Original author: Hill
This article is original by the SevenX research team and is for communication and learning purposes only and does not constitute any investment reference. If you need to cite, please indicate the source.
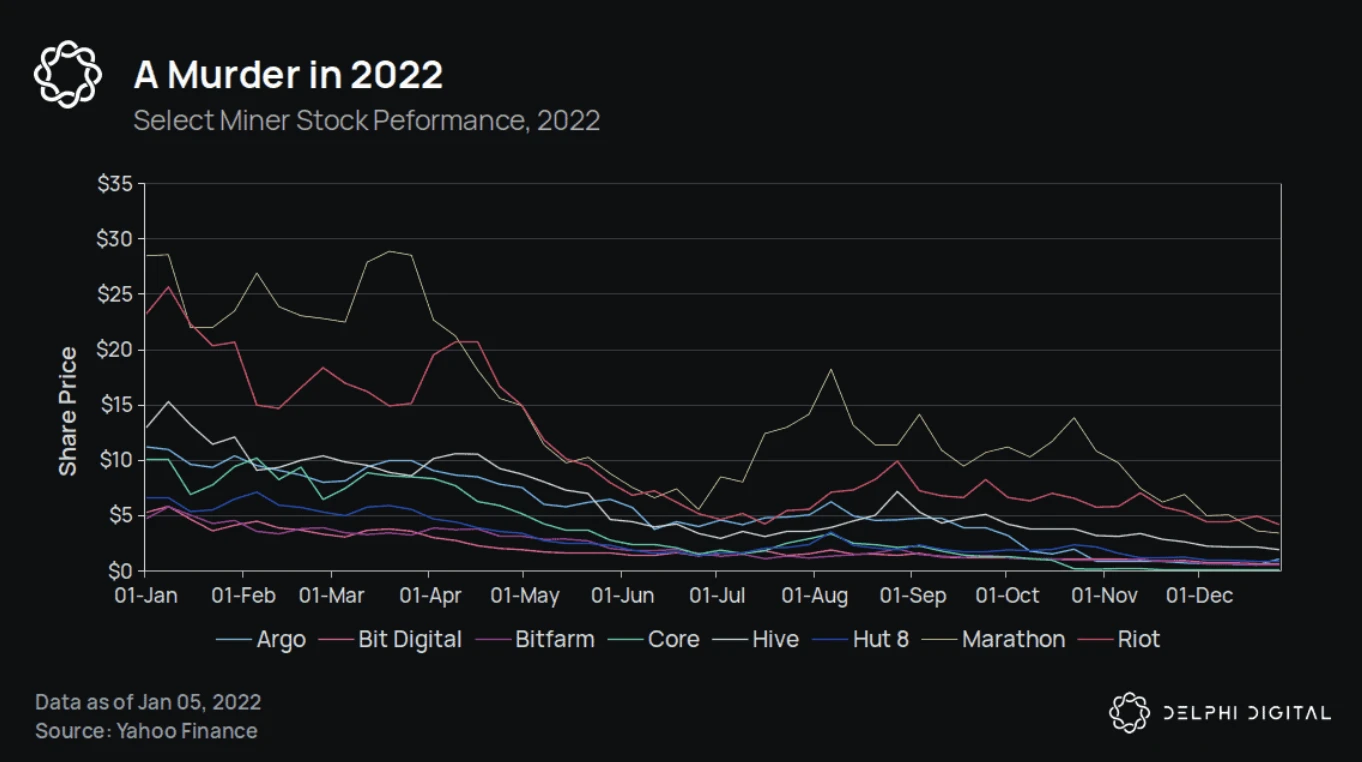
Maintaining Bitcoin’s massive computing power requires an equivalent amount of revenue. With the halving of Bitcoin block rewards, it is urgent to increase fee income. Especially in the context of a bear market, miners need more income. 2022 is a year that will be hit hard by miners, with multiple costs rising at the same time: capital costs soar as interest rates rise, energy prices rise, and mining electricity bills rise. The decline in BTC prices can easily lead to two vicious cycles. The first is the vicious cycle of BTC prices: approaching the shutdown price of mining machines - miners selling - BTC prices fall - miners profits fall - more miners sell. The second is the vicious cycle of mining machine prices: miners go bankrupt - mining machines are sold at a discount - mining machines are acquired at a cost lower than the market price, restarted and returned to the market - hash rate rises - mining difficulty rises - more Miners went bankrupt. The stock price performance of many mining companies in the bear market also fully demonstrates the cruelty of the bear market.
At the same time, new asset classes based on Bitcoin inscriptions, represented by ordinals, have become popular in the market. The handling fees it generated gave miners enough income to survive the harsh bear market until the early stages of the current bull market. We will observe this new asset class from the perspectives of technical roadmap and leading product form, and try to analyze the investment opportunities that exist within it.
Bitcoin technical roadmap upgrade
Main direction 1: Expansion of the original chain
Segregated Witness (“SegWit”) in 2017 changed the transaction structure of Bitcoin and divided it into two parts: transaction data and witness data. This change introduces a new concept of block weighting, where witness data is only weighted 25% of transaction data. This measure effectively expanded Bitcoin’s block size, making it easier and cheaper to store data in the witness portion of transactions. Basically, SegWit increases Bitcoin’s maximum block size from 1 MB to 4 MB (including 1 MB of transaction data and 3 MB of witness data).
The 2021 Taproot upgrade, while hailed by supporters as bringing smart contracts to Bitcoin, has yet to be widely adopted in the more than a year since it went live. Taproot improves privacy and scalability by simplifying the representation of complex smart contracts (such as multi-signature wallets, payment channels, etc.) on the blockchain into ordinary Bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin Script is a simple scripting language used to write and execute the logic of Bitcoin transactions. It is designed to provide a flexible way to set the unlocking and locking conditions of Bitcoin transactions. Two major impacts of Taproot are: allowing advanced scripting in the witness portion of the block, and removing the data limit between the two parts of the block, allowing up to 4 MB of data in the witness portion.
Ordinals & BRC 20
Ordinals, launched in January 2023, combine Taproot with Ordinal Theory to produce sats with additional inscriptions. Serial number theory equates 1 btc to 100 M sats and assigns a unique identifier to each of Bitcoin’s 2.1 quadrillion sats. Individual sats can be inscribed with any inscription such as text, image, video, up to a limit of 4 MB. The use of an ordinal wallet is necessary to prevent inadvertent use of inscribed sats. In contrast to NFTs, Ordinals have serial numbers, are limited in quantity, and are stored entirely on-chain.

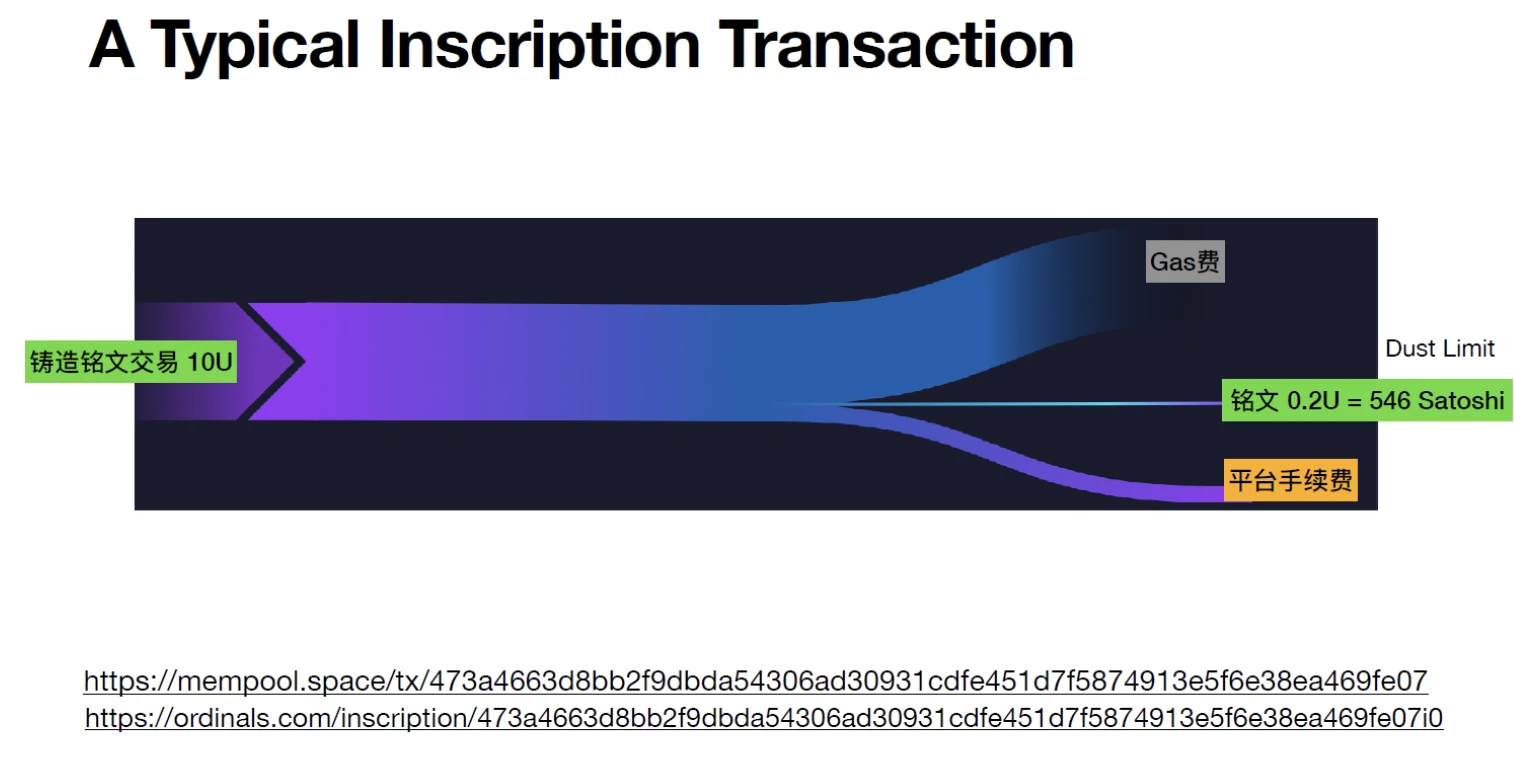
Additionally, benefits brought by Ordinals include increased transaction fee income for miners, improved security, and new narratives. However, it also brings some drawbacks, such as increased node storage, difficulties in content review, and issues that may lead to rising fees. Active players in this space include Xverse, Gamma, and others, who have been quick to add Ordinals support and launch related products. Well-known NFT studios Yuga Labs and DeGods also released projects based on Ordinals last month.
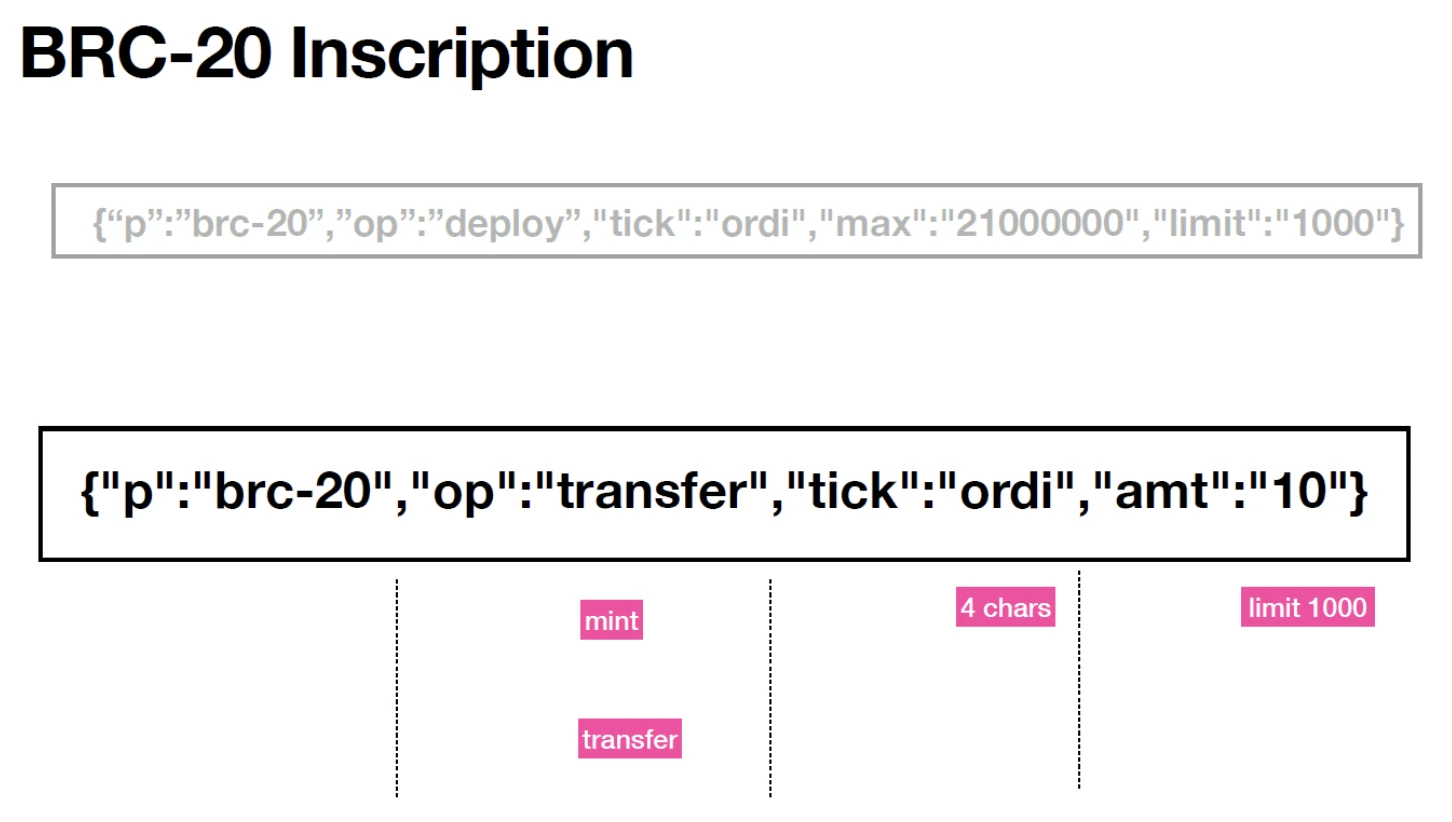
Inscription operations and the rollout of the BRC 20 standard are conducted on a first-come, first-served basis. Everyone can upload Punk to the Bitcoin network, but only the earliest Bitcoin Punk is authentic. This is actually a consensus. However, the craze has cooled down due to some criticism that it consumes network storage resources. When the additional information in the Ordinals protocol is set to a unified standard, the Ordinals protocol can issue not only non-fungible tokens (NFT) but also fungible tokens (FT).
ORC-20
ORC-20 goes beyond the BRC-20 standard in the freedom of token names. Unlike BRC-20, which only allows the use of four-letter words as names (symbols), ORC-20 allows the use of words of any length as ticks. For example, the first deployed ORC-20 token “ORC” consists of three letters. In addition, the ORC-20 standard introduces the ability to modify the total supply and maximum amount per mint after initial deployment, providing more flexibility for token economic experimentation. This functionality can be achieved by correctly specifying the tick and id and engraving the upgrade functionality into the Sat. For example, you could adjust the supply from 21,000,000 to 2,100,000, modify the issuance limit from 10,000 to 1,000, and set ug to false to disable future upgrades. After each upgrade, the version v of the ORC-20 token is automatically incremented by 1. In terms of the UTXO model, ORC-20 introduced this concept for token transfer, which is significantly different from BRC-20. For example, A sends $2 to B, and B originally has $1. Under the UTXO model, Bs balance will be displayed as two separate UTXOs, rather than a simple sum of $3. The advantage of this model is that UTXO can only be used once, effectively preventing the problem of double spending. To send ORC-20 tokens, the corresponding text needs to be inscribed into the Sat, with an inscription added at the end to send the remaining balance back to the sender. This process is similar to how UTXOs are handled, and the transaction can be canceled in the middle if the final inscription is not executed.
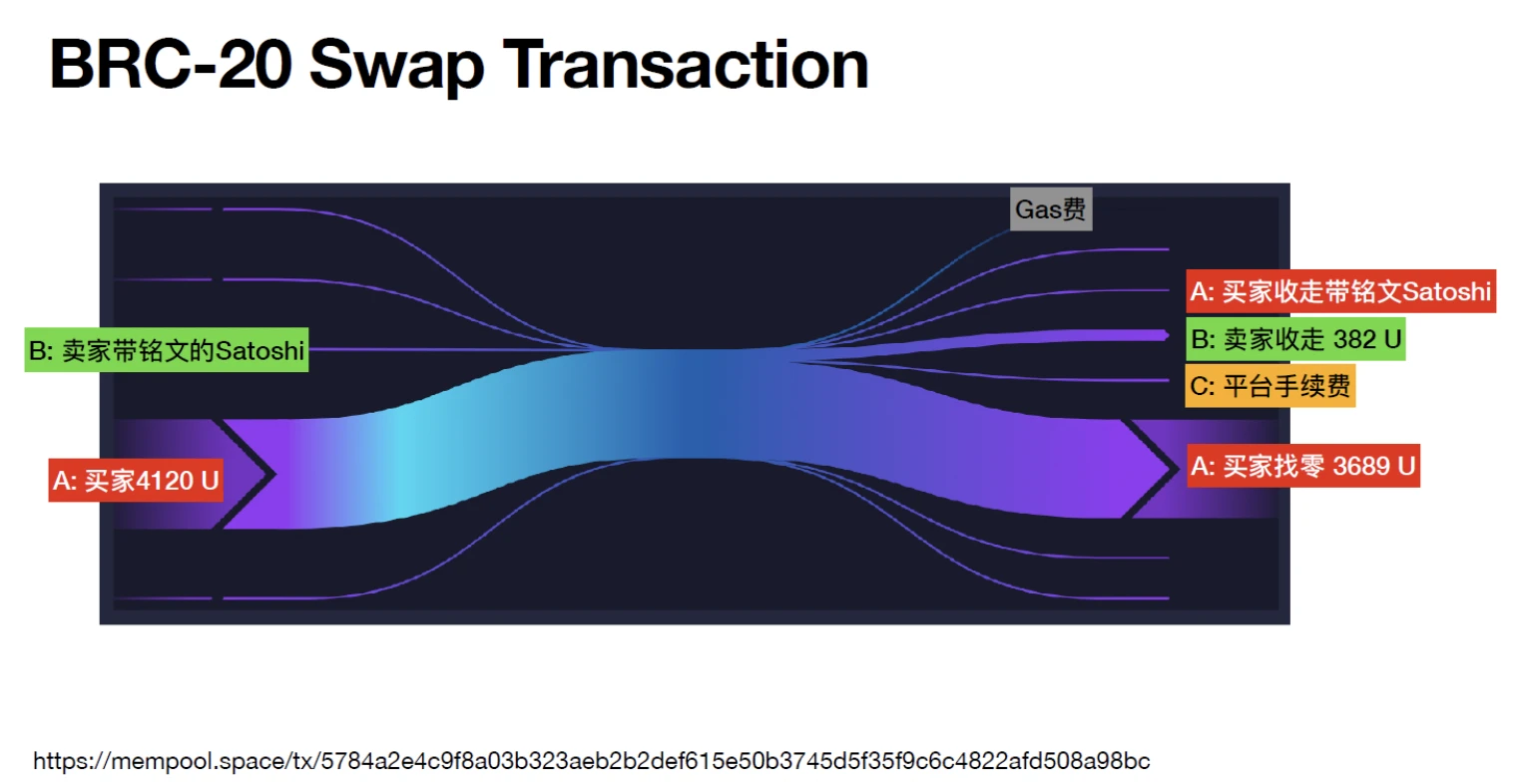
Atomicals
Atomics is an optimization project for Ordinals and BRC 20, focusing on fungible tokens and solving the problem of BRC 20’s over-reliance on centralized off-chain indexing. Atomics utilizes and extends Bitcoins UTXO model, treating the UTXO of each Satoshi (the smallest unit of Bitcoin) as a specific Atomic token or digital object, thereby creating and managing complex digital objects and tokens on Bitcoin. System (ARC 20). POW was introduced in the ARC 20 minting process, where the minter must calculate a hash of a specific prefix character in order to mint. The Atomics protocol provides prefix parameter settings for Bitwork Mining for ARC-20, allowing participants to directly mine inscriptions/NFTs. The ARC-20 token standard remains true to Bitcoin fundamentalist principles, and the emergence of related tools is expected to enhance its liquidity in the future.
Taproot Asset
Bitcoin’s latest upgrade, Taproot, makes it possible to embed asset metadata directly into Bitcoin outputs. It also supports multi-hop transactions on the Lightning Network, ensuring a seamless transaction experience for end users. Additionally, assets issued through this protocol are interoperable across the entire Lightning Network. This interoperability manifests as atomic conversions, allowing for seamless transitions between Bitcoin and Taproot assets. Taproot Assets is a protocol launched by the famous Lightning Labs to create and trade various digital assets on the Bitcoin network and integrate with the Lightning Network. The update of Taproot Assets expands the functionality of the Lightning Network from a simple peer-to-peer transaction payment channel to a peer-to-many model that enables asset distribution and circulation. The feature of Taproot Assets is that Token information is recorded in the UTXO output script of the Bitcoin main network as a registration, and functions such as transfer transactions are implemented in the lightning channel. The biggest difference from BRC 20 and ARC 20 is that Taproot Assets are released in a way that is pre-minted and then distributed by an owner, rather than free-minted. The Taproot asset integrates a sparse Merkle tree to facilitate efficient data retrieval. Additionally, it includes a Merkle-Sum tree to ensure efficient preservation of data. Assets can be transferred via on-chain transactions or via the Lightning Network once they are included in a channel. It is worth noting that participants bear the responsibility for verification and storage costs. Therefore, witness data for Taproot assets remains off-chain, stored in a file called"Universes"in the local data repository. The validity of an asset is proven by its lineage from inception and cross-checked using transaction data files obtained from the Taproot asset gossip layer. To maintain structural integrity and verifiability, Taproot assets employ a sophisticated indexing system, similar to a carefully cataloged library, ensuring timely access and verification of token information. Users can choose to transfer tokens directly or take advantage of the fast Lightning Network. Similar to protecting a certificate of authenticity for a precious item, users are tasked with preserving and verifying the data associated with their tokens, and the protocol provides the means to verify these"Certificate"Tools of Credibility.
NostrAssets
NostrAssets is an open source protocol that introduces Taproot assets and Satoshis (Bitcoin units) to the Nostr ecosystem. Users can send and receive assets at the Nostr protocol layer using Nostr’s public and private keys. The settlement and security of assets rely on the Lightning Network, and the Nostr Asset Protocol itself does not issue assets, but only introduces assets to Nostr through the protocol. Features of NostrAssets include seamless integration of Taproot assets and Bitcoin into the Nostr ecosystem, providing developers with tools to create innovative products, enriching the value of the Bitcoin and Lightning Network ecosystem, and enabling a seamless experience from chat to transaction. In the future, NostrAssets plans to import Taproot assets from other Daemon Universes, allowing for receiving and sending Taproot assets to and from Nostr.
Stamps
Bitcoin stamp images are stored permanently and unchangeably on the Bitcoin blockchain. Rather than saving images on a separate website or server, Bitcoin Stamp embeds image data directly into Bitcoin transactions. To create a Bitcoin stamp, the image needs to be converted to a special format called base 64. This format allows images to be represented as a string of characters. This image string is then added to the description of the Bitcoin transaction and sent to the Bitcoin network using the Counterparty protocol. Each Bitcoin stamp is assigned a number based on when the transaction occurred. This helps organize the stamps in chronological order. The first Bitcoin stamp was the first transaction to include a valid image string in its description. Transactions containing invalid image strings are not considered Bitcoin Stamps. Bitcoin stamps differ from other digital collectibles in that they are stored directly on the Bitcoin blockchain, specifically as Unspent Transaction Outputs (UTXOs). This ensures that the image is securely and permanently recorded on the blockchain. Currently, there are two main protocols used in Bitcoin Stamps: SRC-20 and SRC-721.
DLC
DLC (Discreet Log Contract) is a smart contract based on the Bitcoin blockchain through which complex financial transactions can be executed. Launching the DLC requires both parties to deposit Bitcoin as a stake into a shared 2-of-2 multi-signature wallet. Next, the parties agree to the terms in the contract and sign Contract Execution Transactions (CETs), which represent possible future outcomes. Since these transactions require a signature from Oracle to settle, they will remain unpublished. CETs occur off-chain and serve as payment channels on Bitcoin’s Lightning Network. Advantages of DLC include privacy protection, no need for escrow funds, and lower energy consumption. However, it also has some disadvantages, such as the risk of centralization, difficulty in order matching, and novelty. Its just that DLC is a relatively new concept that has yet to be tested on a large scale,
Main direction 2: Off-chain expansion
State Channel and Lightning network are the two main off-chain scaling methods of Bitcoin. The Taro update is a proposed protocol that allows the issuance of digital assets (FT/NFT) on the Bitcoin blockchain. Sidechain provides new application scenarios based on BTC, such as Liquid and Rootstock. Stacks introduces the POX consensus mechanism to interact with the BTC layer. The Nakamoto upgrade is expected to provide greater security and decentralization in Q4 2023.
Rollup builds a concept on top of BTC via inscription. Although BTC zk rollup can be compressed with validity proof, there are still some performance and security issues. The B 2 Network is a Bitcoin-based second layer solution designed to increase transaction speed and expand application diversity. The RGB protocol is a protocol built on top of the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus layer of the Bitcoin blockchain, and one of its core features is client-side verification, which improves scalability and privacy.
B^ 2 (BSquared)
The B^2 Network is a Bitcoin-based second layer solution designed to increase transaction speed and expand application diversity without sacrificing security. It is the first commitment rollup to implement zero-knowledge proof verification on Bitcoin. B^ 2 runs zkevm on the upper layer of the Bitcoin network, allowing users to directly control their zkevm accounts through btc wallet signatures. Guaranteed developer and user experience. The verification process of zkp in zkevm is broken down into small unit values and stored in the Bitcoin network in the form of taproot transactions. The verification itself does not occur on Bitcoin, but the entire process of verification can be recovered from Bitcoin. If you want to independently verify zkp, users still need to go to the Bitcoin network to retrieve the entire zkp verification process before they can verify it themselves. The verification of B 2s zkp does not achieve the best results. That is, users still need to pay a certain amount of redundant calculations compared to directly verifying zkp in L1, but it still has a considerable advantage over directly recalculating all transactions.
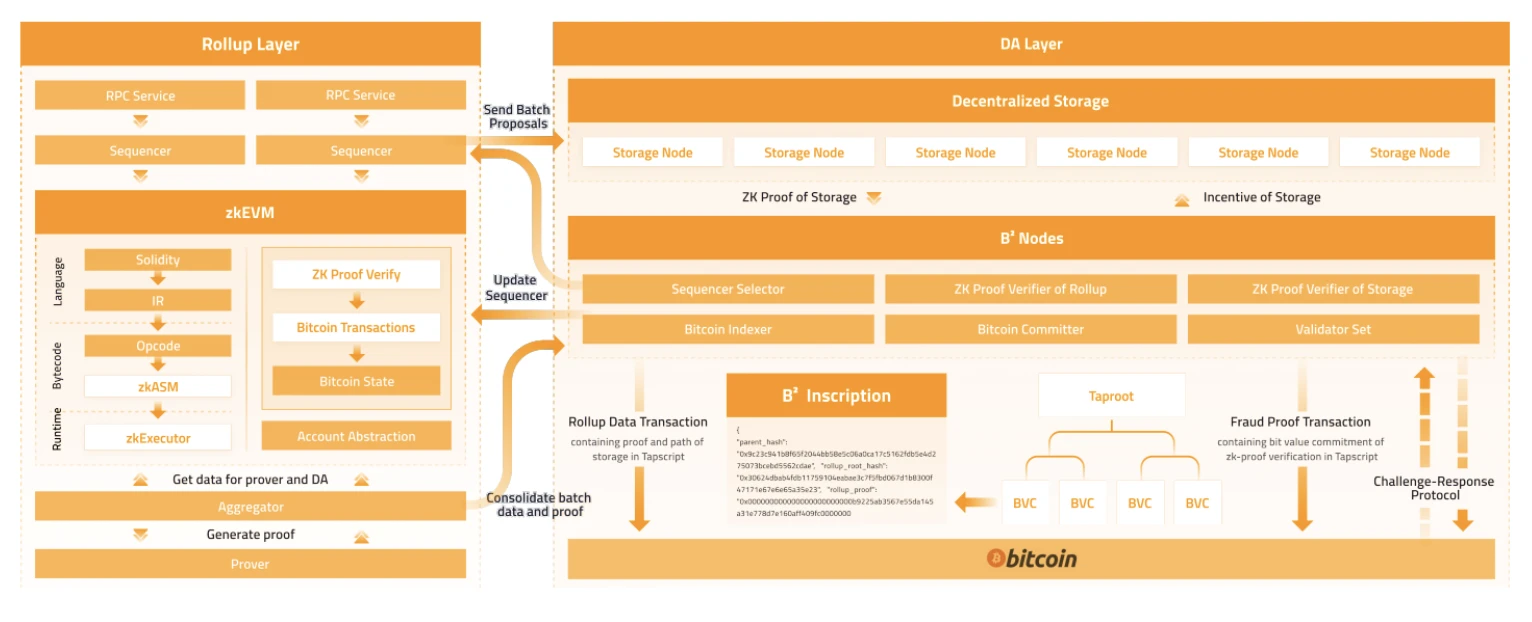 RGB
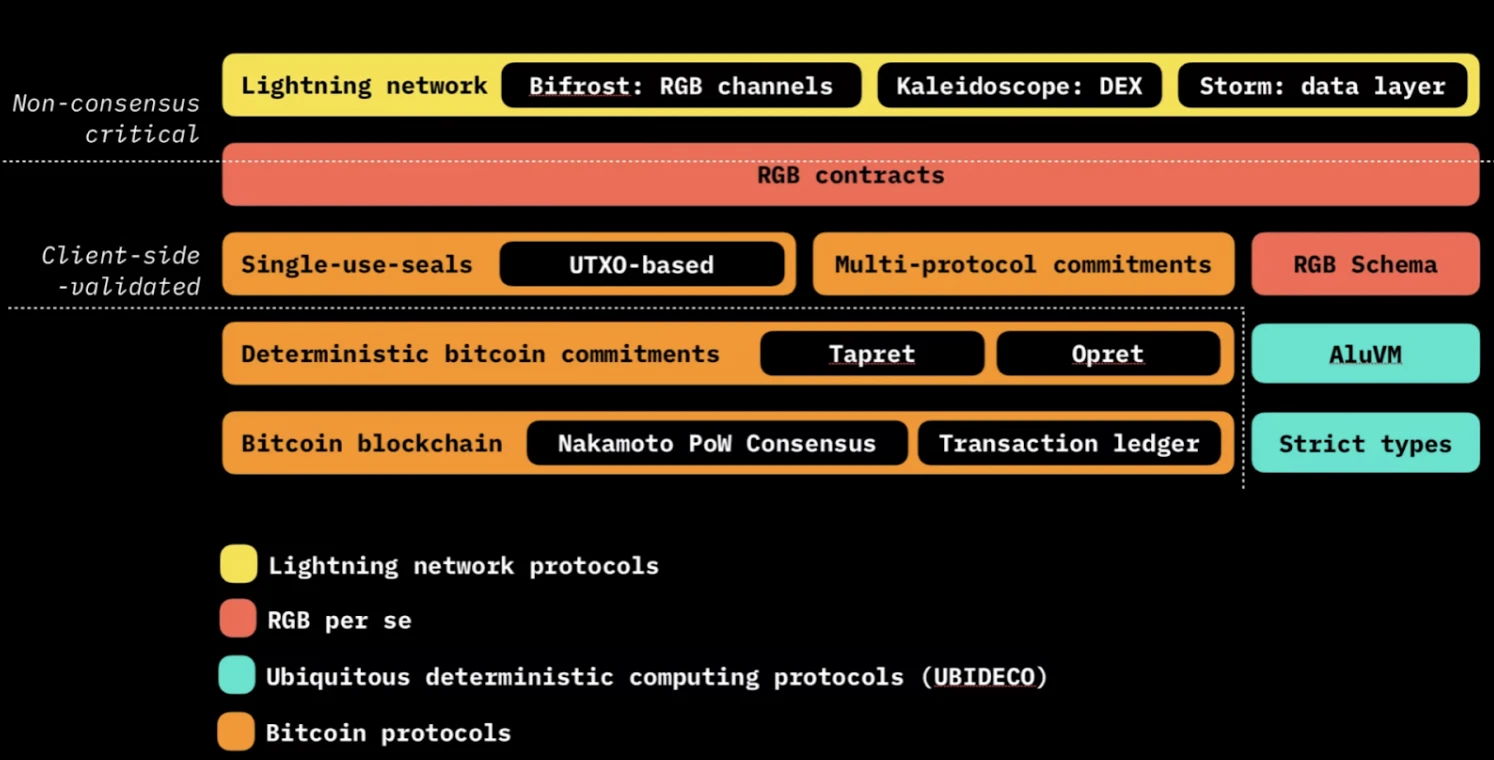
RGB
RGB is a protocol built on top of the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus layer of the Bitcoin blockchain. Using RGB requires no protocol changes to the Bitcoin blockchain or Lightning Network. The protocol acts as a version of a directed acyclic graph (DAG) where participants cannot see the full state of the network. Each new transaction requires confirmation of at least two earlier transactions before being recorded on the network. Client-side validation is powered by RGB mode, which is how smart contract agreements are created between users.
Client verification
One of the core features of RGB is client-side validation, a concept proposed by Peter Todd. Since RGB transactions are not included in Bitcoin or Lightning transactions, scalability and privacy are significantly improved. In addition to storing transaction data off-chain, RGB transactions also use single-use seals (or seals) to close Bitcoin transaction outputs by distributing them into a collection of UTXOs as another security measure. Sealing prevents two different parties from providing different versions of what should be the same data. As such, they allow qualified parties to verify the state history of a smart contract.
RGBs provenance-level schema defines per-state validation rules, ensuring that each successive state owner uses the same schema to validate its history. Thus, the schema guarantees social consensus, verification, and smart contract state. RGB smart contracts include a state, an owner, and actions that participants can perform to update the state.
By default, RGB contracts have well-defined parties with ownership rights to specific state atoms, which are called owning states.
The state of a contract consists of state atoms of different data types, similar to variable types in structural languages (such as Rust).
Operations include genesis operations, state transitions to update or add data, and state extensions to enable public participation.
RGB validation logic ensures that it always produces the same results regardless of the platform or library used. This is achieved through two main components:
The core validation logic leverages the Rust language. All contract-specific verification logic runs on the Alluvium Virtual Machine (AluVM), a highly deterministic and exception-free virtual machine that provides a platform-independent instruction set.
The architecture of the RGB node is the same as the LNP and BP nodes designed and maintained by the LNP/BP Standards Association. The node is composed of multiple microservices and is designed to run on a desktop or server as a single daemon (such as a program that runs in the background without user intervention), in a single mobile application as a thread, in a cloud system, or as Independent nodes combined in a single mobile application. Additionally, all peer-to-peer communications are end-to-end encrypted and work on the Tor network.
All data of RGB smart contracts are completely stored off-chain and run by RGB nodes. The RGB protocol uses UTXO to store state transition proofs to track and verify the status of smart contracts. Users/verifiers can confirm whether the status of smart contracts is correct by scanning UTXO on the Bitcoin network. Utilizing the Bit consensus layer requires only retaining short encrypted submissions of ledger events, a technology that proves the existence of specific data but does not reveal the actual data content. It is usually implemented through a hash function and only stores these submissions on the chain to ensure the authenticity and authenticity of the data. Integrity, thereby reducing the burden of data on the chain. The ledger data designed by RGB is stored off-chain, which means that all contract data and state transitions are kept off-chain instead of on the blockchain. Track and verify the state of smart contracts using single-use seals and state transitions to efficiently process and verify smart contract states and transactions without storing all data on-chain.
ROOS Network
ROOS Network is a Bitcoin Layer 2 expansion solution based on the ZK Rollup architecture and compatible with EVM. It aims to expand Bitcoins smart contract scenarios without sacrificing security and decentralization, and break through the constraints of Bitcoins non-Turing completeness. , improve transaction efficiency and minimize transaction costs. ROOS will allow developers to build a variety of rollups, including sovereign rollups and settlement rollups. According to the official website, the next step for ROOS is to release the ROOS Alpha test network and establish a developer community and network ecological services.
Layertwo Labs
Layertwo Labs built Drivechain to allow developers to create any blockchain application they want through sidechains connected to the BTC network. On sidechain, developers have complete freedom to make any Token, token, smart contract, block There are no restrictions on size, consensus model (PoW, PoS), use cases, DApps, UX and UI, features and rules. . Drive Chain essentially provides a mechanism for building L2 on Bitcoin. There are only 256 positions, and the extra L2 needs to cover the previous ones. It can be understood as turning Bitcoin into a relay chain for Polkadot, without various interoperability functions. Generally, L2 withdrawals in the Ethereum ecosystem are initiated by smart contracts placed in L1, which are usually subject to the multi-signature control of the L2 project party. Some L2s have a force exit mechanism that directly withdraws money from ETH L1 (submitted by the user) Fraud proof or zk proof of ones own L2 status, etc.) Drive Chains withdrawal is essentially a multi-signature signed by all Bitcoin nodes. This multi-signature is signed by all Bitcoin miners in L1 for multiple rounds of computing power. Each withdrawal can complete one multi-signature confirmation per Bitcoin block, and a total of 13,150 multi-signature confirmations are required to unlock the money-out transaction (3-6 months). When a user initiates a withdrawal from L2, L2 will generate a 32 bytes hash (based on the global status of the L2, the users L2 status, L1 payment address and other information). Of course, this hash may be forged by an attacker, so a competition mechanism similar to a signature contest is needed to allow honest withdrawals to win, so that in the end only one honest withdrawal can get the money correctly. The winning condition is that a certain withdrawal transaction receives 26,300 signatures. Starting from 1, the score is +1 for each winning block, and -1 if a block is multi-signed. If the score is reset to zero, the withdrawal will fail. The fastest withdrawal reaching 13150 will be sent to the users L1 payment address. From the perspective of the perpetrators, they need to control more than half of the Bitcoin computing power to influence the results of a single multi-signature, and at the same time predict the account status of prospective users in L2 (need to match the hash that changes in each block, which is difficult , you need to monitor the L2 status (the L2 account and the L1 account are not necessarily connected, and the user behavior is unpredictable) and the global status of the L2 (also difficult), and then sign your own fake withdrawal transaction. Then perform these operations at least 13,150 times in a row (a rollover in the middle may take the entire process more than three months). Cheating is easy to detect (because it is all in L1), and honest participants have enough time to take action. BIP 300 emphasizes slow, transparent, and auditable transactions that are easy for honest users to get right and difficult for dishonest users to abuse.
Platform project
Platforms for minting and trading engraved assets provide similar functionality, basically including:
Engraving tool: allows users to set asset casting details (total amount, minimum and maximum single casting amount, etc.), query existing engraving information and casting progress
Trading platform: Similar to the NFT trading platform, users can check floor prices, pending orders, recent transactions, etc.
UniSat
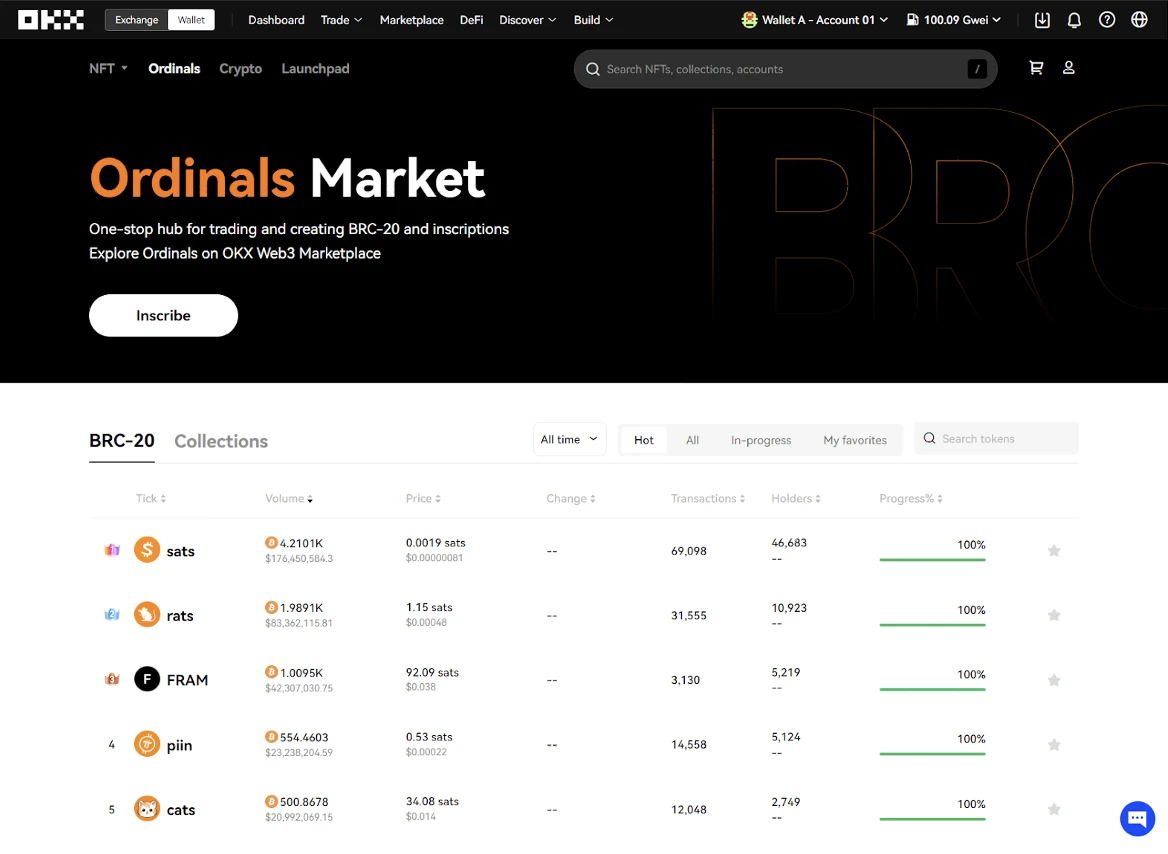
OKX
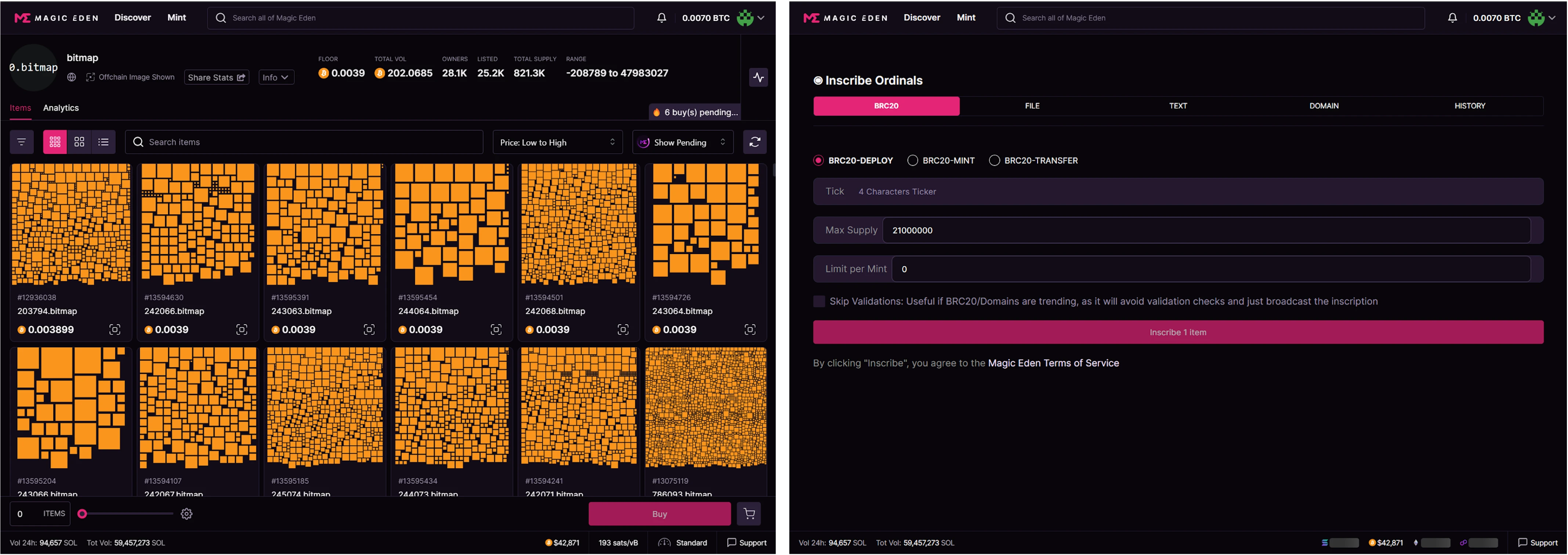
Magic Eden
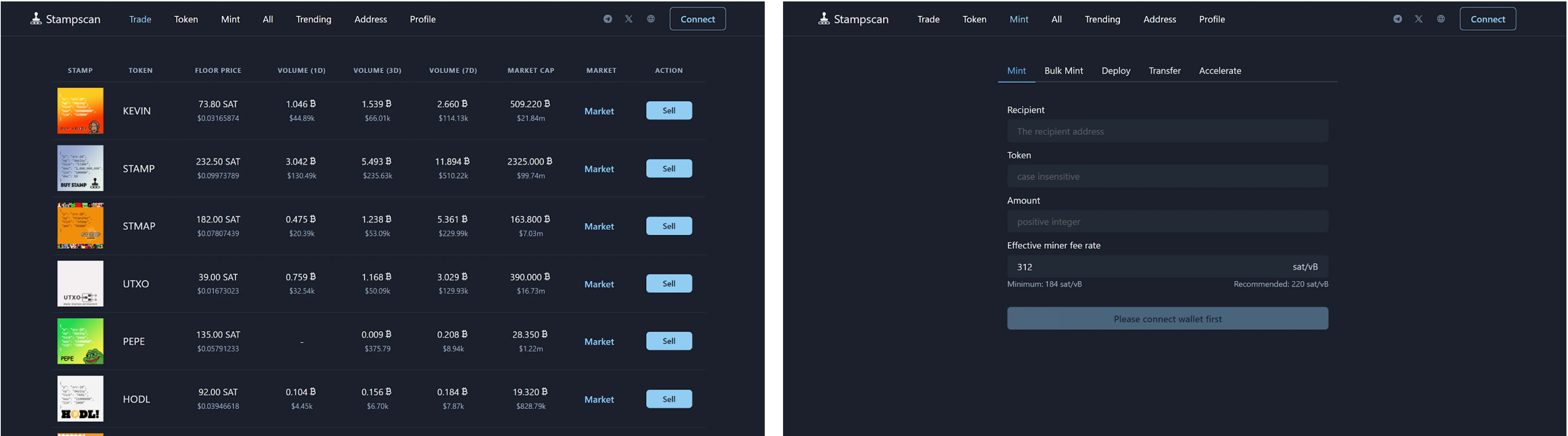
Stamp
List of secondary projects
The current market sentiment is obviously overheated, and everyone has lowered their IQs below 50. Coins are seriously over-issued. More than 50% of the coins have generated no more than 3 transactions after being launched online, and the leading coins have been listed on Binance. Compared with the previous cycle, the author believes that this round of inscription market is similar to the food currency market before the official start of defi summer. The situation of pure air speculation cannot last forever. Investors can consider making early arrangements to be more likely to survive and prosper in the next market period. asset trading and service platform.
Bitcoin ecological inscription assets
Brc 20 ($mcap)
Sats: The smallest unit of Bitcoin, the meme coin with the same name
Ordi: the earliest brc 20 coin
Trac: decentralized indexing
Nostr Asset
Treat: Nostr Asset Protocol Governance Token
Trick: Nostr Asset Protocol Governance Token
Nostr
Atomicals
Atom
Realm
Arcs
Stamp
Stamp
Kevin
Pepe
Bitmap
BRC-420
non brc 20
AUCTION: launchpad + expansion chain
MUBI: cross-chain bridge
BSSB: Asset Platform
Turt:brc 20 launchpad
Other chain inscription assets
ETHS: Inscription assets on Ethereum, based on the facet platform
FACET: An inscription and transaction platform on Ethereum. It has developed its own Ethscriptions VM, which is mainly used to parse inscription transactions on Ethereum.
PAMP: meme coin on Ethscriptions VM
Sols: inscription assets above solana
The driving force behind ecological prosperity
In the past three months, Bitcoin miners’ income has increased significantly, especially in November, with the proportion of on-chain fee contribution rising from 2.4% on August 19 to 23.46% on November 16. This growth was mainly driven by the introduction of Ordinals trading pairs. This shows that the development of the Bitcoin inscription market has significantly increased the proportion of miners’ fee income. It is expected that this ratio may reach 50% by the time of the Bitcoin production cut in April 2024.
Currently, as U.S. Bitcoin mines are operating at a loss most of the time and the semiconductor industry faces process bottlenecks, the competition for mining machine computing power is easing. As a result, miners may turn to Bitcoin Inscription as a new source of income. For example, less than a year after the launch of Ordinals, more than 50,000 tokens have been issued in the market, and the number of mint and transactions has grown rapidly, which has greatly contributed to the increase in miner fee income.
The expansion of the Inscription Track not only drives the growth of miners’ income, but may also become the main driving force for the Bitcoin Inscription Track. However, miners are more concerned about the increase in the number of transactions than the fluctuations in the price of inscriptions.
The main reason is that the handling fee consumed by the inscription itself is staggering. Taking the recent normal price of 200 sats/vB as an example, the image content size of this Bitcoin Frogs is 3078 bytes (3 kb), which requires a handling fee of 61 w sats, not counting other content and the procedure for tx acceleration. fee. 61 w sats is approximately equal to 0.0061 BTC (1 BTC = 100 m sats). The entire collection of Bitcoin Frogs has 1 w coins, so if deployed now, deploying the content alone would cost the team 61 BTC, not counting other expenses. Calculated based on the price of one BTC of 4w, the gas of this picture alone consumes 244 US dollars, and the minimum cost of the entire collection will be 244 w US dollars. During community interviews, we also learned that some teams have spent tens of millions of dollars to deploy NFT. And this is only the cost of issuing coins for the project side. As a user, when making inscriptions, a gas level of around 200 sats/vB will bring gas costs ranging from US$100-300 per transaction/ticket. High costs and decidedly fair launches make for a great meme playground.
Key data
Transaction data on the Bitcoin network shows that the transaction volume of brc-20 and oridinals has accounted for a large proportion, once exceeding 50%. This shows that inscribed assets already occupy a considerable proportion in the Bitcoin ecosystem, and it is difficult to imagine that this asset class will completely disappear.

New assets often appear along with new trading platforms. In the early days, the track was dominated by marketplaces built by communities. As the track gradually matures, it can be seen that the current transaction volume and number of transactions are mainly occupied by the three giants: OKX, Unisat and Magic Eden. In addition to the huge traffic that comes with the original platform, better user experience is also key.
some conclusions
The infrastructure of the BTC ecosystem has improved. Mainly in the following points:
Increase the complexity of information on the chain
Increase off-chain computing and storage capabilities
Many new projects have moved technologies such as zk that have been implemented in the Ethereum ecosystem to the Bitcoin ecosystem to achieve off-chain expansion.
If the progress of these infrastructures is compared horizontally, there is no absolute advantage over other L1 L2s such as the Ethereum ecosystem in terms of scalability, security and decentralization, but it is still a 10X or even 100X improvement in the Bitcoin ecosystem. , enough to support user and asset growth over a period of time. The technical idea of inscription can be simply understood as putting security, consensus and liveness on the BTC chain, and settling on the indexer.
From a use case perspective, Inscription’s fair launch mode is a big enough innovation to support this round of Bitcoin market trends.
Due to programmability limitations, inscriptions are all fair launches, and it is almost impossible to implement more complex logic that treats users differently, such as pre-mine during the ICO period, lock-up of defi tokens, and whitelisting mechanisms for NFTs. Mint will be supported immediately after the standard format of inscriptions is announced (users can even mint in advance, but there is a high probability that it will be ignored by the indexer). Only the miner network decides which users tx is included in the block. The whole process is very fair, and the competition is completely based on the users information gap and willingness to pay for gas.
The threshold for using inscriptions has gradually been lowered with the popularization of tools and the emergence of tutorials. The advantages of retail investors and scientists have been filled by better codeless inscription and trading tools. The advantages of rat warehouses have been filled by bots that monitor the inscription behavior on the chain.
Limited by infrastructure, the environment for serious teams to build more complex use cases is still harsh, and the quality of users does not match. It is difficult to form a competitive advantage with other ecosystems other than new asset classes.
Essentially a market for a new asset class created using existing technology, with upward trends synchronized with the macro environment
The detailed reasons for the emergence of a large number of high-value assets and the phenomenon of ecological prosperity:
The BTC ecosystem has largely missed the past 1-2 bull markets. Miners need new sources of income, and creating better wealth opportunities meets this need.
In the middle and late stages of a bear market, the difficulty of a successful fair launch becomes lower, and market sentiment is easier to mobilize than at the end of a bull market or at the beginning of a bear market.
The absolutely fair launch ensured by technical limitations makes it possible for retail investors to make money in a bear market and an inevitability in a bull market.
The BTC network is robust enough to prevent downtime and errors, ensuring the asset security and user experience of most users.
How will the ecology develop next?
After interviews with a large number of community users and project parties, some preliminary conclusions were drawn and some reasoning was made.
Preliminary Conclusions
Currently limited by infrastructure development, it is difficult to make complex applications. The biggest use case of Inscription is meme.
User acquisition and retention are highly dependent on the attributes of fair launch
Empowering inscription assets is limited to very simple scenarios, such as depositing coins to create new ones, etc.
There are not many teams that work on complex applications seriously.
reasoning
Fair launch is inherently flawed as an asset issuance method
The project side lacks the incentive to do serious work over the long term and can easily end up unfinished.
Users only care about asset return performance, which can easily cause bad coins to drive out good coins.
In the upcoming bull market, more good projects from other ecosystems that have been precipitated by the bear market will be launched, which may attract more funds and cause the average price performance of fair launch projects to further decline.
Inscription is a good way to fairly distribute benefits to users and ensure fairness among users.
Inscription is a cheaper and safer operation than interacting directly with smart contracts
It only needs to consume a simple tx gas
Does not involve the transfer of assets in the users wallet
There may be directions for more market demand
Inscription asset trading platform
New asset classes will create new trading scenarios, which may in turn create new trading platforms.
However, as previous data shows, the ordinals and brc 20 asset classes are currently mainly dominated by OKX, Unisat and Magic Eden, which have occupied the market share of previous community-built exchanges through better user experience.
If a new asset class emerges, trading opportunities may arise for other asset standards. The trading platform with the earliest support and the best product experience may have an opportunity
ORC, ARC,Stamps and other standards
The ecosystem is small and needs time to continue to develop.
Inscribed asset standards for other chains
There has been a certain amount of buzz (the volume is still relatively small), but since other chains generally have lower gas and higher throughput than the BTC chain, opportunities for high-value assets may not easily appear, but the volume of long-tail assets is still considerable.
Faster and more secure L2
When the bull market comes, Bitcoin network gas will rise, and there may be a demand for lower transaction fees from new users entering the market, similar to the opportunities that occurred when L1 gas was too high in the last defi cycle and users entered L2.
The inscribed assets on L2 have lower transaction costs and can produce more complex defi gameplay.
Bitcoin native defi
Defi based on inscription and directly operated on Bitcoin
Opportunities to generate new stablecoins based on transaction demand for inscribed assets, possibly over-collateralized minting of plaintext assets
Cross-chain bridge
Serving liquidity outside of exchanges and entering the Bitcoin ecosystem
High requirements for BD and ecological abilities
Competing products on the market include Thorchain, Multibit, Polyhedra, etc.
More complex protocols based on the brc protocol class, or more complex applications
New asset classes bring in certain users, creating demand for higher-complexity applications (copying the ICO, Defi, games, etc. paths taken by the evm ecosystem)
There may be mechanically innovative gameplay (bringing the operational characteristics of fair launch such as inscription to defi or even into the game).
The engraving behavior is broken down according to the transactions and usage scenarios caused by different use cases, and new tool opportunities for BTC or other chains may arise.
Create and transfer assets through inscription, and perform other logic through on-chain contracts
Allow users to perform operations that need to ensure fairness through inscription, such as receiving airdrops
Engraving allows users to perform other actions required to ensure security, such as registering asset ownership.
Inscription Category Items or Inscription Platforms for Other Chains
Copy proven methods of creating new assets to other ecosystems
Summarize
The emergence of new asset classes always brings new users and new sources of funding. This is an exciting opportunity. These opportunities may appear on the infrastructure side, the platform side and even the application side. The new asset class will definitely repeat the cycle of previous asset classes: consensus is established in the early stage, the market is flooded with air coins, quickly overheats, returns to rationality in stages, the remaining project parties continue to accumulate value, and finally usher in an explosion, establishing the next stage. consensus. Inscription is the renaissance of Bitcoin, and it is not the renaissance of blockchain. The need for fair launches will always exist, and so will air coins. We believe that the Bitcoin ecosystem will experience a new round of turmoil. Existing players may see huge growth opportunities, and new players will also have ample opportunities to challenge the market leaders.










