Original Author: Jam, CloudY
Original editor: Vincero, YL
background
Layer 2 is the recent market focus
Rollups of the ZK series also launched their own ZKEVM and testnet with great interest and expected to capture real users and funds through airdrops, resulting in too many Layer 2 public chains that users need to interact with every day to be too busy for a while. But this also means that the track is very crowded. In particular, Arbitrum has brought a lot of attention to itself with the help of airdrops, and has also issued ecological subsidies to its own ecological projects to encourage ecological development and motivate users.
This makes Arbitrums TVL and Tx more than twice that of Optimism all year round. And ZKSync has also achieved rapid growth in TVL and Tx through era and airdrop expectations.
In addition to being suppressed in terms of data, Optimism, which was the first to issue coins, also faced a large number of token unlocks every month. In order to regain the situation, Optimism used the OP Stack strategy to fight back. When OP Stack was launched, the market did not respond much until Coinbase announced that it would use OP Stack to develop its own Layer 2B ASE, and A16Z would also use OP Stack to issue its own Layer 2 Magi. After that, the release of Layer 2 seems to have become a consensus, and projects in various fields have announced to join the Layer 2 War. The price of OP tokens also went up all the way until the BASE chain went online.
And other established Layer 2 cant help but choose to release their own Stack to compete with Optimism, such as: Arbitrum Orbit, Polygon 2.0, ZKSyncs Hyperchain and Starwares Starknet.
Layer 2 wins stage
The market has different opinions on whether the future Blockchain will be multi-chain or Layer 2. For now, Layer 2 and multi-chains (especially function chains) have indeed made new progress.
At the beginning of 22, we were still discussing whether the future of Blockchian is multi-chain or ETH+Layer 2. Now Cosmos has retreated to the second tier, and has been robbed of attention by Layer 2 such as Optimism/Arbitrum/Polygon/ZKSync. Funds and developers are also Voted with their feet to invest and settle in Layer 2.
After being converted to POS and upgraded in Shanghai, ETH carries the most on-chain assets and is on the road to expansion and deflation. Instead of developing a new public chain without innovation and building a new ecology to capture ETH traffic, it is better to directly ensure security based on the computing power and status provided by Ethereum, use ETH as the GAS Token, and attract developers and liquidity through EVM and incentives. Sex to do value migration, which will help form a flywheel effect. From the data point of view, Layer 2 is now dominant in TVL/number of projects/number of independent users, etc. At the same time, there are many project parties who have announced the release of Layer 2 and are waiting to enter the market. I believe that the multi-chain era of Layer 2 has arrived.
However, although after the Terra incident, Cosmos ecosystems such as the Terra chain/Juno chain have almost withdrawn from the market, such as:
Injective
Canto
Berachain
Sei
dYdX v4
These Cosmos ecosystems are about to launch or have already launched the main network. They are trying to solve the current Blockchain problems in a more radical way and build their own ecosystems.
Cosmos also has Evmos to take the express train of ETH with the help of evm, and obtain ETH liquidity from the ETH ecology. And Cosmos itself has released Cosmos 2.0, hoping to empower ATOM and enhance its ecological importance through inter-chain security and block auctions. However, judging from the current secondary trend and TVL, the Cosmos ecology has not successfully recovered from the decline after Terra, which is also limited by the state of the Cosmos ecology fighting against each other.
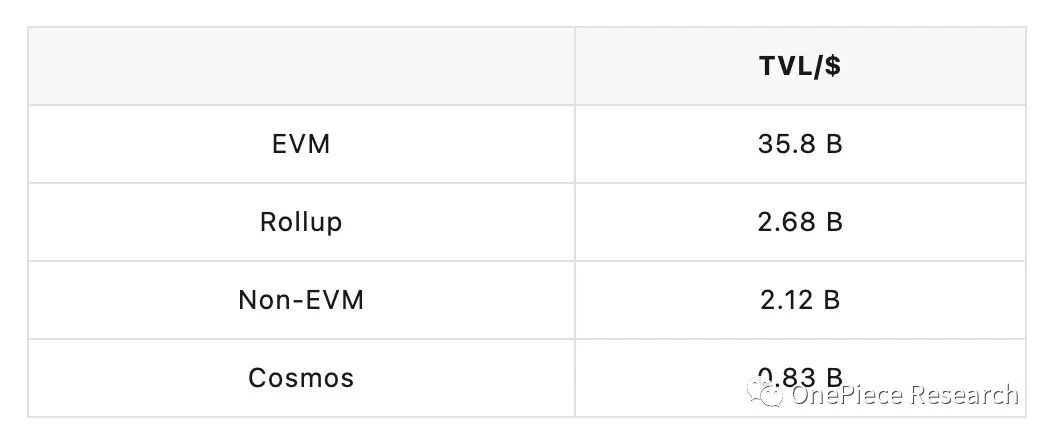
Source: L2 BEAT – The state of the layer two ecosystem, defillama.com, as of 20230821
OP Stack replicates Cosmos style of play
How to describe the multi-chain era of Layer 2? It is actually very similar to the multi-chain narrative told by Cosmos and Polkadot in the past, except that it is not the Cosmos hub or the relay chain that connects the multi-chains, but Ethereum. But in fact, Ethereum only provides security as a DA layer, and does not really communicate with Layer 2s, so this gives Stack an opportunity. Layer 2, as an intermediate Rollup layer, can not only provide public chain custom development services to make money, but also serve as The hub captures other Layer 2 value or charges Layer 3 as a DA layer.
In fact, Layer 2 itself is a step in the modularization of Ethereum. By modularizing Layer 2, you can build a Layer 2 simply and efficiently, and then connect each Layer 2 through a central hub to achieve atomic level cross-chain. On this basis, the central hub can also serve as the DA layer, and then build a Layer 3 application chain on it to liberate the innovation of the public chain.
Like Cosmos, make its own core features into common components, and then provide them to other chains to build its own ecology. Such a competitive advantage is incomparable to a public chain alone. Optimism, on the other hand, chooses low-threshold development similar to Cosmos, without permission to issue chains, high compatibility, cross-chain interoperability and other features to build its own ecology.
The Beginning of a Multichain Narrative: Cosmos
The design of Cosmos encourages collaboration between various blockchain networks to achieve ecosystem interoperability by sharing value and data. It is the first player to explore multi-chain interoperability.
Cosmos is a highly modular and interoperable blockchain ecosystem, including three core components: Tendermint consensus mechanism, Cosmos SDK, and IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication) cross-chain communication protocol.
1.Tendermint consensus mechanism
Tendermint is the network consensus engine of Cosmos Hub, which consists of Tendermint Core and ABCI. It adopts PBFT+Bonded PoS hybrid consensus to ensure that more than 2/3 of the verifiers reach a consensus. Tendermint separates the blockchain application from the underlying consensus, controls the application logic with a state machine, and provides an ABCI interface to interact with the application layer. This architecture supports consensus and access to other chains.
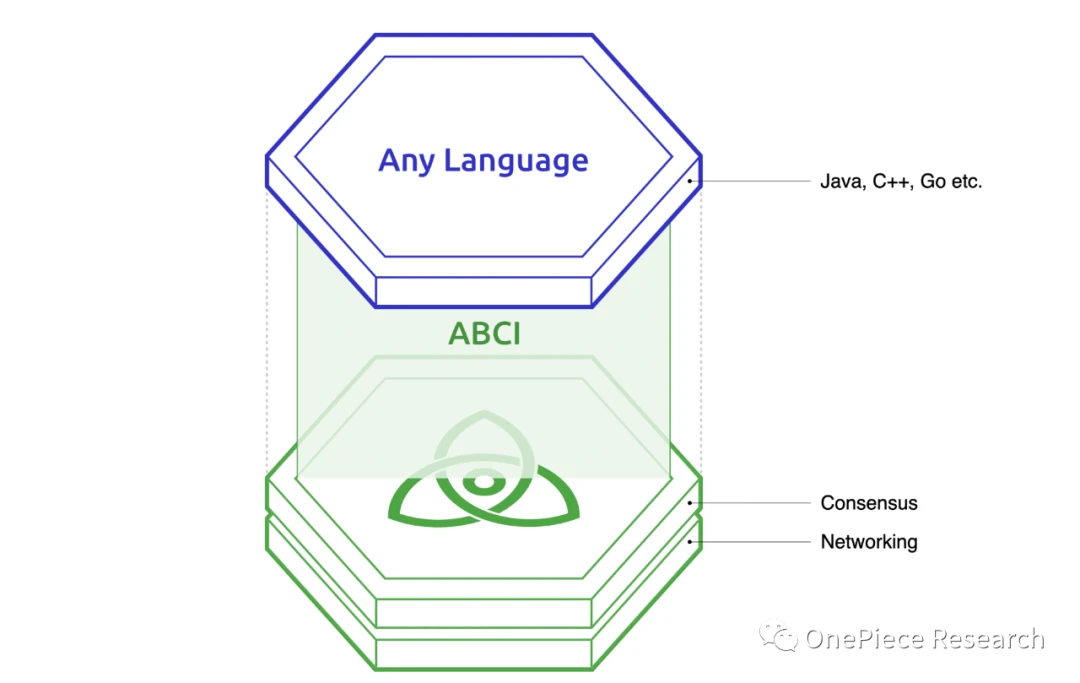
Source: Tendermint Architecture: Picture from official
2.Cosmos SDK
The Cosmos SDK is a developer toolkit that allows building modular state machines on top of Tendermint. Developers can use the SDK to build a new blockchain, or bridge into Cosmos through the Peg Zone. The SDK provides the concept of multiple storage, which divides the application state into different compartments, and each module manages its own state. SDK modules mainly include Bank, Auth, StakingSlashing, etc., which are used to build complex state machines.
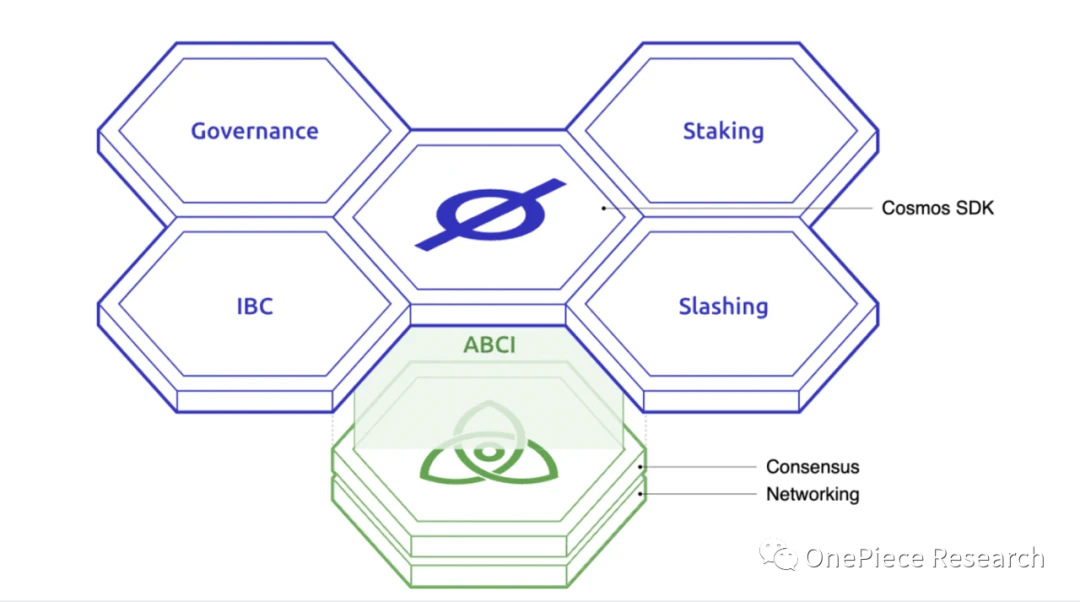
Source: Cosmos SDK Diagram: The picture comes from the official
3. IBC cross-chain communication protocol
IBC is a protocol in Cosmos that implements communication between different blockchains, and is used for cross-chain interaction between Zones. By establishing an IBC connection on a Hub, a Zone can communicate with other Zones connected to that Hub. Through IBC, Zone can send tokens and data packets to realize the transmission of cross-chain assets and information. PG Zone acts as a bridge to connect external blockchains (such as Bitcoin) that cannot be directly accessed through IBC, making them interoperable with blockchains in Cosmos.
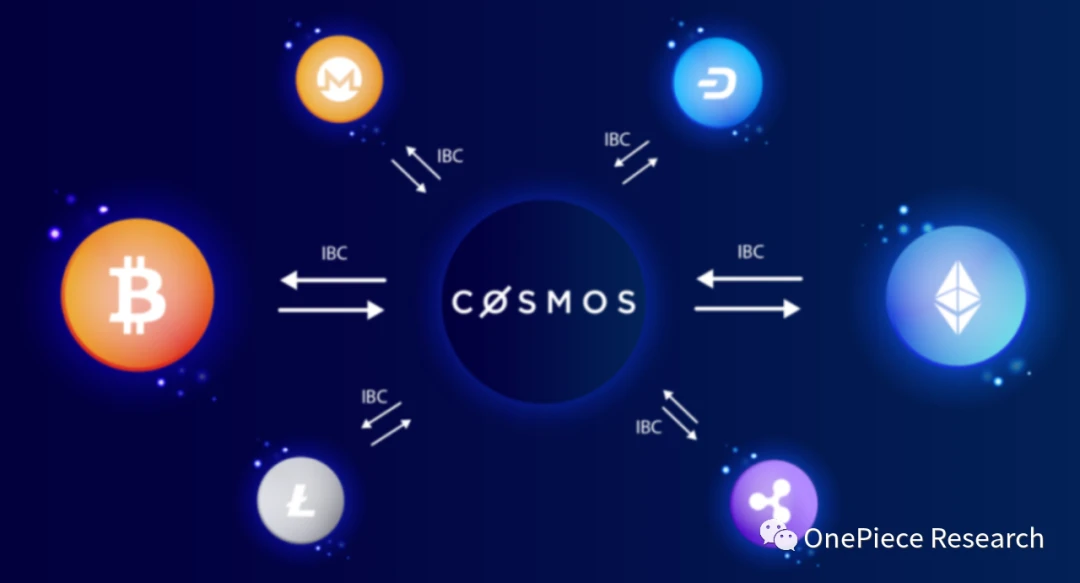
Source: IBC communication diagram: The picture is from the official
The combination of these components enables developers to build secure and flexible applications, enabling cross-chain intercommunication and asset transfer between blockchains.
Cosmos’ Hub and Zone Architecture and Cross-Chain Interoperability
Cosmos adopts the architecture of the Hub and Zone model, where the Hub is the central hub of the network, and the Zone is a public chain that independently accesses the network. The Hub will track and record the status of each Zone, and each Zone needs to feed back the new blocks it generates to the Hub and synchronize the status of the Hub. The state is not directly synchronized between different Zones, but communicated indirectly through data packets sent to the Hub.
Technically, Cosmos Hub and Zone models enable interoperability between different blockchains. Zones communicate through the Hub, which synchronizes the global state in real time. By separating the blockchain application from the underlying consensus and providing an ABCI interface to interact with the application layer, developers can write application logic in any language. This architecture can not only achieve consensus, but also facilitate the access of other blockchains.
Cosmos’ core token $ATOM is mainly used in the Hub ecosystem to pay transaction fees and governance voting, and its token demand is directly related to the development of the Cosmos ecosystem. Cosmos aims to build a general blockchain development framework and solve cross-chain issues to realize the vision of a multi-chain universe.
In terms of the cross-chain mechanism, Cosmos Hub acts as a relay chain, and Zone is a parallel chain, and each chain has its own verifier. As the core of the network, the Cosmos Hub allows different blockchains to be interconnected through the IBC protocol. Zones need to communicate with other Zones through the Hub, and the management methods between different Zones are decentralized. Therefore, if one Zone suffers from an attack or misbehavior, other Zones will not be affected.
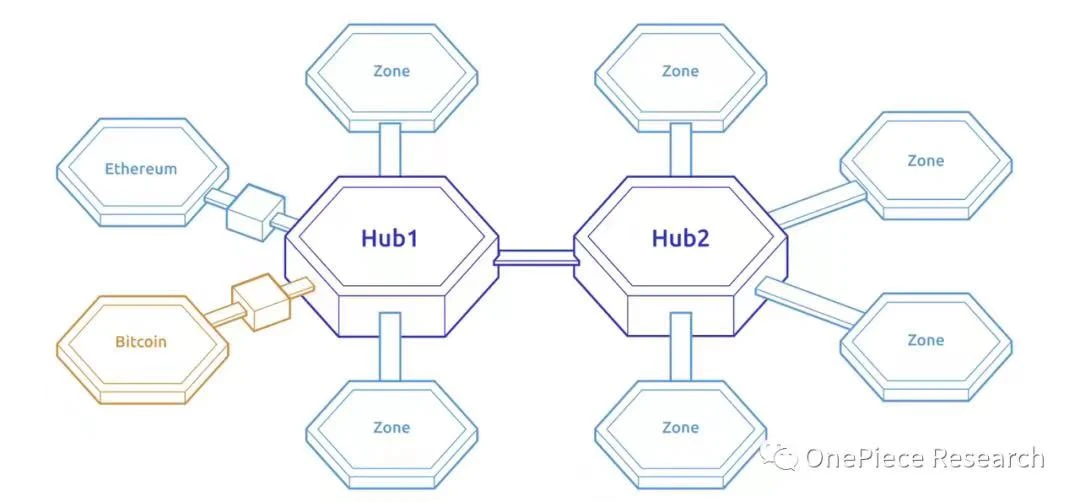
Source: Cosmos architecture diagram: The picture comes from the official
Cosmos as a whole has played a pioneering role in the field of multi-chain interoperability. It realizes seamless communication and cross-chain asset transfer between different blockchains through the Hub and Zone architecture and the introduction of the IBC protocol. Additionally, Cosmos modular architecture provides developers with flexibility. Using the Cosmos SDK, developers can build customized blockchain applications with various functional modules. At the same time, the Tendermint consensus mechanism plays a key role in Cosmos. It adopts PBFT+Bonded PoS hybrid consensus, which ensures high security and scalability. By separating consensus from applications, Tendermint achieves a higher degree of modularity and scalability, while providing an ABCI interface for interaction with application logic.
New multi-chain narrative: Superchain
“The core goal of Cosmos is to achieve interoperability and interoperability between different blockchains, and the current focus of competition in Layer 2 War seems to be moving closer to this goal step by step.”
The common goal of Layer 2 solutions is to increase the throughput and scalability of the Ethereum network to meet the growing transaction demand. However, the focus of competition between these Layer 2s has gradually shifted from pure performance improvement to broader interoperability and interoperability, and even ecology.
Interoperability: As more blockchain projects and Layer 2 solutions emerge, users and developers want to be able to seamlessly transfer assets and data between different blockchains. The realization of interoperability will provide users with greater flexibility, allowing them to move freely among different blockchain networks.
Interoperability: Competition among Layer 2 solutions drives developers to create more common technical standards to achieve interoperability between different Layer 2 solutions. This interoperability will facilitate collaboration and data exchange between different Layer 2 networks, creating a richer ecosystem.
Synergy: Similar to Cosmos Hub-and-Zone architecture, interoperability between Layer 2 solutions can create synergy. The interoperability between different Layer 2 solutions will strengthen the value of the entire ecosystem and attract more users and developers to participate.
Reduce friction cost: Achieving interoperability between different blockchains and Layer 2 will reduce friction cost for users. Users no longer need to perform cumbersome exchanges and transfers between different networks, thereby improving user experience and engagement.
The following is a comparison of solutions and paths for Layer 2 s:
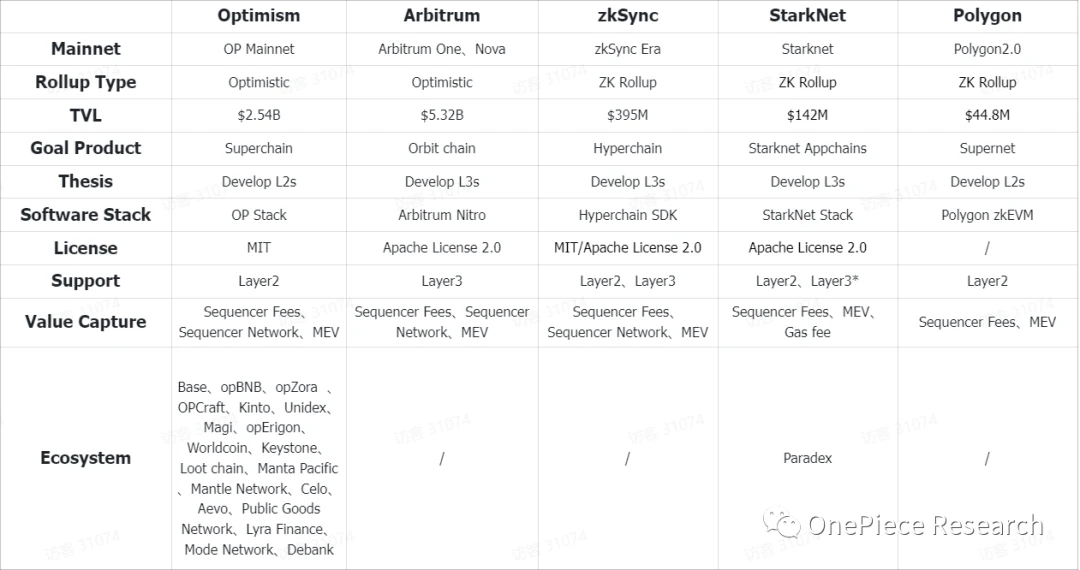
Source:Stacy Muur、l2 beat、OP Research| 20230827
Optimism
“OP Stack is like giving a big family gathering more seating so everyone can attend without having to relocate.”
Optimism Rollup and OP Stack
Optimism Rollup (ORU) is a Layer 2 (L2) expansion solution based on Ethereum (L1). Its design concept is to use the consensus mechanism of L1 to ensure the security and scalability of L2 and avoid the introduction of additional independent consensus. mechanism. As part of the parent chain-child chain model, ORU positions the parent chain as L1, where Ethereum acts as the parent chain.
In the operation mechanism of ORU, there are three main steps.
The first is data storage (Blockstorage), transactions on L2 are organized and written into blocks, and then these blocks are written into L1 in a compressed format. This practice maintains data availability, ensuring that transactional data can be retrieved whenever needed.
Second, the Blockproduction phase involves the operation of the sequencer, which is responsible for building and executing L2 blocks. This process includes confirmation of transactions, construction of new blocks, and passing relevant information to L1 for transaction submission.
Finally, the block execution (Blockexecution) stage ensures the receipt of new blocks and maintains the stable operation of the L2 network.
On the other hand, OP Stack serves as a standardized development stack supporting Optimism technology. From a concrete point of view, from bottom to top, the first is the data availability layer (DALayer), which defines the original data source of L2. Currently, the Ethereum main chain plays a major role at this level. The second is the sequencing layer (SequencingLayer). The functions of this layer are assumed by the sequencer, which is responsible for transaction confirmation, status update and the construction of L2 blocks. Then there is the Derivation layer: The Derivation layer defines how to process raw data in the data availability layer to form processed inputs, which are sent to the execution layer through the standard Ethereum Engine API. The execution layer (ExecutionLayer) defines the state structure of the L2 system, supports the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) or other virtual machines, and adds some L1 data fees to transactions. The settlement layer is responsible for sending the transaction data confirmed by L2 to the target blockchain for final settlement. Finally, there is the Governance Layer. The current solution [1] is to share the same set of governance standards with multiple OP Stack-based chains.
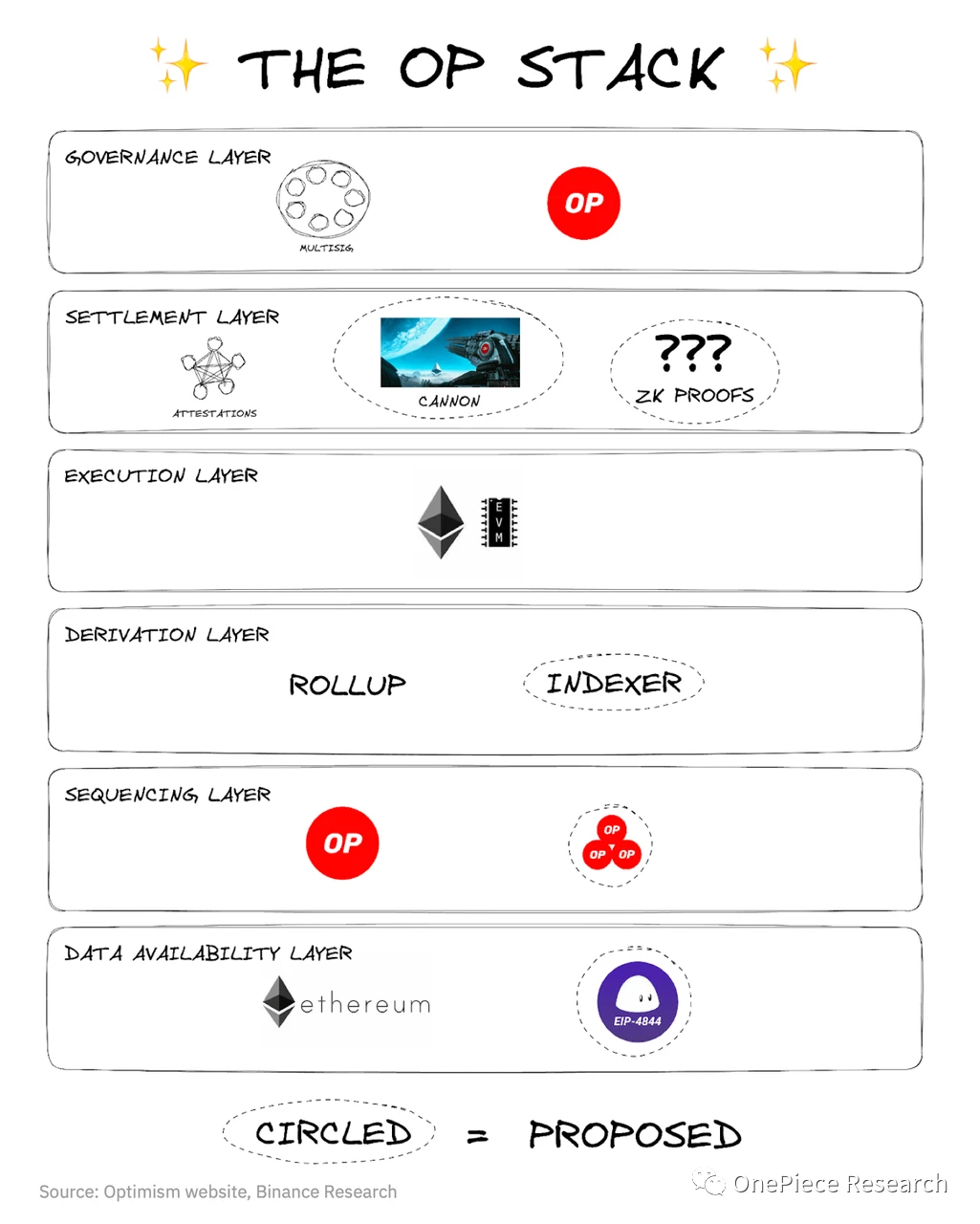
Source: OP Stack Structure|Source: Binance Research
*Note [ 1 ]: optimization.mirror.xyz
Superchain
Superchain enables different Layer 2 (L2) to work together by sharing security, communication layers, and development kits (OP Stack).
In traditional L1 designs, scalability and performance often become limiting factors, while Superchain provides stronger scalability and performance by integrating multiple L2 networks together. This horizontal expansion not only allows the system to have higher capacity, but also provides a better experience for developers and users.
Superchain based on OP Stack will be the connection point of different L2 solutions, providing support for large-scale operation of various blockchains and decentralized applications (dApps). As a standardized development stack supporting Optimism technology, OP Stack integrates different L2 networks and promotes interoperability between these networks. By integrating multiple L2s into the super chain, more efficient and flexible cross-chain communication can be achieved, allowing users to seamlessly transfer assets and information between different L2s, thereby realizing more possibilities. One of the key attributes of Superchain is modularity. By using OP Stack as the development basis, each L2 network can select layer modules as needed, and flexibly combine different technical components to meet specific needs. This modular design not only improves system customizability, but also provides easy access to new technologies and innovations. In addition, Superchain also emphasizes interoperability, enabling different L2 solutions to achieve more efficient resource sharing and information transfer. Superchain based on OP Stack can provide lower-cost deployment options, allowing more developers and projects to participate. This helps drive the development and adoption of the broader L2 network.
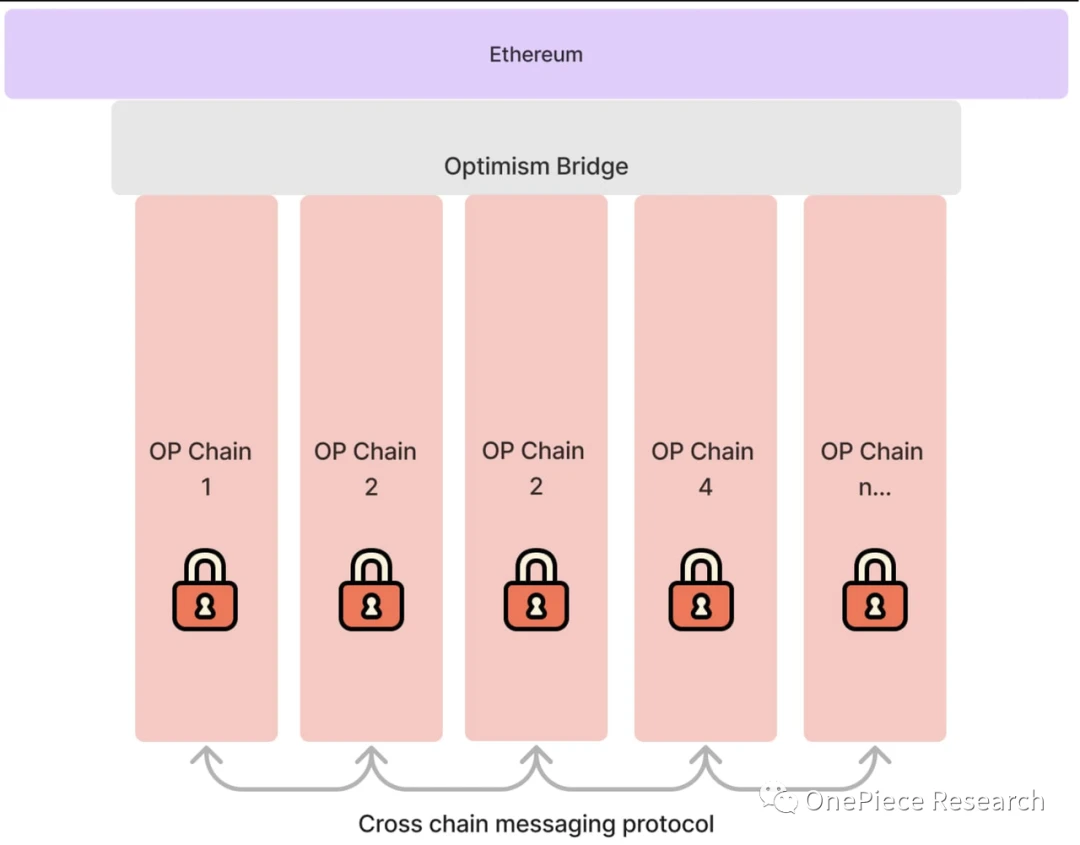
Source: Superchain Architecture: From OP official
In fact, using OP Stack to issue more Layer 2 is only the first step in the establishment of Superchain. The formed OP Stack requires Layer 2 to be able to share the sequencer exchange economy and information, and establish a unified security governance mechanism and inter-chain ecology.
Taking BASE as an example, the cooperation between Optimism and BASE has two main components. The first is protocol management. BASE complies with the Law of Chains and joins the operation of op-geth and op-node clients. At the same time, it adopts the op-reth failure designed by paradiagm Prove the client and set up a Pessimism pessimistic monitoring system; the second is economy and governance, BASE will use 2.5% of its own sorter income or 15% of the public chain profit after deducting L1 Gas (whichever is higher) as the cost of using OP Stack, And Optimisim will also provide BASE with up to 2.75% of the total OP supply as a reward for participating in governance. BASE and Optimism will jointly establish a Security Council to manage multi-signatures that control contract upgrades and formulate a challenger key management scheme to prevent team members from doing evil unilaterally. Generally speaking, any blockchain network based on OP Stack can flexibly combine different levels of OP Stack modules according to requirements to build L2s. And Optimism (now called: OP Mainnet), as its first L2, jointly builds the ecological chain of Super chain. This makes the entire ecosystem more resilient to a variety of different needs and innovations.
Arbitrum
Different from Optimisms Superchain strategy (building L2s based on OP Stack), Arbitrums Orbitchain strategy allows the creation and deployment of layers on the Arbitrum mainnet (including: Arbitrum One, Nova and Goerli) based on Arbitrum Nitro (technology stack, similar to OP Stack) 3, also known as application chain.
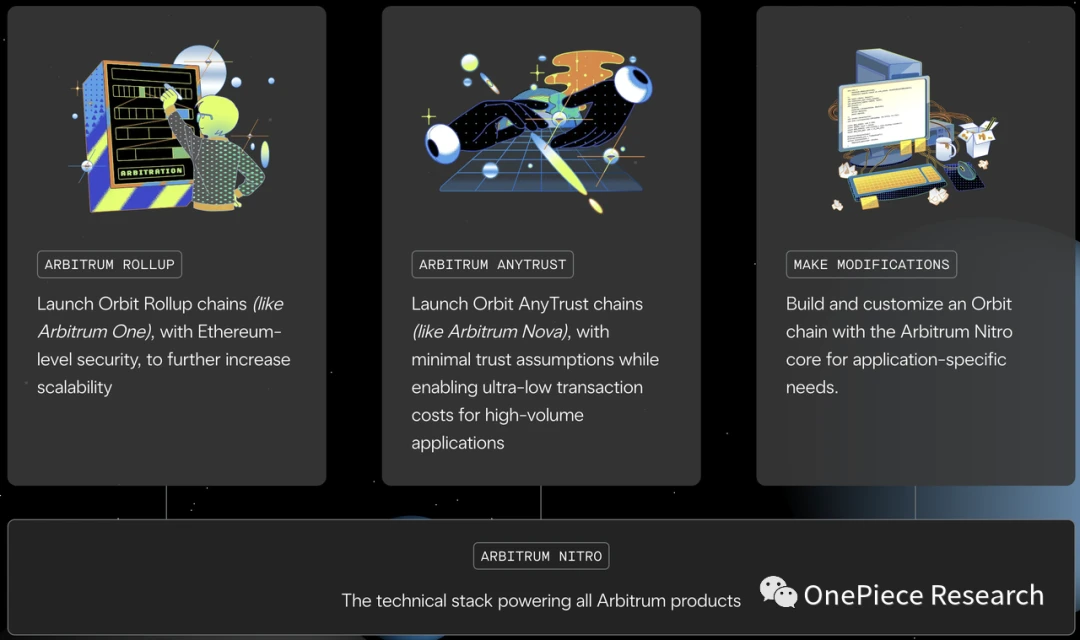
Source: Orbitchain Architecture: ARB official website
Unlike Optimism’s Superchain, Arbitrum takes a more flexible and customizable approach. Orbit is a development framework that allows any developer to build L3 (application chain) based on ARB, and its final architecture is Orbit chain. Orbit chain is designed to be compatible with the upcoming Arbitrum Stylus upgrade. This compatibility facilitates developers building decentralized applications (dApps) using programming languages such as C, C++, and Rust. By leveraging these programming languages, developers have more freedom to build feature-rich dApps without having to migrate to a new technology stack. This creates greater flexibility and choice for dApp developers to better suit the needs of different projects.
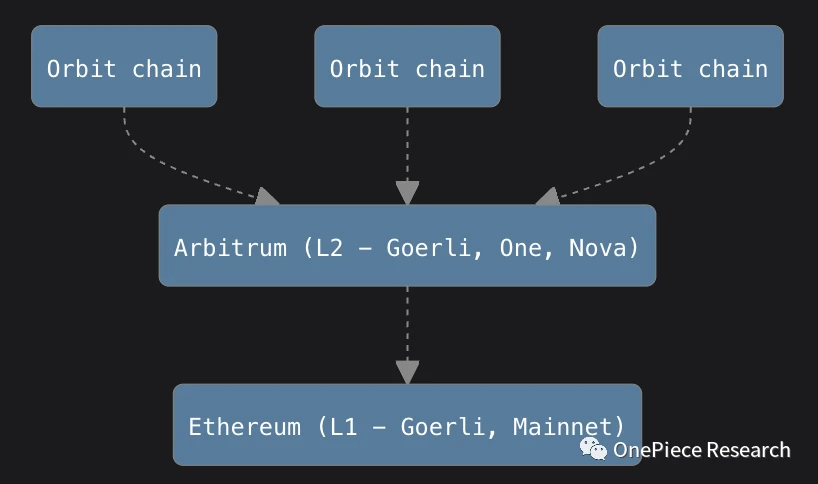
Source: Orbitchain architecture: from ARB official documents
But at present, Arbitrum Orbit is still in the stage of a test network, and has not yet reached the module integrity of OP Stack.
ZKSync Era
Sovereignty and seamless connection is the core narrative of ZK Stack.
Developers have full autonomy to customize Hyperchain. Hyperchain operates independently and only relies on Ethereum Layer 1 to ensure security and liveliness. The Hyperbridge network enables Hyperchains to connect to each other.
Launched at 20230623, ZK Stack aims to build custom ZK-supported L2 and L3 based on the code of the ZKSync Era. This is a framework for building modular, sovereign, ZK Hyperchains. Therefore, its technical architecture is no different from OP Stack.
ZK Stack is a framework for building modular, sovereign, zero-knowledge technology-based Hyperchains. It looks at solving the challenges presented in ZK Credo, which aims to provide the foundation for a decentralized blockchain network. The core features of ZK Stack include free open source, composability, modular customization, proven security, and future scalability.
The framework was developed by Matter Labs under the MIT/Apache open source license. Hyperchains built using ZK Stack can seamlessly connect in a trustless network with low latency and shared liquidity. Developers can customize Hyperchains according to their needs, while ensuring security and reliability. Based on the code of ZKSync Era, ZK Stack realizes the interoperability between super chains with the help of Hyperbridge, achieving fast and low-cost interoperability. Developers can customize hyperchains as needed and interconnect them through Hyperbridge to achieve trustless, fast, and low-cost interoperability.
ZK Stack is suitable for scenarios that require customized Hyperchains or asynchronous connections in a wider ecosystem, because the L1-L2 bridge is asynchronous. From an architectural point of view, ZKSync Era has 2 application scenarios:
1) As one of the Hyperchains of L2s, it is interconnected with L2s of the same level, sharing liquidity and other ecological resources.
2) As the DA Layer of L3s.
Hyperchain solves the trust problem by verifying off-chain calculations, and uses zero-knowledge proofs to ensure security. Hyperbridge connects hyperchains to achieve data transfer and interoperability. Hyperchain bridges through Hyperbridge, which has the characteristics of verification bridge, local bridge and data availability, so as to build a unified liquidity network. From the users point of view, Hyperchain realizes seamless interoperability and cross-chain wallet management to ensure user experience. Technically, Hyperchains based on verification bridges, shared validators and data availability, etc. form the basis of Hyperbridges.
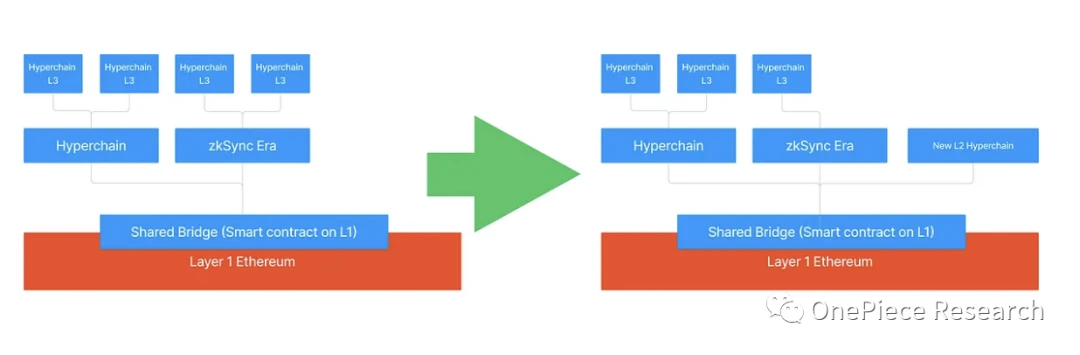
Source:matter-labs
Taken together, Hyperchain’s scalability and composability are the core of its design. Hyperchains L3 can not only interconnect with L3 of the same level, but also directly use Ethereum as the DAlayer. In this case, the L3 is essentially an L2. In the picture below, the second hyperchain L3 on the upper left is the most direct case proof. However, as the public chain of ZK Rollup, Layer 2 s not only needs to solve the gap with the Solidity programming language, but also needs to have a certain ability to independently develop the ZK circuit circuit system, otherwise it can only share ZKPorter to run. However, ZKSync currently does not have a complete component sharing mechanism. It can be seen that Hyperchain restricts the entry of a large number of developers in terms of programming language and technology. In addition, although ZK Rollup can technically realize the transaction volume of millions of PTS while achieving decentralization, the cost of ZK Proof is also higher, coupled with the centralization of the sorter, and the Gas fee of complex smart contracts requires Higher is also prone to failure due to poor compatibility, which makes it difficult for ZKSync to develop rapidly in a short period of time, so coins will not be issued to promote development. In response to this, ZK Sync has made some optimizations on its Hyperchain architecture - the systems LLVM compiler supports Solidity and any other modern programming languages, and it also adds support for languages such as Rust, C++, and Swift. Developer accessibility. But overall, Hyperchain is the most difficult to develop.
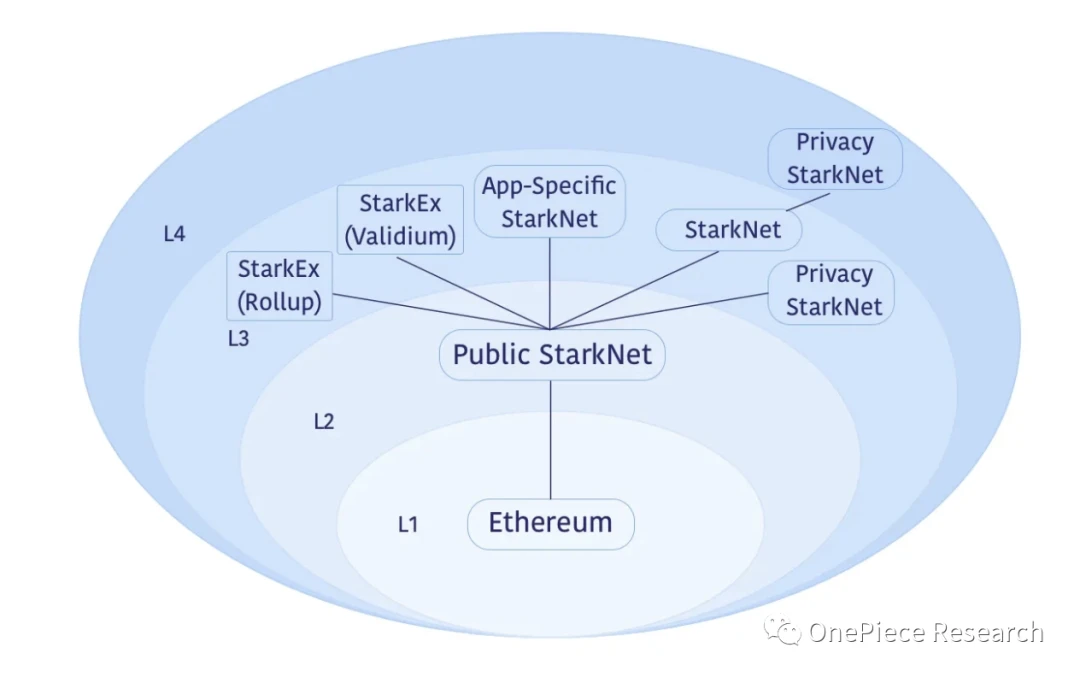
Source: Official Documentation
Overall, the Starknet Stack is still in the early stages of development, and the development of the ecosystem on the chain is still at a very early stage.
Polygon 2.0
In the whole design idea, Polygon 2.0 hopes that its own Polygons PoS Mainnet and ZKEVM will become the pillars of Polygon, and at the same time introduce the Supernets application chain to strengthen Polygons ecology, and the real profit is the POL token, because the Supernets of Polygon 2.0 need to pledge POL tokens are used to run nodes to ensure the security of the public chain. In order to achieve this goal, Polygon gives three options for users to choose: PoS node/ZKEVM node/Miden VM. In order to expand its appeal, Polygon is also equipped with Polygon DID based on zero-knowledge proof and a Web3 game development guide named Blueprint. It can be seen that Polygon 2.0 chooses to strive for a richer ecology for itself from the perspective of incubation. In addition, the Supernets introduction of Polygon 2.0 mentioned the concept of enterprise blockchain many times. From Polygon’s cooperation with Starbucks/Nike/Warner Music, etc., it can be seen that another moat is the low-threshold high-customization application chain of the enterprise version.
Structurally, Polygon 2.0 is similar to OP Stack, and it also divides itself into several layers, namely:
Staking Layer
Interop Layer
Execution Layer
Proving Layer
Link
Network
Transport
Application Layer
Its layered form is:
These are borrowed from Internet protocol components, each protocol layer is responsible for a specific sub-process, known as the technology stack.
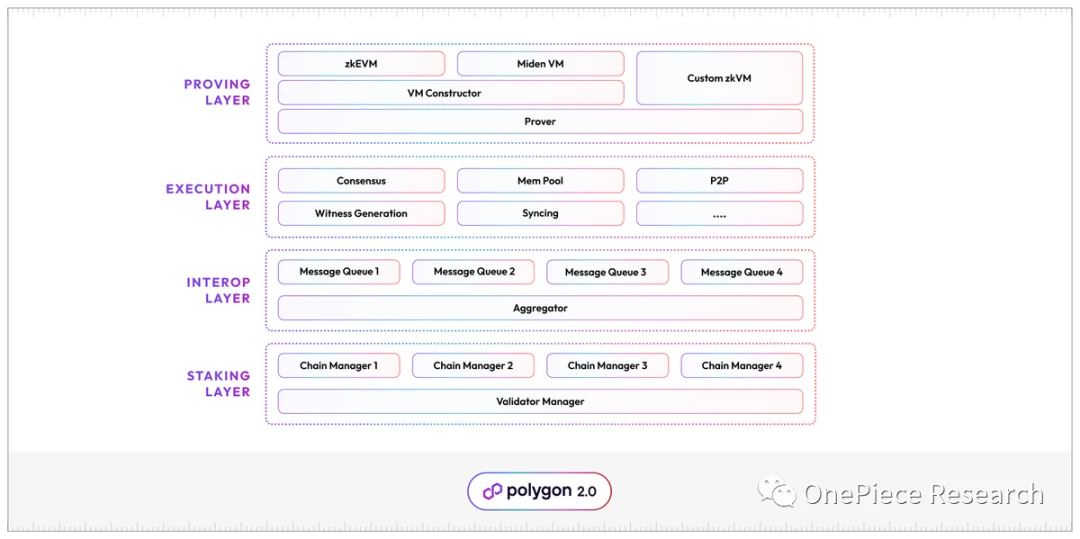
Staking Layer
The function of this pledge layer is basically the same as that of Ethereum’s PoS (Proof of Stake), but it is not only used for the Polygon main network:
In addition to the original Polygon main network, Polygon also has ZKEVM, Supernets, etc. Therefore, Validators will provide services for many chains, using a mode similar to restaking, and managed by Validator Manager.
The Chain Manager contract is used to manage the Validators belonging to each chain. Each chain has its own Chain Manager contract to determine the number of validators and additional requirements for validators, such as regulations to be complied with or Tokens that must be additionally staked, meaning that validators may need to additionally stake the chain’s own tokens to participate in its validation.
In fact, this pledge layer is the focus of Polygon 2.0. Unlike Optimism and Arbitrum, if Supernets want to run, they must have the support of a Validator that has pledged $POL. The more Polygon chains, the more Validators are needed, and the POL generation The value of the currency will be higher. But the Restaking model also helps the Supernets team focus on utility and community rather than infrastructure, lowering the entry barrier to public chains.
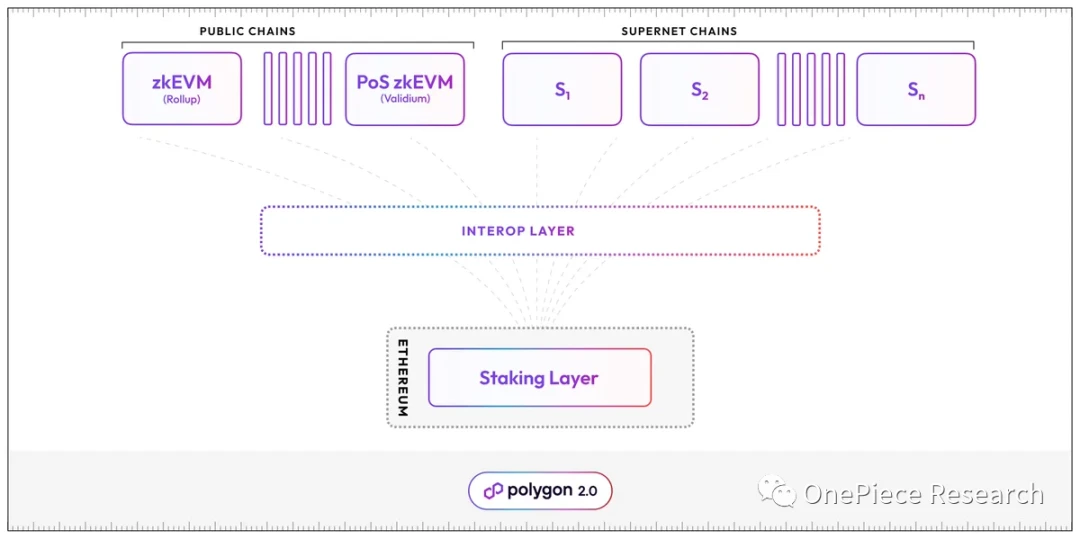
Interop Layer
Interop Layer uses ZK Proof to implement native cross-chain like Cosmos. By extending the LxLy protocol used by Polygon ZKEVM rolllup, Polygon introduces an Aggregator to achieve atomic-level cross-chain interoperability. First, it can receive ZK proofs and Message Queues. In addition, it can aggregate multiple ZK proofs into a single ZK proof and submit it to Ethereum for verification. So its a middleware between Polygon and Ethereum.
Therefore, when the Message Queue and ZK proof sent by chain A are received by Aggregator, then chain B as the target chain can directly receive messages from chain A, thereby realizing seamless cross-chain interaction. Of course, Polygon also tries to decentralize Aggregator in the form of PoS Validator.
Execution Layer
Its execution layer plays a relatively similar role in each chain. Then, among these are P2P/Consensus/Memepool/Database, and the Witness generator unique to ZK proof.
Proving Layer
The proof layer is a unique level of ZK-Rollup, which is essentially a protocol for producing ZK proofs for all transactions in the Polygon chain.
It is mainly composed of a general prover and a state machine. The general prover inherits Plonky 2 using recursive SNARK technology, and the state machine has ZKEVM and MidenVM provided by the Polygon team, or built by the public chain team itself, such as ZKWASM.
summary
technology open source perspective
OP Stack is welcomed by many projects, and there is a reason why more than a dozen projects including Base/Magi/opBNB/Worldcoin have announced the use of OP Stack.
The first is the openness of the license. From the picture we can see that Optimism uses the MIT License, while Arbitrum/ZKSync/Starknet/Polygon uses the Apache License 2.0. Although they are all open source, the two licenses There are different levels of openness. The MIT License only requires that the original license statement and copyright statement be retained, and allows commercial use, distribution, modification, private use, additional agreements, and even the sale of MIT-licensed code. Apache License 2.0 requires that the modified source code be described in the modified file. Derived projects need to contain the Apache-2.0 protocol in the original project code, as well as trademarks, patent statements, and other instructions stipulated by the original author. In the derived project, if a Notice file is included, the Apache-2.0 protocol must also be included in the Notice file.
Simply put, the MIT License is the most permissive, while the Apache License is more stringent.

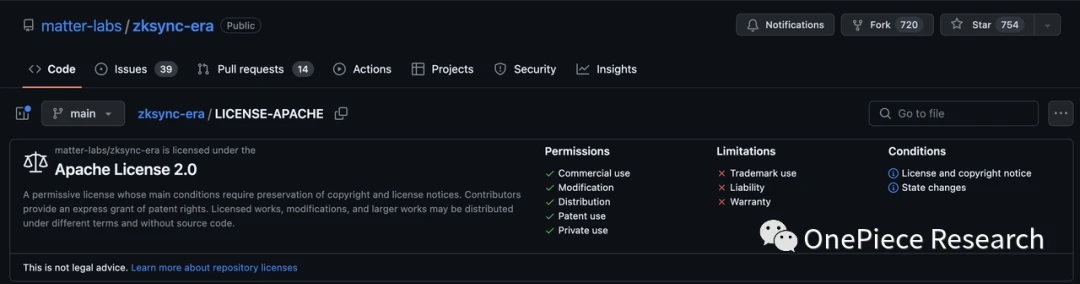
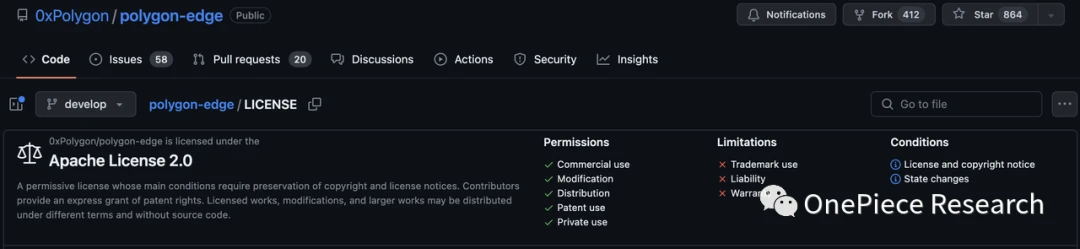
Compatibility Angle
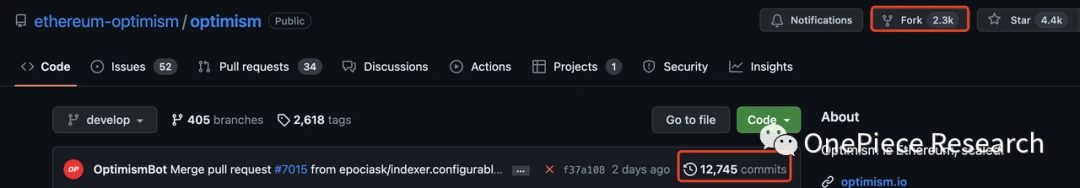
1) Optimism is highly compatible with Ethereum EVM. Optimism’s code has 12,745 commits and 2.3k forks, which means a large number of code updates and a very high developer adoption rate.
2) In addition, from a technical perspective, the ZK system makes full use of the security and consensus mechanism of Ethereum and directly relies on its security. Compared with the OP series, the ZK series can directly verify status changes without waiting for underlying status updates, simplifying the design and improving cross-chain efficiency. The OP is limited in asynchronous cross-chain calls and needs to wait for underlying verification and confirmation.
Technical architecture perspective
1) At present, Optimism and Polygon are focusing on expanding L2s, while Arbitrum, ZK Sync and Starknet are focusing on expanding L3s. Layer 3 application chains have a higher degree of freedom/scalability and autonomy, but the market is still developing on Layer 2, and Layer 3 is still in the relatively distant future. And the most critical thing is that Layer 3 cross-chain interoperability has not been fully realized technically. Currently, no one can advertise that it can achieve Layer 3 cross-chain interoperability. In this case, dApps that focus on composability will inevitably choose Layer 2 to build DeFi Lego.
2) Modularization and SDK components are the unified path of the current blockchain. Whether it is the public chain for dApp or the Stack for Layer 2/Layer 3, it is the minimum programming threshold and maximum customization to reduce the developers construction The cost of the project allows it to focus on product design and community operations. There are more projects like AltLayer that specialize in Rollup As A Service as their core business, so code-free chains and projects will definitely become popular with the improvement of infrastructure.
Development Progress Angle
At present, only OP Stack and Polygon 2.0 are developed rapidly, but OP has the fastest ecological development and has a public chain, while Arbirtum, ZKSync and Starknet are still in the very early stages of development. Especially when the ZKSync and Starknet mainnet ecology is not well established, it can be inferred that they may be more of a development strategy to cope with the competition of OP Superchain. But in terms of the degree of decentralization, Starkwares ZK proof generator STARK Prove-Stone was open sourced under the Apache 2.0 license on August 31, and OP Stack, with the help of Base, has no schedule for a decentralized sorter. It can be seen that Starkware may be in a leading position in the process of decentralization.
Comparison between multi-chain narrative and super-chain narrative
Layer 2 cross-chain with IBC and Keplr wallets
A major narrative of Layer 2 multi-chains is atomic-level cross-chain transactions. OP Stack achieves the same inter-chain communication effect as IBC through shared sorters. Polygon 2.0 uses public validator sets and re-staking shared security to become a Polygon Hub. .
However, the Layer 2 cross-chain is still in the narrative stage, and only the EVM cross-chain (wormhole/layerzero/axelar) based on the cross-chain bridge mode can be used. The gap between this and IBC is still very obvious.
SEI’s cross-chain airdrop some time ago demonstrated this gap well:
USDC, which uses Wormhole to cross-chain from Ethereum/Arbitrum/Polygon/BSC, has to wait 24 hours to cross-chain out of the SEI chain because it exceeds Wormholes cross-chain quota in SEI.
However, ATOM and OSMO, which cross from Osmosis to SEI through IBC, can cross back to the original chain at the moment of crossing. Axelar USDC, which also belongs to the IBC ecosystem, is also favored for this reason. However, it is limited by the Axelar cross-chain mechanism of the SEI official bridge. There is a waiting time of about half an hour when crossing into and out of the SEI. However, if you use the direct crossing to the IBC public chain, Its also instant. 24 hours and instant payment, which one is better is clear at a glance.
Compared with Keplr, the experience of Layer 2 interchain switching on MetaMask also has a significant gap. With the increase of Layer 2 public chains, the demand for conversion between different chains has gradually increased. However, the assets and interactions of each chain are independent of each other on MetaMask. Third-party tools must be used for unified management, but this also increases financial risk. However, the Keplr wallet can display the amount and status of funds in the entire ecosystem. The Layer 2 Stack strategy may require a Super Wallet similar to Keplr to unify its own ecological assets.
Shared sequencer with ISC and block auction
The sequencer is the key to Rollups revenue and security. Sharing the sequencer allows the new Layer 2 to skip the construction and maintenance of the sequencer, and can also obtain the MEV income of all chains, strengthening the value of the Superchain. But sharing the sorter also means sharing the underlying security. The current Layer 2 Stacks sorters are too centralized. Only the PoS sorter and multi-organization multi-signature implementation can be considered a step towards Vitaliks Stage 2, so sharing in the future Sequencers and decentralized sequencers are the only way to expand revenue and ensure security.
As one of the keys to Cosmos’ self-rescue, ICS lowers the entry barrier for the Cosmos ecological public chain and provides more value capture for the Cosmos hub to empower ATOM tokens. In the past, the Cosmos ecosystem each used PoS to ensure its own security, and ATOM was only used to ensure the security of the Cosmos hub, making staking ATOM for airdrops and taking PoS basic benefits the only things ATOM can do, which is different from the current Layer 2 The current situation is very similar, except that OP Stack chose Layered Security using Superchain, while Polygon 2.0 chose Mesh Security using Restaking. The block auction prices MEV and resolves MEV from the business model, that is, quantification of the value of the sequencer. With the establishment of the shared sequencer, the value of MEV will naturally increase exponentially. Superchains MEV income cannot simply be collected by the sequencer, so Stacks block auction will definitely go online soon after the launch of the shared sequencer.
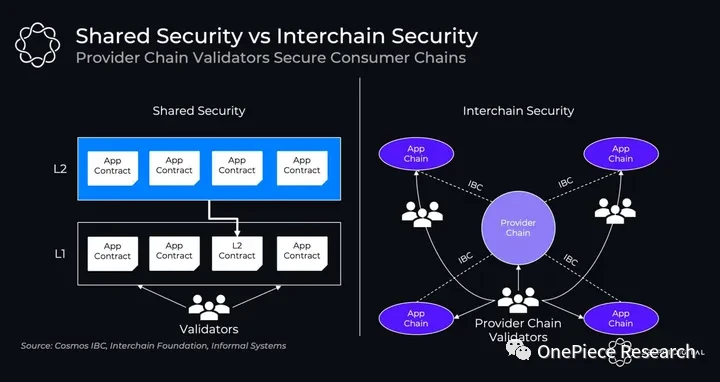
Source:Delphi Digital
Conclusion: Becoming Cosmos is the final form of Layer 2
In view of the recognition of the Cosmos model by Layer 2 Stacks, the unique mechanisms in the current Cosmos ecosystem will surely be optimized and adopted soon, such as learning from public chains such as Berachain/Injective/Sei/Canto and introducing public chain-level underlying liquidity/ Terra-style native stable currency/public chain-level native lending/Gas sharing mechanism/modular deployment contract/block auction, etc. to establish Layer 2. Or, as mentioned above, develop a Stack ecological wallet similar to the Keplr wallet to integrate ecological assets.
But the most important thing, and one of the Cosmos mechanisms that Stacks currently lacks, is actually the complete version of inter-chain security. Different Layer 2 Stacks can share sequencers with each other, that is, the decentralization of the sequencer layer, not just each company’s The sorter is decentralized to avoid the risks of a single sorter. At the same time, the PoS-based sequencer can also implement multiple sequencers to provide services for the same chain through a similar heavy pledge method. That is, Layered Security and Mesh Security of Cosmos ICS.
There will definitely be a role of Cosmos or OP superchain in the market.
The market is indeed looking for a role similar to Cosmos or OP superchain, which will act as a hub connecting different blockchain networks to achieve the growth of the entire ecosystem by creating synergies and sharing ecological resources. If the OP Stacks approach proves not feasible, a new solution may emerge in the future to fill the void.
Whether it ends up being something like ARB Orbit or OP Superchain or ZK Stacks, they will all play an important role in the path to Layer 2 scaling. As ZK technology matures and becomes de-thresholded, it is likely that ZK series or OP series Stacks that introduce ZK technology will take over the banner of Layer 2 multi-chains. ZK technology comes with high TPS and decentralization, which is exactly what it means. Apart from compatibility, these are the two most critical attributes for capacity expansion, and they are also the technical guarantee in the case of high sharing security. Although the development progress of ZKSync and Starknet is slow, their TVL and user volume growth are obvious to all, so we can look forward to whether OP Stacks first-mover advantage and compatibility performance will quickly occupy the Stack market, or ZK Stacks high TPS and decentralization Chemical energy will strike after the technology matures.
Reference
[ 1 ] The reason behind Layer 2s four kings vying to lay out the Stack
https://haotiancryptoinsight.substack.com/p/layer2stack
[2] The Coming of Super Chain: An In-depth Interpretation of the OP Stack Jointly Created by Coinbase and Optimism
https://www.8btc.com/article/6806138
[ 3 ]《Crazy Multichain Universe, Crazy OP Stack》
https://medium.com/ybbcapital/crazy-multichain-universe-crazy-op-stack-acb63be8d5 15
[ 4 ]《Introduction to Hyperchains》
https://medium.com/matter-labs/introduction-to-hyperchains-fdb33414ead7
[ 5 ]《Introducing the ZK Stack》
https://medium.com/matter-labs/introducing-the-ZK-stack-c24240c2532a
[ 6 ] ZKSync Ecological Process and Variables of Decentralization Process
https://twitter.com/tmel0 211/status/1663034763832344576
[ 7 ]《A gentle introduction: Orbit chains》
https://docs.arbitrum.io/launch-orbit-chain/orbit-gentle-introduction
[ 8 ]《The Starknet Stack’s Growth Spurt》https://starkware.co/resource/the-starknet-stacks-growth-spurt/
[9] The difference between open source licenseshttps://www.geek-workshop.com/thread-1860-1-1.html
[10]《The Appchain Universe: The Risks and Opportunities》https://medium.com/alliancedao/the-appchain-universe-the-risks-and-opportunities-9a22530e2a0c
[11]《Application-Specific Blockchains: The Past, Present, and Future》https://medium.com/1kx network/application-specific-blockchains-9 a 36511 c 832
[ 12 ]《The Inevitability of UNIchain》https://medium.com/nascent-xyz/the-inevitability-of-unichain-bc600c92c 5 c 4
Data Sources:
[ 13 ]https://defillama.com/chains
[14]https://dune.com/Marcov/Optimism-Ethereum
[15]https://dune.com/gopimanchurian/arbitrum
[16]https://dune.com/gm365/L2










