) BTC and are rewarded with STX. Like PoW, PoX uses a Nakamoto-style single leader election: PoX miners bid by simply spending BTC, and they have a leader with bid weights as random probabilities. Leader election takes place on the Bitcoin chain and new blocks are written on the Stacks layer. In this way, PoX reuses work already done by Bitcoin miners and does not consume any significant additional power: only a functioning laptop/computer is required to conduct Stacks node bidding using BTC.
Another part of PoX is"Stacking", which allows holders of Stacks tokens to participate in the security of the network. If the holder chooses"Stacking"their tokens, then they are regularly rewarded with Bitcoins. This is a unique mechanism that allows participants in the Stacks chain to receive Bitcoin directly as rewards, further strengthening the Stacks network’s connection to Bitcoin.
Stacks’ Satoshi upgrade is expected to be implemented before next year’s halving.
For Stacks, the main significance of Nakamoto’s upgrade is as follows:
(1) Shared network security with BTC: transactions are settled on the Bitcoin network. This feature makes Stacks transactions more secure and reliable, and becomes a true Layer 2 rather than a side chain with its own independent state.
(2) Launch of sBTC: The introduction of the Bitcoin-linked asset sBTC enables smart contracts to run faster and cheaper, and can easily transfer BTC into or out of Stacks L2. Conducive to the development of the Bitcoin DeFi market.
When converting BTC to sBTC: Send BTC to a multi-signature address and initiate a transaction on the Stacks network, triggering a smart contract that will send BTC to the multi-signature address and create a corresponding number of sBTC assets on the Stacks network .
Convert sBTC back to BTC: Send a message to the smart contract and initiate another transaction on the Stacks network, triggering another smart contract that will destroy the corresponding amount of sBTC assets and send the corresponding amount of BTC to the user.
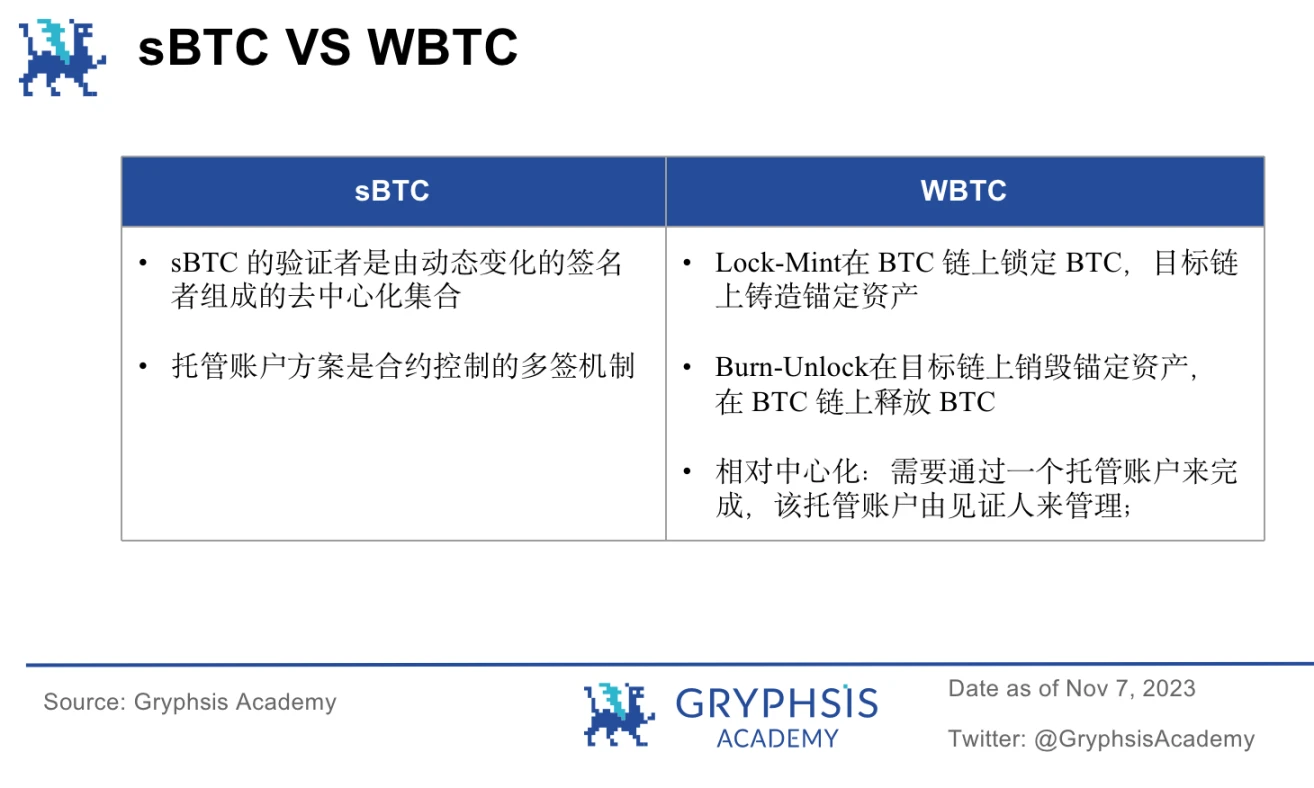
(3) Supporting BTC atomic swap, Bitcoin addresses can own and move assets defined on the Stacks layer, such as STX, stable coins and NFT, and transfer them through Bitcoin L1 transactions.
(4) Clarity language: The security of smart contracts on the chain can be greatly improved
(5) Bitcoin status reading: It can completely read the data of the Bitcoin chain, supports reading Bitcoin transactions and status changes, and executes smart contracts triggered by Bitcoin transactions. The Bitcoin reading function can synchronize Bitcoin L1 network data and L2 network data.
(6) Fast block generation: The current block generation time is 10 minutes. After the upgrade, it can reach a block generation speed of 4-5 seconds, breaking the 10-minute block generation limit of BTC. The transaction hash will be generated every time a Bitcoin block is generated. Writing to Bitcoin keeps the network secure.
(7) Customized subnets support multiple development languages: Scalability layers such as subnets can make different tradeoffs in performance and decentralization than the Stacks mainnet. The subnet can support other programming languages and execution environments (such as Ethereum’s Solidity and EVM), which allows all Ethereum smart contracts to use Bitcoin-anchored assets and be settled on the Bitcoin chain.
Ecological situation
The total TVL of the ecosystem has reached 670 M, but most of it is contributed by Liquid Staking. There is only one protocol left, ALEX, which is the Dex platform on Stacks.
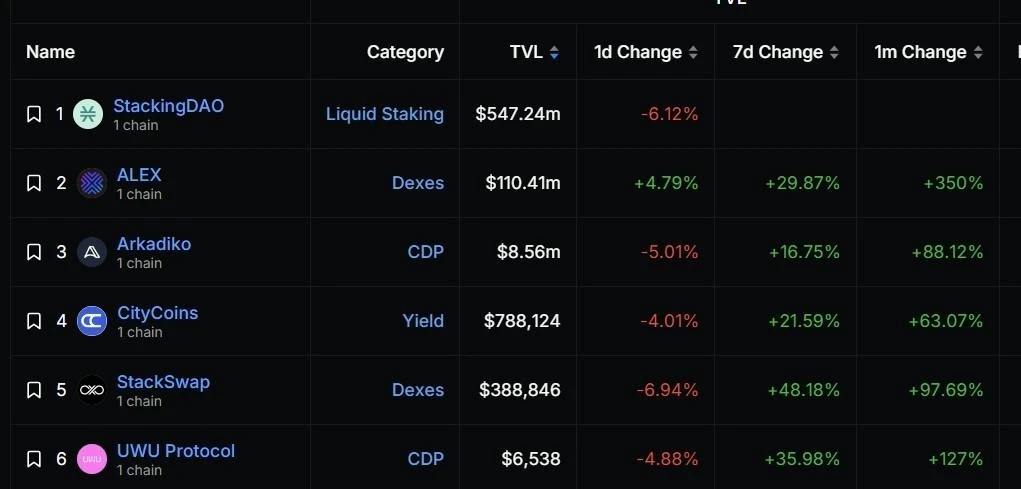
source:https://defillama.com/chain/Stacks
The current circulating market value is about US$2 billion. Due to the popularity of the Bitcoin ecosystem this year, the price of STX has also increased significantly.
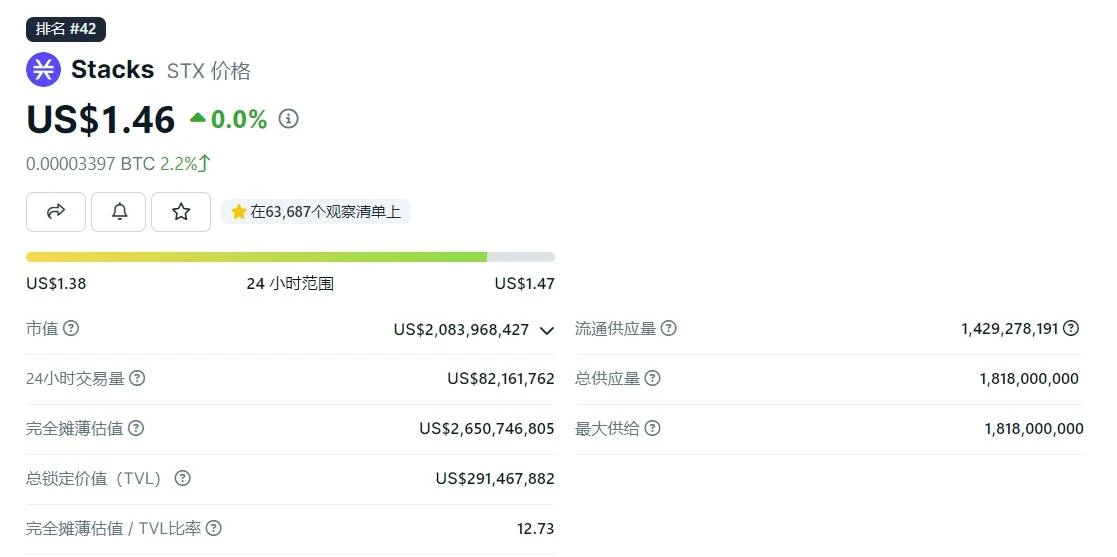
Source: https://www.coingecko.com/zh/digital currency/stacks
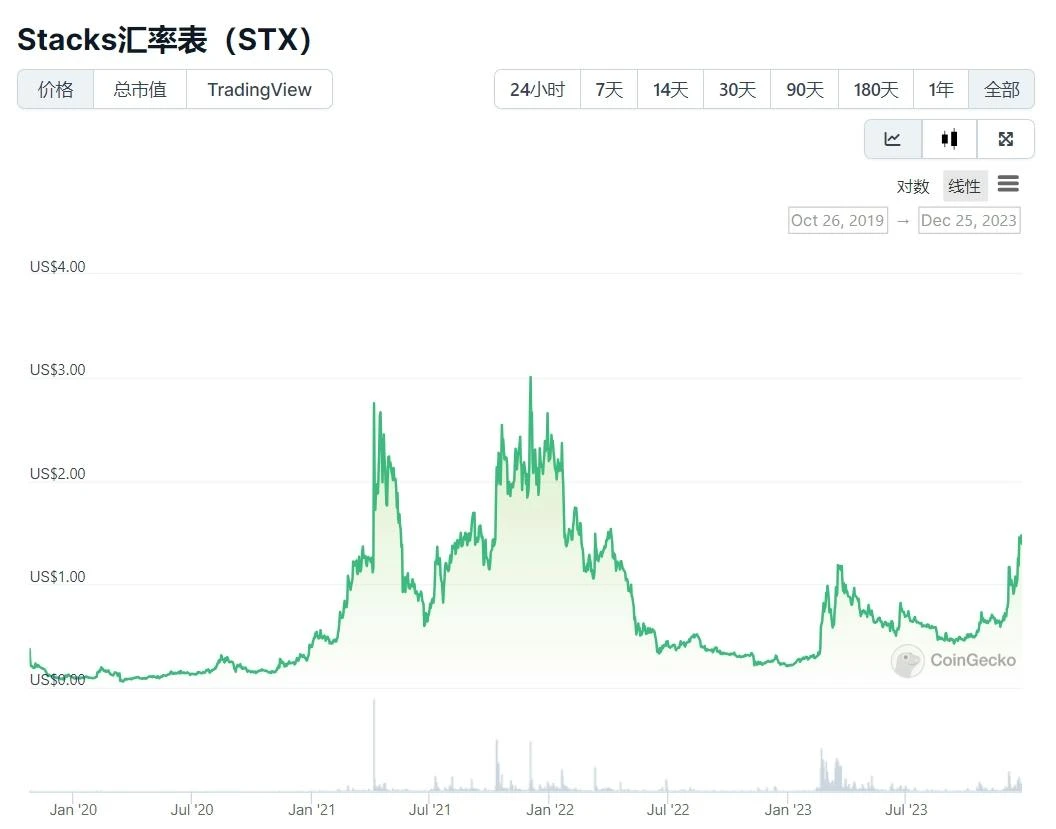
source:https://www.coingecko.com/en/digital currency/stacks
evaluate
Stacks currently has a very low TVL on the chain, transactions are inactive, and the unique development language Clarity will increase the threshold for developers, resulting in an inactive development ecosystem. After the Satoshi Nakamoto upgrade next year, it will be more closely integrated with the security and ecology of Bitcoin. At the same time, it will support customized subnets and make it easier to access the EVM ecology. The current focus is more on expectations for future development.
5. SATS
main timeline (https://www.binance.com/zh-CN/feed/post/1275458907377):
March 9, 2023: $SATS was deployed, with a total amount of 2100 trillion, with a maximum of 100 million each, for a total of 21 million. At that time, I not only lamented who had such a big idea, but also deployed such a behemoth in 1:1 sats. At that time, no one thought that it would be defeated.
May 11: The number of currency-holding addresses exceeded ordi, boosting the development of SATS.
May 15th: SATS inscription progress reached 1%, and the number of currency holding addresses reached 7,309, a milestone.
May 16: Due to the success of the Unisat market, everyone is keen to buy Unisat points, and Mint SATS has become the first choice.
June 29: SATS inscription progress 13.69%, number of currency holding addresses 19,831, Mint cost 1.35 U, market 0.8 U. A large investor purchased SATS for $25,000 at one time. In June, more and more SATS communities began to be established, and big names gradually began to build positions.
July 30: SATS inscription progress is 36.87%, the number of currency holding addresses is 26,905, Mint cost is 0.65 U, market is 0.43 U. In July, due to the decline of BTC, the entire BRC 20 ecosystem is in a state of malaise, with gas as low as single digits , this is the best time to open a position in SATS. At the same time, because OKX makes markets in the Ordinals market, many users also make some profits by moving bricks.
September 24: The SATS inscription progress is 100%. It took more than 6 months and cost tens of millions of dollars to complete this impossible task.
September 27: Unisat launches brc 20-swap testnet and puts SATS first.
Total FOMO on SATS in September and was quickly wiped out. At the same time, more KOLs began to promote SATS, and more and more communities were established to spontaneously promote SATS, creating a very strong community atmosphere.
October 10: Unisat announces use of SATS for service charges.
December 12: Binance announced the launch of SATS, and the price soared from 25 U to 54 U before the launch.
evaluate
SATS took more than 6 months and spent tens of millions of dollars to complete the entire Mint. This also makes it the BRC 20 token with the highest number of currency holding addresses and the largest total cost of Mint. In addition, after Unisat launches UniSat Indexer, it will mine through sats and use sats as service fees, further empowering SATS and breaking away from the traditional meme currency attributes. Indexer, as the most important infrastructure project of BRC 20 tokens, will most likely be implemented using a separate chain, with SATS as its base currency, which has a lot of room for imagination.
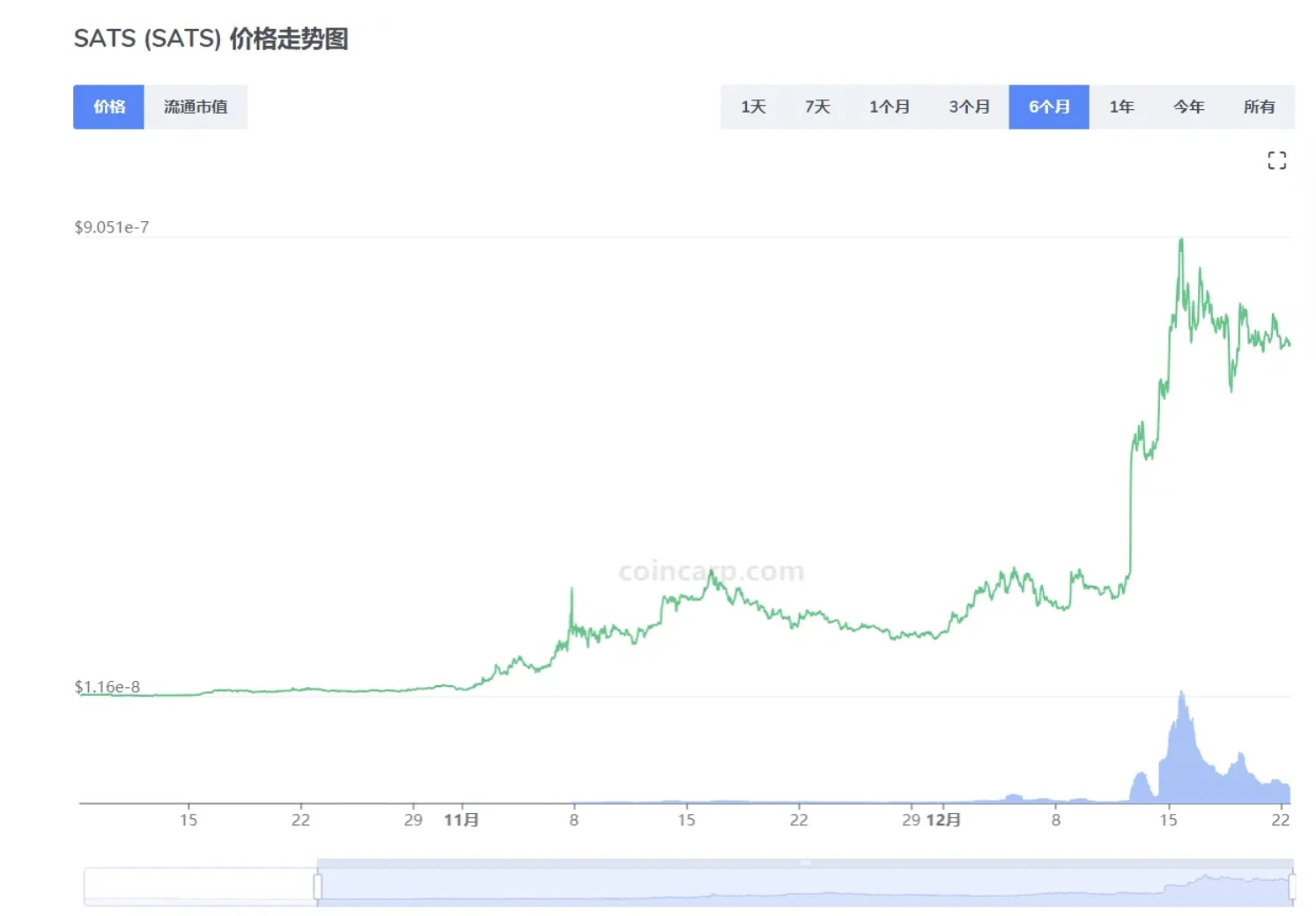
source:https://www.coincarp.com/zh/currencies/sats/
SATS currently has a market capitalization of nearly $1.5 billion, surpassing ORDI to become the BRC 20 token with the largest market capitalization.
source:https://www.coincarp.com/zh/category/brc20/
Reference article:
An article explaining MAP Protocol in detail: Provable decentralized full-chain infrastructure
The Development History of Inscription SATS in the Currency Circle
BTC Ecological Accelerator: Upgrading from Stacks’ Nakamoto to discuss the investment value of $STX
About E2MResearch
From the Earth to the Moon E 2 M Research focuses on research and learning in the fields of investment and digital currency.
Article collection:https://mirror.xyz/0x80894DE3D9110De7fd55885C83DeB3622503D13B
Follow on Twitter :https://twitter.com/E2mResearch️
Audio Podcast:https://e2m-research.castos.com/
Small universe link:https://www.xiaoyuzhoufm.com/podcast/6499969a932f350aae20ec6d
DC link:https://discord.gg/WSQBFmP772










