first level title
text
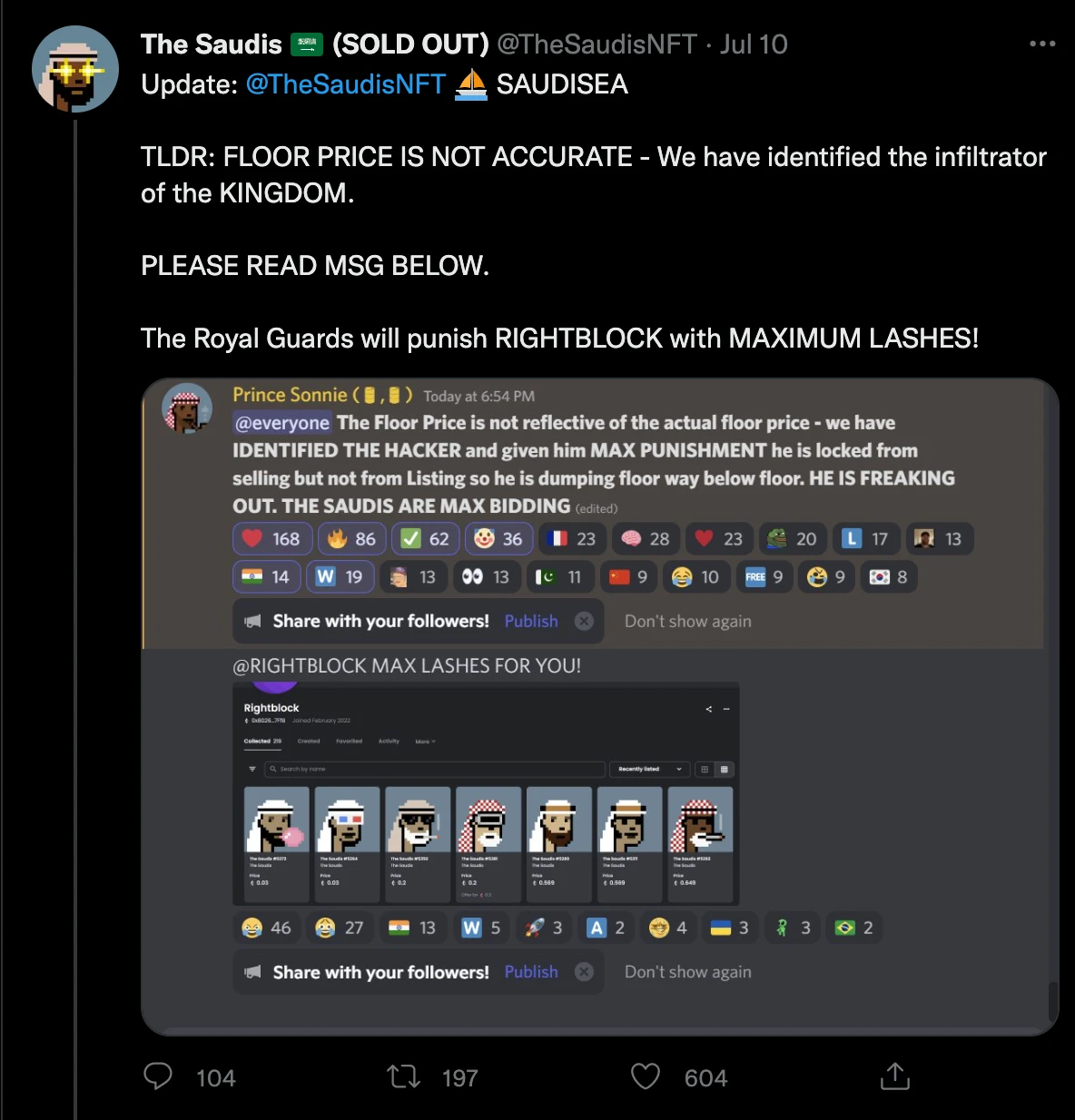
On July 10, 2022, TheSaudis, a popular NFT project, launched a freemint event (whitelist users can mint their NFT for free). And just after the mint event ended, a user named RIGHTBLOCK sold a large number of NFTs in the market. After finding out, the project party quickly locked the user and made changes to the contract to transfer a large number of NFTs in the users hands Back, they then promised to give these NFTs back to community users.
first level title
Diamond Protocol Introduction
EIP-2535 is a proposal on Ethereum to modularize the code of contracts. Its purpose is to allow large smart contracts to break through the maximum size limit of 24kb, and to make it easier for contracts to update their functions.
To understand the Diamond Protocol, there are several related concept definitions that need to be known:
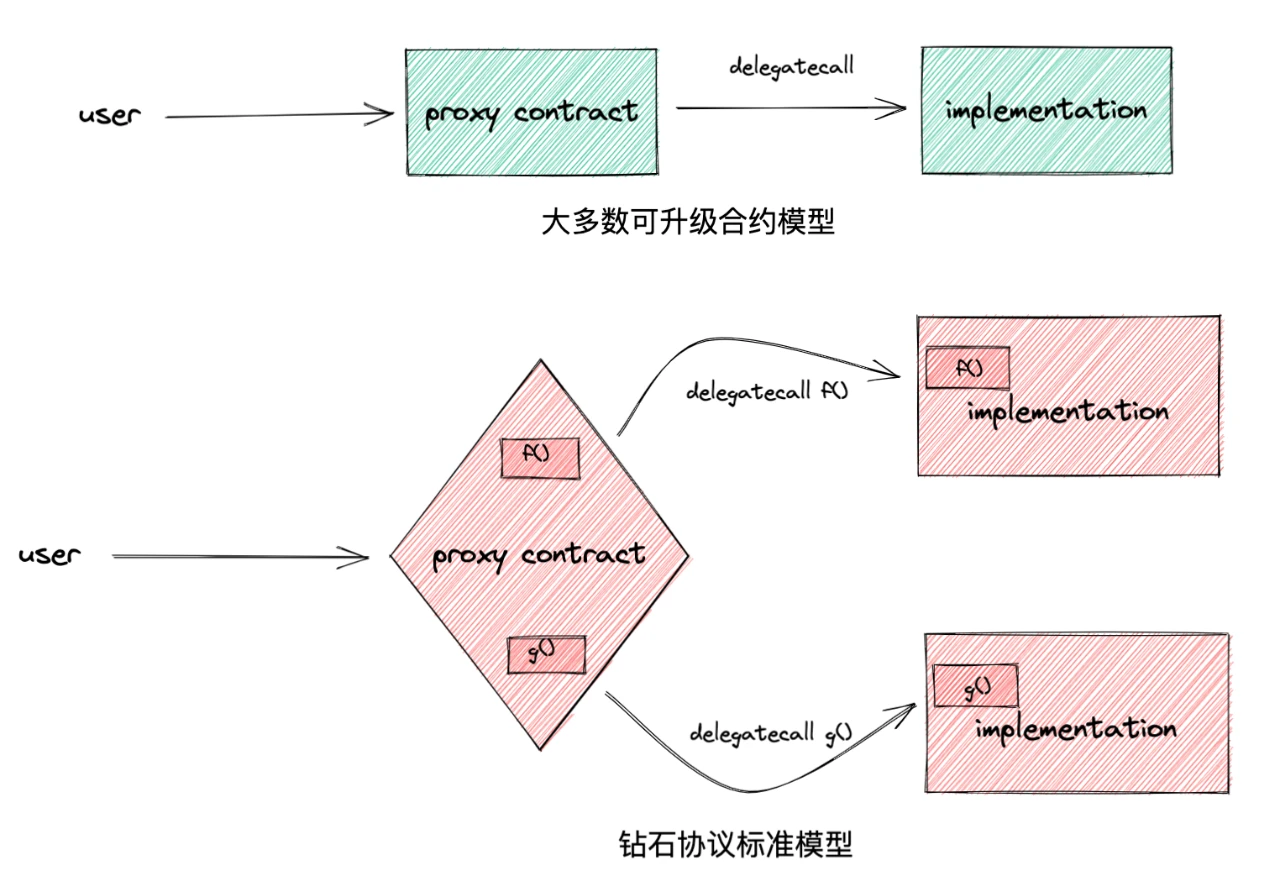
Diamond (diamond):Diamond can be understood as a proxy contract (Proxy), which is also the main contract for interacting with users
Facets:Just as a real diamond has different aspects, a diamond contract also has different aspects. Each function of the diamond contract needs to call a contract corresponding to an aspect, so it can also be understood as the realization of the contract (Implementation)
Diamond Cut (diamondCut):The diamond agreement standard extends a function called diamond cutting, which mainly functions to add, replace or delete facets and functions from diamonds, which can be understood as contract upgrades (Upgrade)
The Loupe:The function of the magnifying glass in the Diamond Protocol standard is mainly to return the information about the facet and the existence of the diamond. This information is stored in the internal storage structure of the Diamond Contract——DiamondStorage
The entire diamond model is similar to the following figure:
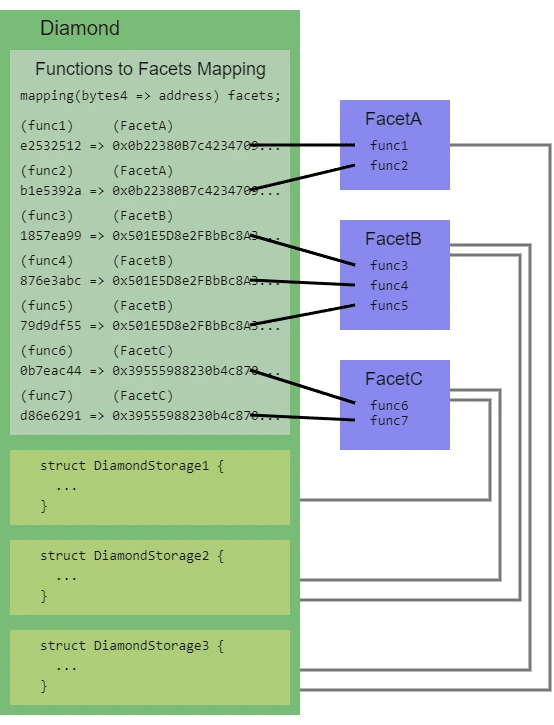
By using the diamond standard specification to create a diamond contract, this contract can use the code of any number of other aspect contracts just like the code of the current contract.
Different functions in the diamond contract need to be implemented by calling the codes of different aspect contracts, and the diamond cutting function can be used to modify (add, replace or delete) the functions in the diamond contract.
first level title
event analysis
Next, go back and analyze some details of the incident in The Saudis. In the DiamondCutFacet.sol contract of the project, you can see the function that implements the diamondCut function.
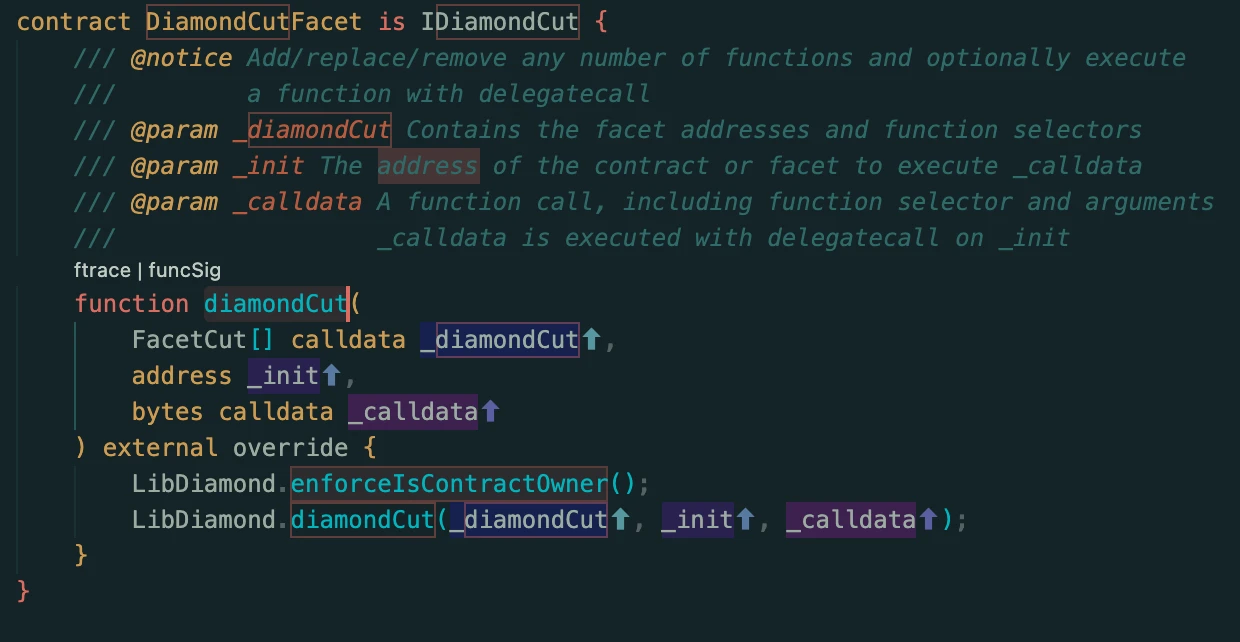
This function will first call the enforceIsContractOwner function of the LibDiamond library to determine whether the caller is the owner of the contract. If it is called by the owner, it will call the diamondCut function of the LibDiamond library to implement the function update of the diamond contract.
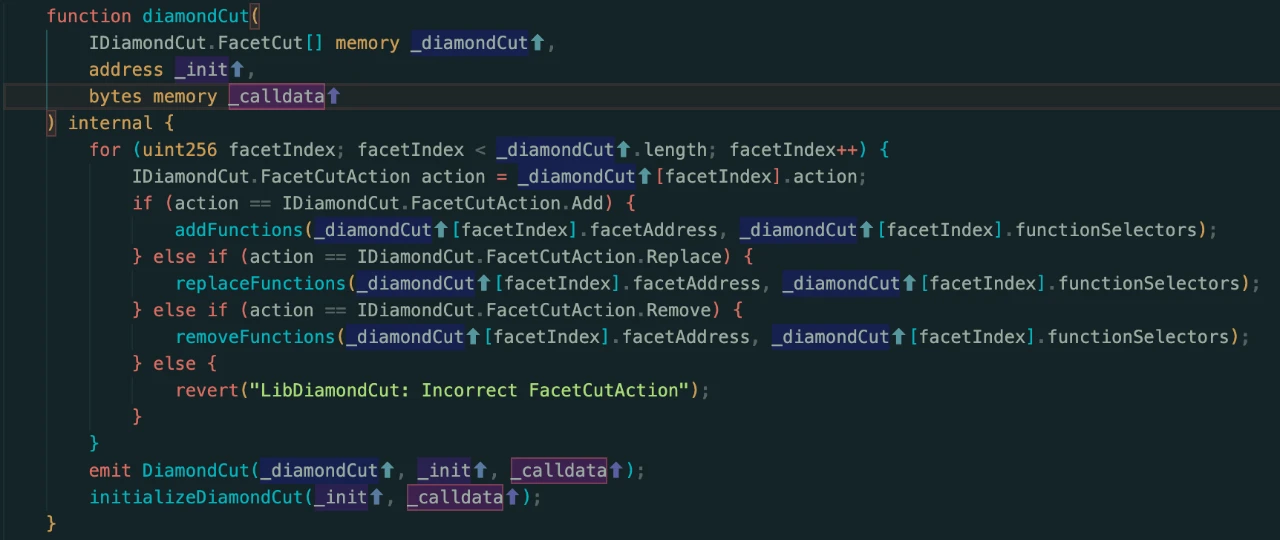
Following up on this function, we found that Diamond Cut will add, replace or delete functions according to the different actions passed in, so we will follow up to see the transactions that the project party calls this function.
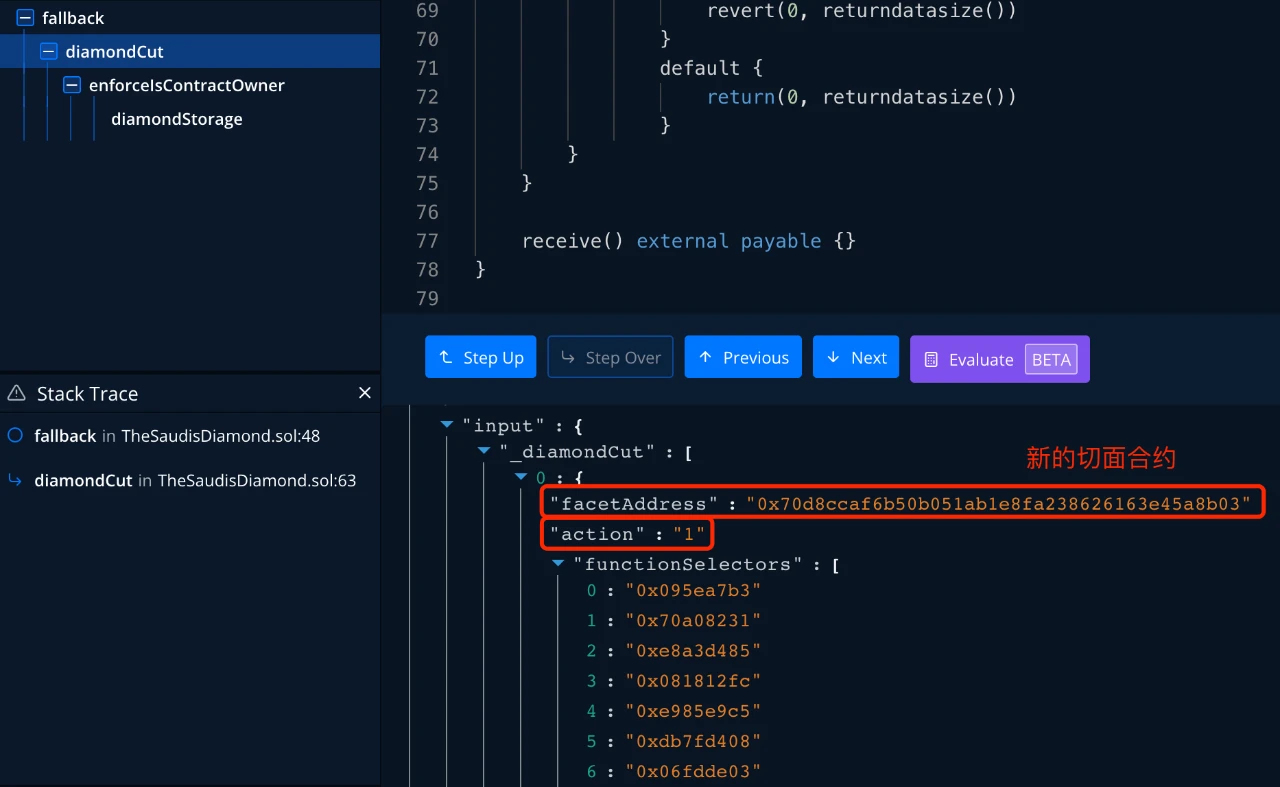
We found that a new aspect contract 0x70d8ccaf6b50b051ab1e8fa238626163e45a8b03 (not open source) was passed in, and if the incoming action is set to 1, it should be that replaceFunctions is called to implement the replacement function.
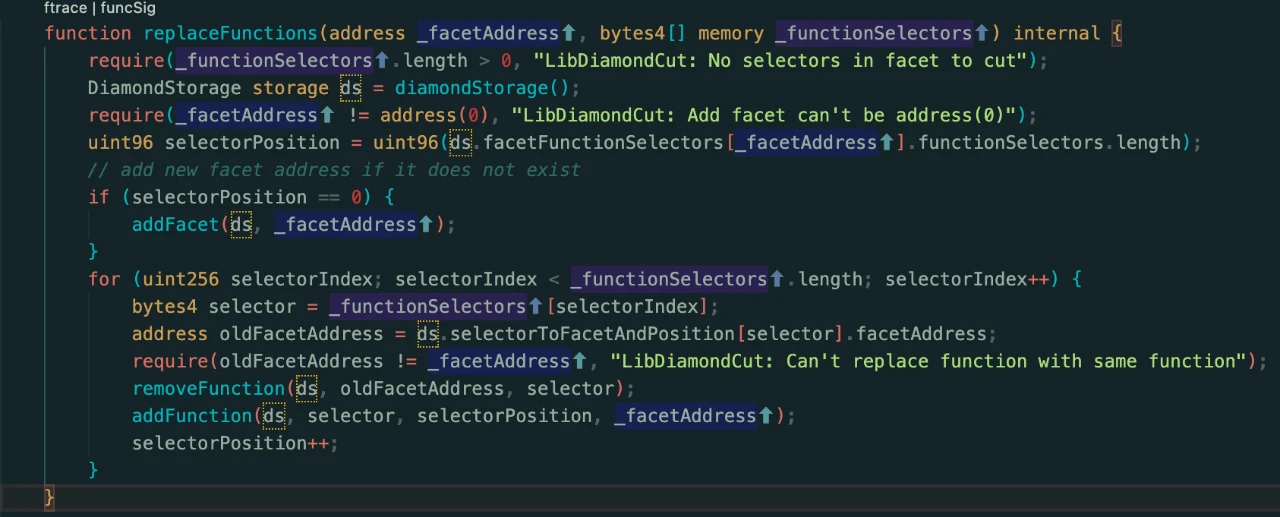
From the replaceFunctions function, it can be analyzed that this function will first add a new aspect for the incoming address, and then loop through the storage to read the old aspects corresponding to each function selector passed in and delete them, and create new aspects for these functions. Added as the incoming new aspect address.
first level title
Related Information
The Saudis contract address:
0xe21ebcd28d37a67757b9bc7b290f4c4928a430b1
User Rightblock address:
0x80266b1e3f0C2cAdAE65A4Ef5Df20f3DF3707FfB
The project side updates the transaction of the contract:
0xbc559a72f73e6c9a53416fd13a3ebaaa76dca5855ff8b79511585f514eaf2390










