Original author: TechFlow

This round of bull market has made people a little uncomfortable. This cycle has just been awarded the title of Meme Bull Market, and not long after, the market has heard a series of wailings - yes, the old players who rushed to Meme were trapped again, and the most uncomfortable thing is not being trapped in the rush to Meme, but selling the old coins that have been held for many years and have not moved at the price in order to rush to Meme. At this time, the old players began to frantically pull the price.
XRP, XLM, HBAR, XVG... Recently, the names that appear on the exchanges daily gain list are all familiar but unfamiliar to old investors. In less than a month, XRP has soared 400%, and its market value has surpassed SOL. Old group friends have sighed: What year is it now?
The old trash that has been FUDed for a long time has suddenly risen up, which is contrary to its usual behavior. Although it has a bit of the flavor of sector rotation, in essence, it may still be the markets value discovery of these assets again.
There is no need to say much about the positive impact of Trumps victory on cryptocurrencies. This can be seen from the crazy rise of Bitcoin. Just one month after his victory, Bitcoin successfully broke through the $100,000 mark. Trumps many friendly statements on cryptocurrencies have also made Wall Street regain its valuation of the broader payment attributes of cryptocurrencies. For example, XRP, XLM, etc., which have risen this time, are not only mostly linked to the payment track, but also have one thing in common: they belong to the ISO 20022 concept.
ISO 20022, the common language of finance
Is ISO 20022 a new narrative that suddenly emerged? No, in fact, ISO 20022 had its prototype as early as 2004, long before the first Bitcoin was mined.
ISO 20022 (Financial Services - Universal Financial Industry message scheme) is an international financial communication standard developed by ISO (International Organization for Standardization) Technical Committee TC 68 (Financial Services). After years of development, it has become a unified standard for global financial messaging, covering multiple financial fields such as payment, securities, trade, cards and foreign exchange.
From a technical perspective, ISO 20022 is:
A global unified standard for financial communications
A set of standardized data formats and rules
A framework for financial messaging
Let me give you an example, maybe you will understand it better.
Suppose you want to transfer $1,000 to a friend abroad. The money has to go through several levels of circulation:
Your bank sends payment instructions in its own format
SWIFT wants to translate this instruction into its own format
Intermediate rows may be processed in another format
Finally, the receiving bank has to translate it into a format that it can understand.
Just like playing a game of telephone, every time the message is passed, some information may be lost. Even some important information (such as payment purpose, invoice number) may disappear directly during the conversion process. Cross-border payments seem simple, but they have to go through countless translations behind the scenes - because each financial institution speaks its own dialect.
Therefore, ISO 20022 can be understood as the “global financial Mandarin.” Just as Mandarin allows people from different regions to communicate with each other, ISO 20022 allows different financial institutions around the world to exchange information in the same way.
With ISO 20022, all financial institutions speak the same language, and the payment information contained in the communication is richer (expanded from the original 140 characters to 9,000 characters), the data structure is more standardized (its like everyone uses the same template), and the processing is smarter (machines can directly read and process it). In the past, cross-border transfers were like sending a telegram in Morse code, but now its like sending a structured email, which can not only have attachments, but can also be automatically classified and processed.
Cryptocurrency that actively embraces ISO 20022
If a cryptocurrency complies with the ISO 20022 standard, it will be assigned an official ISO code. Financial institutions can easily use cryptocurrencies for cross-border payments. In addition, regulators may be more relaxed about ISO 20022 tokens, and tokens that comply with ISO standards may be used on a large scale, which is equivalent to being incorporated into the global financial payment system and having an orthodox payment purpose.
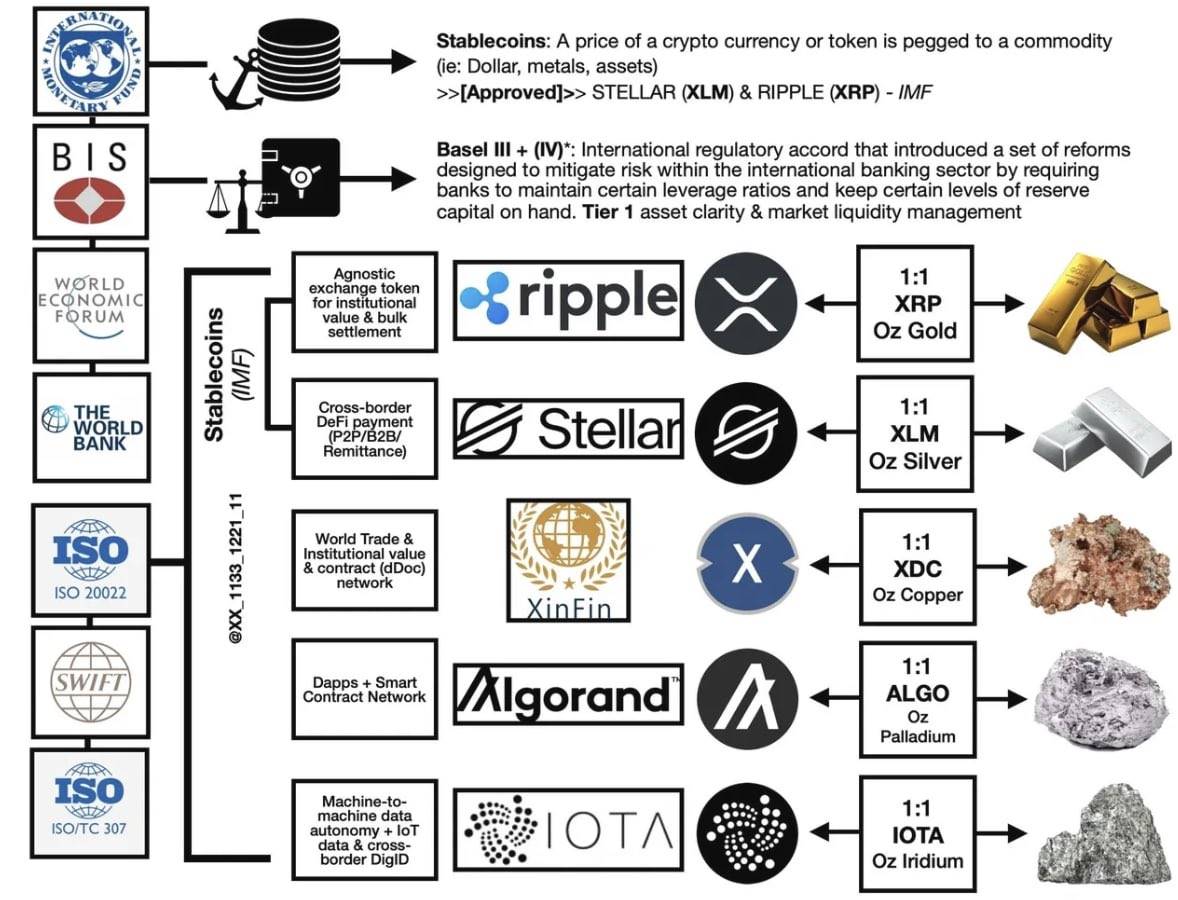
Note: This is a system diagram widely circulated on Twitter, for reference only
So what are the ISO 20022 concept tokens that are recognized by the market now?
XRP (Ripple)
Official certification status: The only cryptocurrency project to receive official ISO 20022 certification
Specific implementation:
RippleNet fully integrates ISO 20022 messaging standards
Provide real-time gross settlement (RTGS) system
Support end-to-end tracking of cross-border payments
Established partnerships with more than 200 financial institutions
Main cooperation:
Interoperability testing with SWIFT
Cooperate with central banks of multiple countries on CBDC projects
Establish direct payment channels with major banks
XLM (Stellar)
Official certification status: Not an official certification member, but technically supports the standard
Specific implementation:
Uses ISO 20022 compliant message format
Providing cross-border payment and remittance services
Support asset tokenization
Main cooperation:
Established a strategic partnership with MoneyGram
Partnering with over 350 banks in countries including Argentina
Cooperate with Circle to issue USDC
ADA (Cardano)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
Support for ISO 20022 with Atala PRISM Identity Solution
Adopting an academic research-driven approach to standards implementation
Support for smart contracts and tokenized assets
Main cooperation:
Partnering with the Ethiopian Ministry of Education
Establish government-level cooperation with multiple African countries
Partnering with financial institutions to develop identity verification solutions
QNT (Quant)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
ISO 20022 compliance through the Overledger platform
Providing cross-chain interoperability solutions
Supporting multi-chain CBDC implementation
Main cooperation:
Established strategic cooperation with LCX Exchange
Participate in CBDC project development
Collaborating with enterprises and financial institutions to achieve blockchain interoperability
ALGO (Algorand)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
Supports ISO 20022 standard message transmission
Providing high-performance first-layer blockchain solutions
Support smart contracts and asset tokenization
Main cooperation:
Collaborating with multiple CBDC projects
Establish payment network cooperation with financial institutions
Support stablecoin issuance and cross-border payments
HBAR (Hedera)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
Uses ISO 20022 compliant message format
Distributed ledger technology that provides high throughput
Support smart contracts and token services
Key Features:
Outstanding performance in implementing ISO 20022 standards
Providing enterprise-level solutions
Support cross-border payment and settlement
IOTA (MIOTA)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
Support ISO 20022 through Tangle technology
Focus on IoT payment and data transmission
Provides zero-fee transactions
Main cooperation:
Cooperation with EU institutions
Participate in smart city projects
Developing IoT payment solutions
XDC (XDC Network)
Official certification status: Unofficial certified member
Specific implementation:
Supporting ISO 20022 standards for trade finance
Providing enterprise-level blockchain solutions
Support for smart contracts and tokenization
Main cooperation:
Partnering with trade finance platforms
Supporting supply chain finance
Establish partnerships with financial institutions
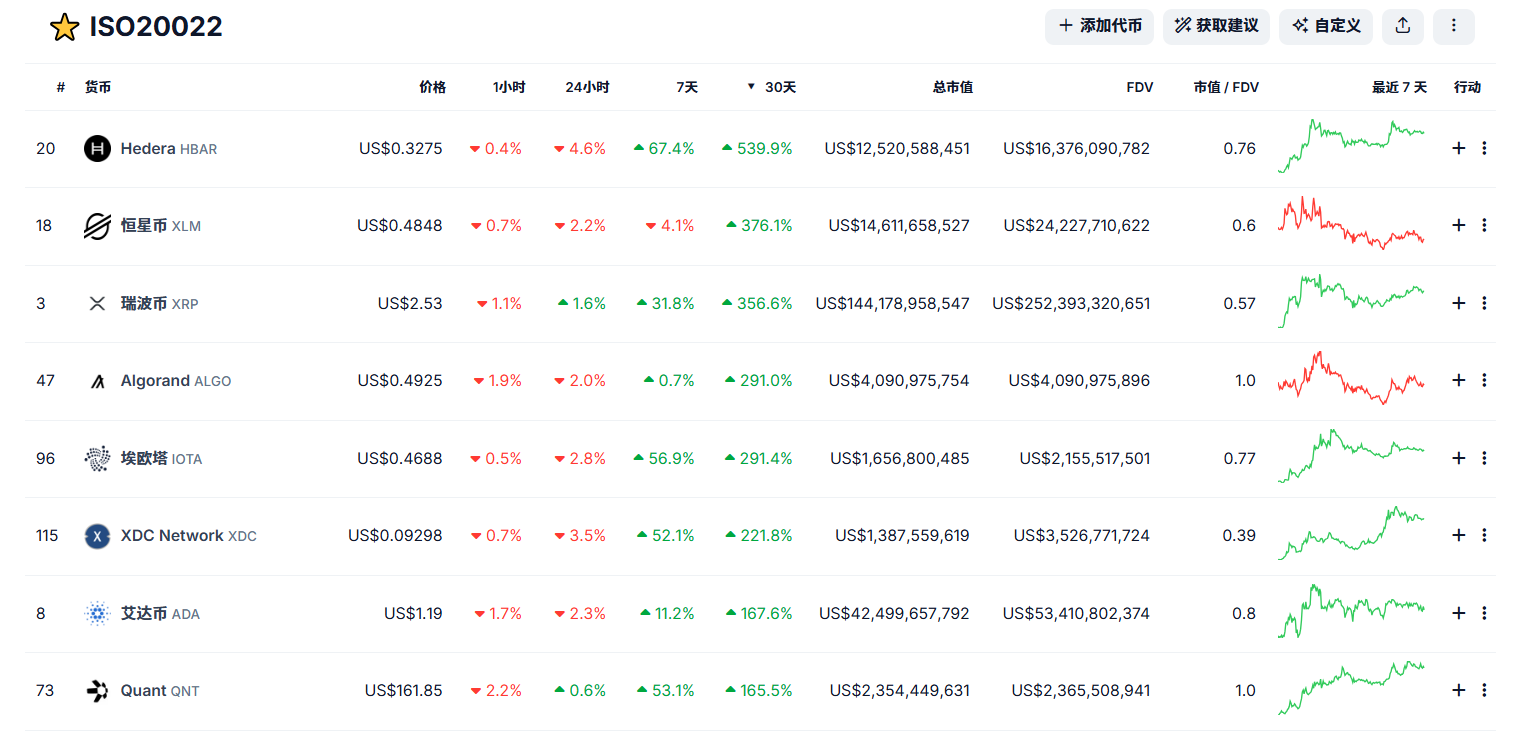
Does “legitimacy” really matter?
There have always been two different voices in the discussion about ISO 20022. Some people insist that only officially certified XRP is the only concept currency of ISO 20022; while others point out that ISO 20022 is essentially an open technical standard, and there is no so-called official certification mechanism at all. Projects such as Ripple, Stellar, and Cardano only support this standard at different technical levels - just like HTTP to the Internet.
What is more worthy of attention is the actual implementation of the project. The officially certified Ripple has indeed made substantial progress in the field of cross-border payments. Similarly, the cooperation between Stellar and MoneyGram, as well as the implementation of Cardanos project in Africa, have also made achievements from the perspective of practical application. From this perspective, whether a project is truly officially certified does not seem to have a necessary connection with its market potential.
Therefore, instead of worrying about whether a project has obtained the so-called official certification, it is better to spend time to understand what problems the project is solving, whether the solution is really feasible, and whether it has a competitive advantage in the current market environment.
After all, when faced with a long-term narrative, if you invest money with the idea of making a quick buck from short-term speculation, you are more likely to be punished by the market.











