
Non-Fungible Token (hereinafter referred to as NFT) is an encrypted token on the blockchain, which represents the ownership of a unique item. NFT can represent both real assets (such as a piece of land) and digital assets (such as rare virtual cards). Bitcoin is a homogeneous token because one bitcoin can be exchanged for any other bitcoin. In contrast, each NFT is unique, which essentially represents the scarcity of assets in a digital way, and this scarcity is verifiable.
The concept of storing unique items as data on the blockchain is not new to most of the NFT community. The blockchain is a standard medium for displaying and trading NFT assets. These assets are open and transparent, tradable all over the world, and have higher liquidity. Blockchain also provides a secure environment for storing the entire trusted history of an asset from its creation to the present.
first level title
Dynamic NFTs capable of interacting with off-chain data and infrastructure
Next, NFT will transition from static to dynamic, that is, the perpetual smart contract accesses the oracle and interacts with off-chain data and systems. With an oracle, it is possible to use off-chain data and systems to create NFTs, conduct P2P transactions, and view status. For example, if the oracle informs the smart contract that a football player has scored a hat-trick in a match, the smart contract can automatically create a limited-edition virtual card for the player.
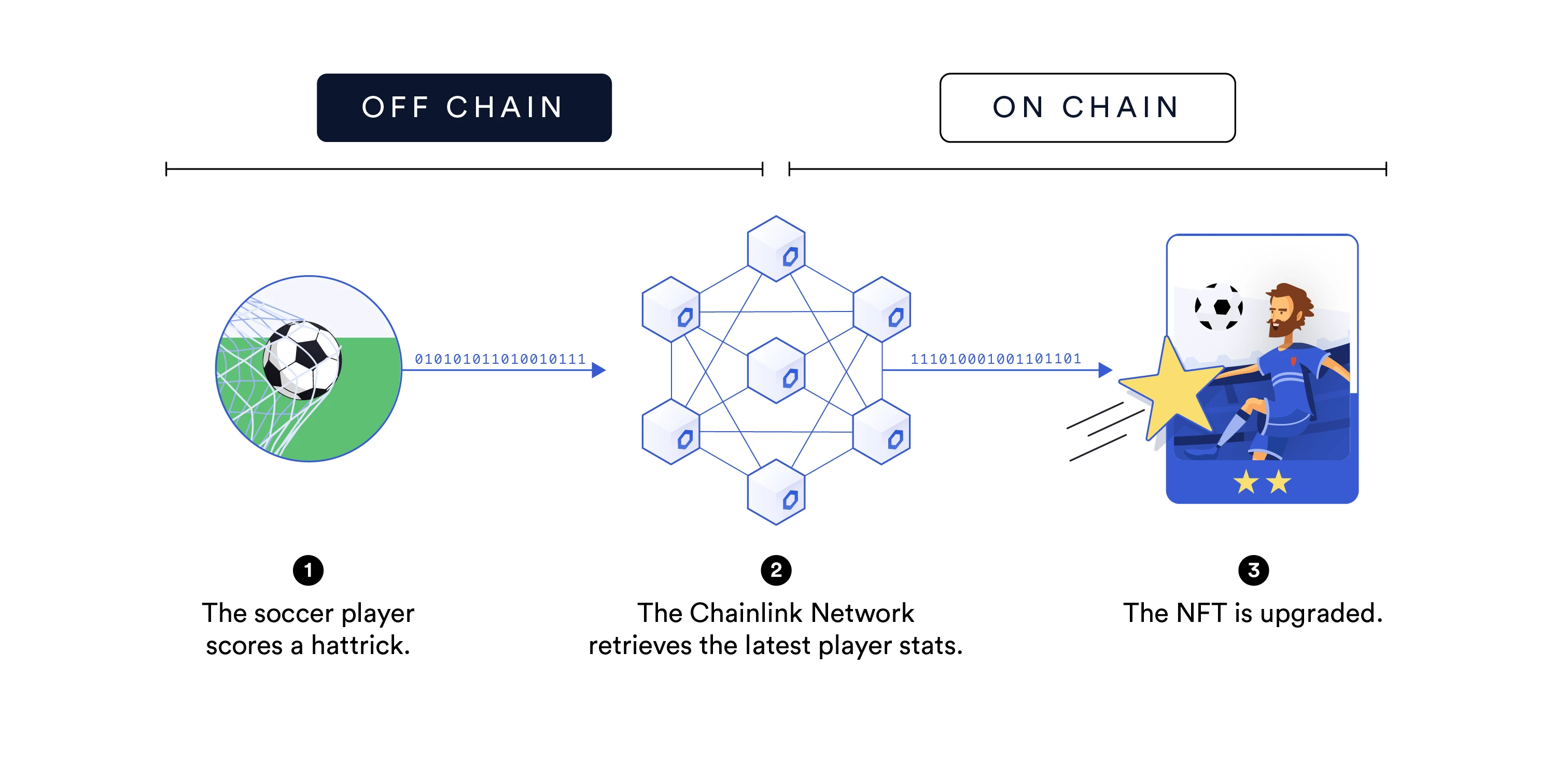
A simple framework for creating dynamic blockchain NFTs with Chainlink oracles
Chainlink is a decentralized oracle network that can securely and reliably connect smart contracts to off-chain data and systems. Chainlinks oracle machine framework includes multiple independent oracle machine nodes, verifies and aggregates data from multiple data sources, obtains data for user smart contracts, and avoids the risk of single point failure.
Developers can use Chainlink to securely connect NFTs to IoT data, web APIs, and various data providers. Among other things, they can leverage Chainlink VRF to obtain verifiable random numbers, interact with off-chain backend systems, and even trigger cyber-physical systems. All of these functions can be used to create dynamic NFTs, respond to data requests and fully integrate into traditional infrastructure.
first level title
Competition NFT
secondary title
1. Game scores
secondary title
2. Verifiable random numbers
image description
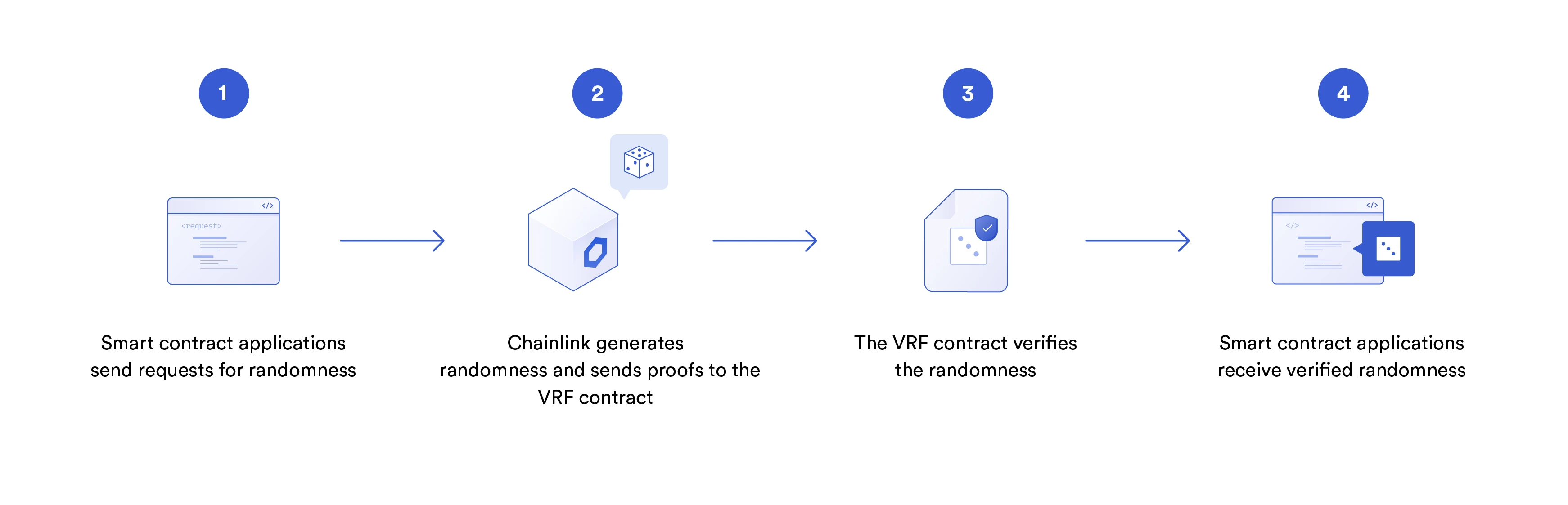
Basic working principle of Chainlink VRF
3. Augmented reality
Pokemon Go has opened up a new mode of interaction between games and reality, and players from all over the world can compete in the game together. With Chainlink, NFTs can be created in the real world based on subjective data (i.e. data unique to the user) or objective data. NFT can be randomly placed through Chainlink VRF, or it can be placed in a designated place.
4. Fantasy sports games based on reality
first level title
Reward and Governance System
Enterprises have always hoped to innovate their user incentive mechanism and maintain interactive communication with users. They can use NFT digital tokens to create new user incentive models.
5. Digital Collections
NFTs can be used to create digital collectibles for interested people to collect, a concept similar to collecting baseball cards. Create limited cards based on NFT and link them to specific real events. For example, WAX and Topps have discussed issuing limited-edition baseball cards linked to real game data such as a players home run record. Chainlink can connect smart contracts to web APIs, verify game data, and create digital cards.
6. Lifestyle Rewards
Another interesting direction to explore is to reward users in the game based on their completion of off-chain tasks. For example, if the number of steps recorded by a childs sports bracelet reaches a certain threshold, or the test score exceeds a certain score, then the game can reward them with special NFT tokens, such as special game props, so that the child will be motivated to go Exercise or study. Binding exercise or learning to game incentives can create a virtuous cycle. Chainlink can access IoT data and transmit it to smart contracts to determine whether users can get NFT rewards.
7. Event-Based Rewards
Event-based NFTs can also serve as rewards. For example, if a football player scores a hat-trick in a game, three limited edition tokens will be created across the city, and whoever finds them will be honored to meet the player. Or, if the Lakers score 100 points in a game, 20 McDonalds 50% off coupons will be distributed citywide, which can be found through augmented reality.
8. Consumer Participation Rewards
Businesses reward consumers for frequent engagement, often with the option of issuing physical or digital coupons. And now, they can create time-limited NFT coupons that are directly linked to consumer engagement. Chainlink can connect IoT data to create coupons based on verifiable engagement data, such as the 1,000th customer who walks into a store, or the 10th store visit.
9. Crowd voting
first level title
Authenticity verification
Another transformation direction of NFT is to interact with traditional systems, especially to use it to track special assets and integrate into traditional financial and trade chain processes. If the traditional infrastructure cannot interact with the NFT blockchain, it will be difficult for NFT to be promoted and applied in reality.
10. Origin Verification
NFTs are especially useful for tracking physical assets such as luxury goods, rare cultural relics, and supply chain products. Tokenizing these assets has two major advantages, quality control and anti-counterfeiting, since anyone can view the records on the blockchain to verify the origin of the goods. Businesses can use smart contracts in global trade processes, plug into Chainlink oracles, connect to payment systems, provenance information blockchains, and traditional backend systems. This keeps the process transparent and smooth, including cargo verification, payment, and automatic upgrades of corporate back-end systems. You can also set a specific time limit and process end point, and once the time limit or end point is reached, the NFT will be automatically destroyed.
11. Authentication
Several projects are already underway to develop digital identities that can interact with existing applications. In this way, users can plug and play their identity information in other applications while protecting their privacy. Chainlink allows smart contracts to initiate requests to blockchains that require identity authentication, verify personal identity information, and attach data output from external business processes to personal identity information. It is worth mentioning that in the future, identity information may play a role in cyber-physical systems, and electronic identities will authorize users to enter a certain physical system.
12. Certificate
first level title
Valuation update
Asset values are not static, so asset valuations need to be constantly updated when assets are traded or used as collateral for loans and certifications. Chainlink oracles can be connected to off-chain trusted APIs, aggregate multiple data sources, and provide reliable valuations for on-chain assets.
13. Real estate
Several projects are currently developing real estate and its associated asset tokens on the blockchain. These include home mortgages, rent and titles. Chainlink can transfer off-chain data to on-chain, adjust virtual currency home mortgage loan amounts, or provide the latest property valuations. Chainlink can also verify property ownership for off-chain applications, or send payment instructions to traditional payment service providers to issue rent.
14. Land
Land ownership is also gradually being developed on the blockchain. Chainlink oracle machines can be connected to IoT devices/drones to determine the production status of land, and can also hire evaluation agencies to provide independent valuations. They can also access web APIs to view historical data such as weather to accurately value land. Chainlink can use this data to more objectively value land for better transactions or mortgages.
15. Financial Cash Flow
image description
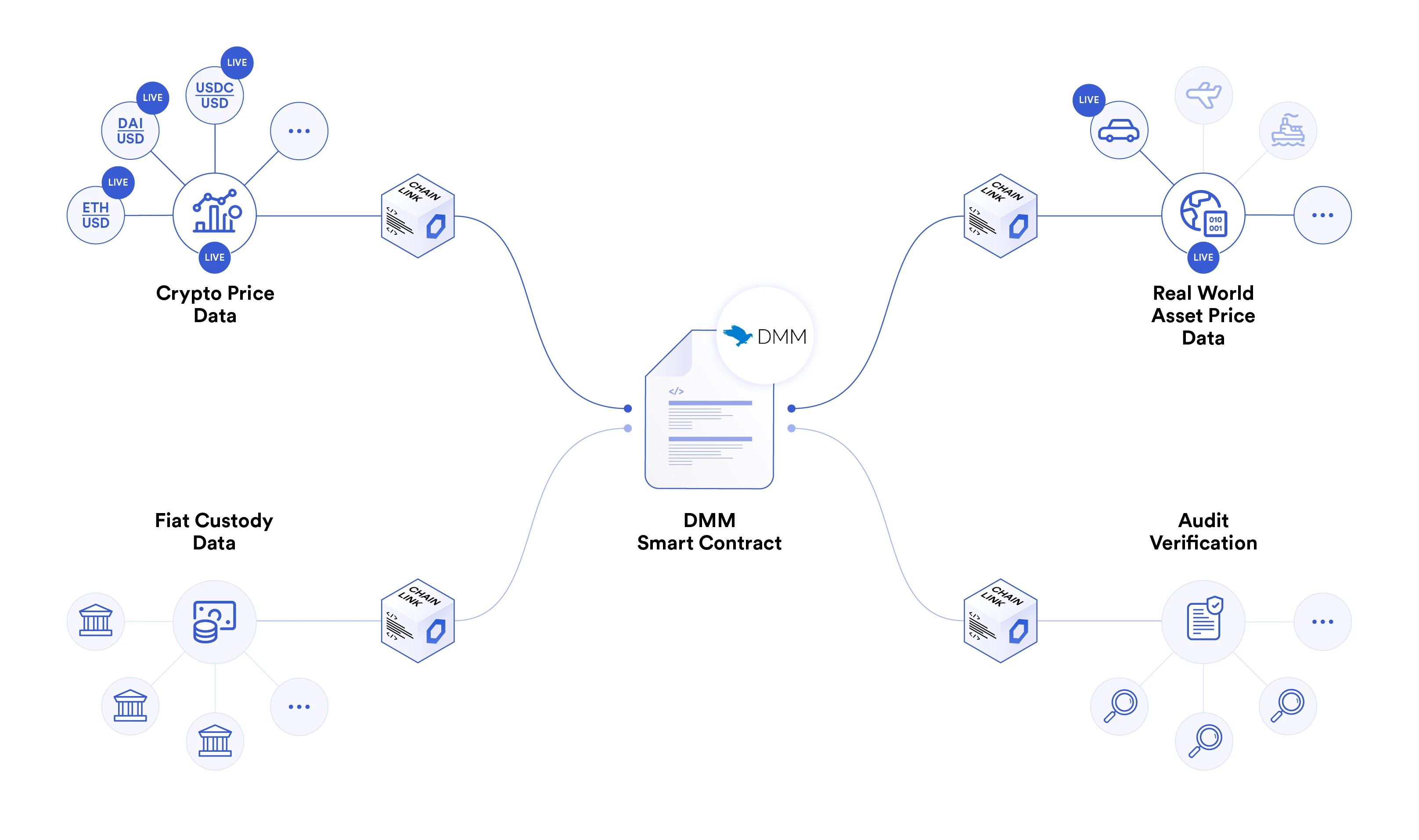
DMM integrates Chainlink oracles to provide on-chain valuations for its lending business
16. Physical Commodities
first level title
Start creating dynamic NFTs today!
If you want to create NFTs in blockchain projects, or upgrade Dapps to dynamic NFTs, or explore this new field for enterprises, please feel free to contact Chainlink.
Check out Chainlink’s developer documentation or join our technical discussions on Discord.










