summary
Recently, former US President Donald Trump reiterated his policy plan to impose high tariffs on Canada, Mexico, and China, causing severe shocks in the global financial market. As a result, the stock market, foreign exchange market, and cryptocurrency market have all experienced significant fluctuations, and the price of Bitcoin (BTC) once fell below the $92,000 mark. Although the market has been impacted in the short term, in the long run, the trade war and high tariff policies may be beneficial to decentralized assets such as Bitcoin.
This report will deeply analyze the impact of Trump’s tariff policy on Bitcoin and the entire crypto market from multiple perspectives, including macroeconomics, monetary policy, market structure, and investment sentiment, and explore the possible future operating trends of Bitcoin.
1. Overview of Trump’s Tariff Policy
1.1 Tariff Policy Background
1.1.1 The return of trade protectionism
In the context of globalization, trade relations between countries are becoming increasingly close. However, the US trade policy in recent years has gradually tilted towards protectionism, especially during the Trump administration (2017-2021). The Trump administration believes that the United States has long been at a disadvantage in international trade, with the main reasons including:
Widening trade deficit: The U.S. trade deficit with countries and regions such as China, Mexico, Japan, and the European Union has remained at a high level for a long time. Trump believes that this deficit has led to the loss of U.S. manufacturing jobs.
Industrial hollowing out: Over the past few decades, U.S. manufacturing has been outsourced to Asia and other regions, causing the domestic manufacturing industry to shrink. The Trump administration hopes to encourage companies to return to the United States by raising tariffs.
National security considerations: Trump and his advisory team believe that Chinas technological rise poses a threat to the United States, so they are trying to curb Chinas industrial development by restricting the export of high-tech products and imposing tariffs.
1.1.2 Background of the 2024 US Election
In the 2024 US presidential election, Trump once again became the Republican presidential candidate and vigorously promoted the America First policy during the campaign. The core measures include:
Imposing tougher trade sanctions on China: Promising to impose tariffs of at least 60% on all Chinese imports.
Re-examining trade agreements with Mexico and Canada: If elected, he may re-evaluate the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA).
Put trade pressure on allies such as Europe and Japan: require them to reduce their trade surplus with the United States, otherwise they will face high tariffs.
The introduction of these policies has led to increased uncertainty in the global market about the future trade environment, which in turn has affected global capital flows and market sentiment.
1.2 Main tariff measures
The core of Trumps trade policy is to impose high tariffs on major economies around the world, especially on goods from China, the European Union, Japan and Mexico. The following are possible specific measures:
1.2.1 Imposing tariffs of more than 60% on Chinese goods
Trump imposed a series of tariffs on Chinese goods from 2018 to 2020, but if he is re-elected president, the tariffs planned on Chinese goods will be even more severe.
Product coverage: including electronic products, automobiles, solar panels, industrial equipment, chip manufacturing equipment and other key industries.
Impact: Could lead to higher import costs for the United States and increase instability in the global supply chain.
1.2.2 Adjustment of tariff policies towards Europe, Japan and Mexico
Europe: Trump may raise tariffs on German cars, French wine and Italian fashion brands to reduce the trade deficit between the US and Europe.
Japan: May require Japan to further open its market, otherwise import tariffs on Japanese cars and parts will be increased.
Mexico: Trump has threatened to impose additional tariffs on Mexican exports to the United States in order to force Mexico to strengthen border controls. If re-elected, similar policies may be resumed.
1.2.3 Support policies for the domestic manufacturing industry in the United States
Tax breaks: Tax incentives are given to companies that invest in manufacturing in the United States to encourage them to move their production bases back to the United States.
Government procurement tendency: Strengthen the Buy American policy and require government agencies to purchase more domestically manufactured products.
The implementation of these measures may further tense the global trade environment, affect market stability, and indirectly drive demand for decentralized assets such as Bitcoin.
2. Impact of tariff policies on the global market and economy
2.1.1 Impact of the trade war on the global economy
Trump’s tariff policy may bring the following negative impacts:
Slowing global economic growth: Higher tariffs will increase production costs for companies, which could lead to lower consumer spending and thus curb global economic growth. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) has warned that a trade war could reduce global GDP growth by 0.5%-1%.
Supply chain disruptions: Tariffs may cause companies to readjust their supply chains, increasing uncertainty. Companies such as Apple and Tesla may have to find alternative suppliers, increasing operating costs. Rising global inflationary pressures The implementation of tariffs will lead to higher prices for imported goods, which in turn will drive up inflation. The Federal Reserve may adjust its monetary policy as a result, affecting market liquidity.
2.1.2 Impact of tariff policy on the U.S. economy
Although the Trump administration believes that raising tariffs can promote US economic growth, it may actually bring the following risks:
Higher costs for consumers: Since many everyday consumer goods are imported, higher tariffs could lead to higher spending for U.S. consumers.
The 2018-2019 tariff policy resulted in more than $80 billion in additional costs for American businesses and consumers.
Decreased corporate profitability: Tariffs may squeeze corporate profits, leading to layoffs or reduced investment. Industries such as manufacturing, retail, and agriculture may be hit hard.
The Fed’s monetary policy adjustment: If inflation continues to rise, the Fed may delay rate cuts or further raise interest rates, affecting market liquidity. A high interest rate environment may put pressure on the stock and bond markets, leading to increased market volatility.
2.1.3 Impact of tariff policies on Bitcoin and the crypto market
Although the market may take a hit in the short term, the trade war could indirectly benefit Bitcoin in the long term for the following reasons:
Increased market demand for risk aversion: Faced with global economic uncertainty, funds may flow from traditional markets to decentralized assets such as Bitcoin.
Rising expectations of dollar depreciation: If the trade war leads the Federal Reserve to implement loose monetary policy, the dollar may depreciate, thereby enhancing the appeal of Bitcoin.
Capital flight drives crypto market growth: Historically, whenever global markets face shocks, demand for Bitcoin increases.
2.2 Response of traditional financial markets
Trumps tariff policy has exacerbated market uncertainty, dampened investor confidence in the economic outlook, and led to a rise in risk aversion in global markets. From the stock market to the precious metals market, the price trend of various assets has been affected.
2.2.1 Stock market crash: Investors’ concerns about economic growth intensified
After Trump announced the increase in import tariffs, the three major US stock indexes - SP 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) and Nasdaq Composite Index (NASDAQ) - all fell by 2% -4%. The decline in the stock market was mainly driven by the following factors: rising corporate costs, impaired profitability, falling consumer spending, limited market demand, rising risk aversion in the market, and capital flows to low-risk assets.
When market uncertainty increases, investors tend to withdraw from the stock market and transfer funds to safe-haven assets (such as gold, US dollars and US bonds). Due to the outflow of funds from the stock market, the market is further under pressure and a downward trend is formed.
2.2.2 US Dollar Index (DXY) Strengthens: Safe-haven demand pushes up the dollar
Despite the negative impact of Trump’s tariff policy on the global economy, the US dollar index (DXY) has strengthened in the short term. This is mainly due to the market’s expectation that the Federal Reserve will not cut interest rates immediately, while investors seek the US dollar as a safe-haven asset.
Impact of the Fed’s monetary policy: Tariff policies may lead to rising inflationary pressures, making the Fed reluctant to cut interest rates in the short term to prevent inflation from getting out of control. The market originally expected the Fed to cut interest rates in the coming months, but the introduction of tariff policies changed this expectation and pushed the dollar up.
Global capital flows to US dollar assets: As market uncertainty about the economy intensifies, global investors tend to hold US dollar cash or invest in US Treasury bonds to avoid risks. During the US-China trade war in 2018, the US dollar index once broke through 100 and rose sharply. A similar situation may happen again.
Pressure on risk assets such as Bitcoin: A stronger dollar usually puts pressure on dollar-denominated risk assets such as Bitcoin, as funds tend to flow into the dollar market rather than the crypto market.
In the short term, a stronger dollar may cause the price of Bitcoin to fall, but in the long term, market concerns about the US dollar credit system may in turn promote the growth of Bitcoins value.
2.2.3 Precious metals rise: Gold breaks through $2,800/ounce
Against the backdrop of rising risk aversion, the precious metals market has seen a rise, especially gold prices breaking through $2,300 per ounce. This is mainly due to:
Safe-haven funds pour into the gold market: As a globally recognized safe-haven asset, gold is usually favored by funds when the market is turbulent.
Institutional investors and hedge funds may increase their gold holdings during stock market turmoil to hedge market risks.
As inflation expectations rise, golds attractiveness increases: Tariff policies may push up inflation and increase golds value storage function.
Past historical data shows that gold tends to perform well in high inflation environments. For example, during the stagflation period of the 1970s, gold prices rose sharply.
2.3 Severe fluctuations in the crypto market
Compared with traditional financial markets, the crypto market is more volatile, mainly affected by market sentiment, leverage liquidation and liquidity shocks.
2.3.1 Bitcoin’s short-term plunge: a safe-haven asset or a risky asset?
Although Bitcoin is regarded as digital gold by some investors, the impact of this tariff has caused its price to plummet in the short term, falling below $92,000 at one point, a drop of more than 10% from its highest point.
In the short term, Bitcoin is still considered a risky asset: due to the increased participation of institutional investors, the correlation between Bitcoin and US stocks has increased. When the market panics, investors often choose to sell Bitcoin and turn to the US dollar and gold.
In the long run, Bitcoins safe-haven properties may increase: if the market begins to doubt the credit system of the US dollar, Bitcoin may regain its safe-haven properties. For example, during the US-China trade war in 2019, Bitcoin experienced a sharp rise and became a safe haven for global funds.
2.3.2 Margin liquidation exacerbates market sell-off
The high leverage characteristics of the crypto market determine the nonlinearity of its price fluctuations. When the market falls, high-leverage long positions are forcibly liquidated, resulting in a waterfall-like decline.
The liquidation volume of the entire network contract market exceeded US$2 billion: Data shows that during the Bitcoin plunge, the liquidation volume of the entire network cryptocurrency contract market reached US$2 billion, of which more than 80% were long positions.
The automatic deleveraging (ADL) mechanism of the exchange further exacerbated market volatility.
Market sentiment is extreme, and panic selling is increasing: As the crypto market is mainly dominated by retail investors, extreme market sentiment has led to panic selling, amplifying the decline. The Fear Greed Index turned from greed to fear within 24 hours.
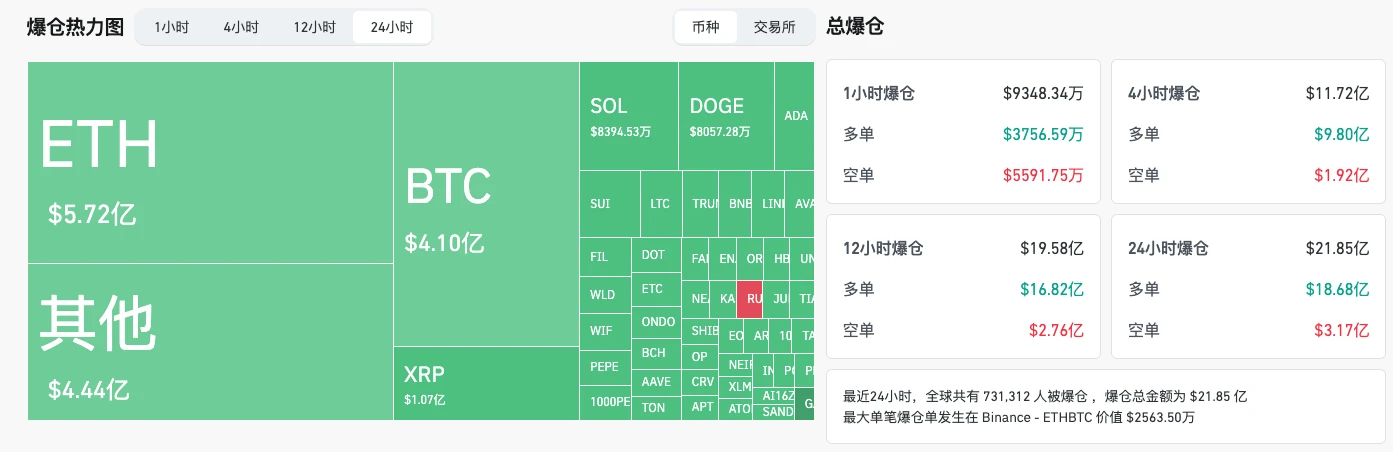
2.3.3 Altcoins fell more
Compared with Bitcoin, the performance of the altcoin market is even worse, with declines generally exceeding 15%.
Liquidity dries up and prices fluctuate sharply: Due to the low trading depth of some altcoins, when the market sell-off comes, there is insufficient buying, resulting in a rapid price collapse.
The DeFi ecosystem has been impacted: Due to the decline in the value of collateral assets in the DeFi ecosystem, a large number of liquidation events have occurred, further exacerbating market panic.
3. How Trump’s policies will benefit Bitcoin in the long run
Although Trumps tariff policies have caused sharp market fluctuations in the short term and even led to a temporary drop in Bitcoin prices, in the long run, these policies may become a driving force for Bitcoin. The main reasons are: the trade war may lead to a depreciation of the US dollar, capital flight drives demand for Bitcoin, and the global trend of de-dollarization accelerates, and Bitcoins status as a reserve asset may be further consolidated. This section will analyze in detail how these factors are beneficial to Bitcoin in the long run.
3.1.1 Trade war may lead to depreciation of the US dollar
Trump’s tariff policies and trade protectionism could undermine the U.S. economy’s growth potential and ultimately lead to a weaker dollar, while Bitcoin typically performs well when the dollar depreciates.
3.1.2 The Federal Reserve may be forced to cut interest rates, leading to a depreciation of the US dollar
If the U.S. economy comes under pressure from the trade war, the Fed may be forced to adopt a looser monetary policy, including cutting interest rates or restarting quantitative easing (QE). The uncertainty of the trade war may lead to slower economic growth, and the Fed may have to cut interest rates to stimulate the economy. Cutting interest rates will reduce the attractiveness of the dollar, leading to capital outflows and a depreciation of the dollar. A depreciating dollar is usually good for Bitcoin
As a scarce asset, similar to digital gold, Bitcoins attractiveness increases when fiat currency depreciates.
For example, when the Federal Reserve implemented large-scale quantitative easing (QE) in 2020, the price of Bitcoin soared from $4,000 to $69,000.
3.1.3 Institutional funds may turn to Bitcoin
Institutional investors seek assets to hedge against a depreciating dollar: Institutional investors may reduce their allocation to dollar assets (such as U.S. Treasuries) and turn to hedging tools such as Bitcoin. In 2021, companies such as MicroStrategy, Tesla, and Square purchased Bitcoin to hedge against the risk of a depreciating dollar. Bitcoin is seen as digital gold: Over the past few years, Bitcoins safe-haven properties have gradually strengthened and its correlation with gold has increased.
As the dollar depreciates, Bitcoin may become a hedging tool for more and more investors.
3.2 Capital flight drives demand for Bitcoin
In an environment of increased uncertainty, capital tends to flow from traditional financial markets to decentralized assets, such as Bitcoin. Trump’s tariff policy may indirectly drive capital into the Bitcoin market.
3.2.1 The trade war exacerbates market uncertainty, and funds seek safe havens
Market uncertainty rises, funds seek safe-haven assets: Tariff policies have caused market turmoil, and many investors may seek safe-haven assets such as gold and Bitcoin. During the US-China trade war in 2019, Bitcoin rose while global stock markets fluctuated.
The attractiveness of decentralized assets increases: In an environment where government policies are unpredictable, decentralized assets such as Bitcoin become more attractive due to their censorship resistance and global liquidity. Funds are no longer limited to gold or US dollars, but will also partially flow into the crypto asset market.
3.2.2 The wealthy class in the United States may transfer their assets to Bitcoin
The wealthy seek tax avoidance and asset protection: If Trumps tariff policy continues, leading to a deterioration in the US economy or increased tax pressure, the wealthy may seek asset havens. Bitcoins global liquidity and decentralized nature make it an ideal wealth storage tool.
Bitcoin halving in 2024 may boost capital inflows: In 2024, Bitcoin will usher in a new round of halving events, and miner rewards will drop from 6.25 BTC to 3.125 BTC. The reduction in supply may push up Bitcoin prices. Combined with global economic uncertainty, wealthy investors may deploy Bitcoin in advance to hedge risks.
3.3 The trend of de-dollarization intensifies, promoting Bitcoin as a reserve asset
Trump’s protectionist trade policies may accelerate the global “de-dollarization” process, and more countries may consider using Bitcoin as a reserve asset.
3.3.1 The global trend of de-dollarization is accelerating
The United States frequently uses financial sanctions to encourage countries to de-dollarize: In recent years, the United States has frequently used the dollar system to impose financial sanctions on other countries (such as sanctions on Russia and Iran).
To circumvent the limitations of the US dollar settlement system, many countries have begun to seek alternatives, such as RMB settlement, digital currency, and Bitcoin.
Trumps policies may strengthen the process of de-dollarization: The trade war may prompt China, the European Union, Russia and other countries to reduce their dependence on the US dollar and accelerate the process of de-dollarization. In 2023, the BRICS countries have begun to study the establishment of a new trade settlement system to reduce their dependence on the US dollar.
3.3.2 Countries or institutions may consider Bitcoin as a reserve asset
The possibility of Bitcoin entering the central banks reserves as digital gold increases: In recent years, some countries (such as El Salvador) have begun to include Bitcoin in their national asset reserves. In the future, if global confidence in the US dollar system declines, some countries may consider Bitcoin as part of their reserve assets to diversify risks.
Institutional investors asset allocation strategies may turn to Bitcoin: In the past five years, institutional interest in Bitcoin has increased significantly, including giants such as BlackRock and Fidelity, which have launched Bitcoin-related products. In times of global economic turmoil, institutional investors may increase their allocation ratio to Bitcoin.
4. Market trend analysis: How will Bitcoin react?
After Trumps tariff policy caused global market turmoil, Bitcoins price trend may experience short-term shocks, medium-term rebounds, and may eventually usher in a long-term breakthrough of historical highs. In this process, the market will be affected by multiple factors such as the macroeconomic environment, the Feds policies, institutional capital inflows, and on-chain data. This section will conduct an in-depth analysis of key support and resistance levels, market sentiment, on-chain data, and market evolution paths.
4.1 Key support and resistance levels: key price levels in the market
Bitcoin has several key support and resistance levels both technically and psychologically. Market movements tend to fluctuate around these important price areas.
4.1.1 Analysis of main support levels
$91,000 (short-term support): This is the support area that Bitcoin initially tested during the decline, and if market sentiment improves, it could become a short-term bottoming area. A break below $90,000 could trigger further market panic and leverage liquidation.
$85,000 (Medium-term Support): This is a stronger technical support level and could be a major area of involvement for institutional money.
If the market reacts negatively to the Fed’s policy, BTC may further pull back to this area to find support.
$70,000 (support in extreme cases): If the market turmoil caused by the trade war continues and risk aversion rises, this key level may be tested. This area will be an important buying opportunity for long-term investors, and a large amount of funds may appear to buy at the bottom.
4.1.2 Analysis of main resistance levels
$105,000: This is an important level that the market is paying close attention to. A breakout could lead to accelerated capital inflows. Institutional investors may test market liquidity in this area.
$110,000 (all-time high): This is a key target that BTC may hit in the bull market, and a breakthrough may usher in FOMO (panic buying). If global funds flow into Bitcoin at an accelerated rate, BTC may form a new price discovery in this area.
$150,000 (forward potential resistance): If Bitcoin enters a super cycle driven by institutional funds, this area may become a new market target.
4.2 Possible market evolution paths: Analysis of BTC’s trends in different cycles
The market trend of Bitcoin may go through three stages: short-term shock consolidation, medium-term rebound, and long-term breakthrough of historical highs. Each stage has different driving factors in market sentiment, capital flows, and macro environment.
4.2.1 Short-term shock consolidation (1-3 months): Market repair stage
Market characteristics
Price range: $80,000 - $100,000
Market sentiment: Panic eases, wait-and-see sentiment strengthens
Macro drivers: Fed policy, market liquidity, institutional buying
Short-term market factors:
Market sentiment is restored and bargain hunting funds are involved: If the $90,000 level stabilizes, market panic may gradually subside and funds will be re-deployed. If the exchanges stablecoin reserves begin to rise, it indicates that investors are ready to re-enter the market.
The Feds policy has become the focus of the market: If the Fed delays the rate cut, the market may continue to fluctuate and wait for clearer signals. If the Fed turns dovish, the market may rebound.
On-chain data monitoring: Fund flow: Bitcoin holding address analysis: If long-term holders (LTH) reduce selling, it indicates that the market has begun to stabilize. Exchange Bitcoin outflow: If a large amount of BTC flows out of the exchange, it means that market confidence has recovered and investors choose to hold for the long term.
4.2.2 Mid-term rebound (3-6 months): Market repair and enter the recovery channel
Market characteristics
Price range: $100,000 - $120,000
Market sentiment: cautious optimism, capital inflows accelerate
Macro drivers: Institutional funds enter the market at an accelerated pace, and the Fed’s policy direction is clear
Medium-term market factors
If the Fed turns dovish, liquidity will improve: If the Fed announces a rate cut or pauses rate hikes, market liquidity will improve and Bitcoin may enter an upward channel. In 2020, when the Fed massively eased, Bitcoin prices soared 1,600%, and history may repeat itself.
Institutional funds deploy Bitcoin, driving price recovery: After the launch of ETF (Bitcoin spot fund) in 2024, institutional demand for BTC may further increase. Similar to 2021, institutions such as Grayscale and MicroStrategy may continue to increase their holdings of BTC.
On-chain data supports the upward trend
Increase in BTC holding addresses: If large BTC holding addresses (whale addresses) increase, it indicates that institutions have begun to buy.
BTC supply on exchanges decreases: Bitcoin liquidity on exchanges dries up, indicating strong buying in the market.
4.2.3 Long-term breakthrough of historical highs (6-12 months): Ushering in a bull market cycle
Market characteristics
Price range: $120,000 - $150,000+
Market sentiment: FOMO (panic buying), funds pouring in
Macro drivers: Global capital seeks safe havens, Bitcoin becomes a global reserve asset
Long-term market factors
As the global trade war continues, capital seeks safe havens in Bitcoin: If the trade war becomes protracted, safe haven funds in the global market may flow into BTC.
After the Bitcoin halving in 2024, the market supply and demand will be tight, further pushing up prices.
Bitcoin market value enters the scope of institutional asset allocation: If the market value of Bitcoin exceeds 2 trillion US dollars, it may be included in the investment portfolios of more institutions around the world. Similar to gold, Bitcoin may become one of the assets allocated by global sovereign wealth funds.
The scale of Bitcoin ETF continues to grow: At present, the scale of BTC spot ETF is still in its early stages and may attract more institutional funds in the future. If ETF funds flow in faster, BTC may enter a new round of super bull market cycle.
4.3 Conclusion: Bitcoin will experience a long-term rise after short-term fluctuations
Summary of market development path
Short term (1-3 months): The market is volatile, with support at $90,000, awaiting the Feds policy signals.
Medium term (3-6 months): Bitcoin gradually recovers to $100,000, and institutional funds flow in at an accelerated pace.
Long-term (6-12 months): If the trade war becomes prolonged, BTC could break through $120,000 and set a new all-time high.
Although Trump’s tariff policy has caused market panic in the short term, in the long run it may accelerate the process of Bitcoin becoming a global safe-haven asset.
5. Conclusion: Short-term volatility, long-term positive trend
Trumps tariff policy has undoubtedly brought great volatility to the global market, especially the cryptocurrency market. In the short term, the price performance of Bitcoin is strongly affected by market sentiment. Bitcoin has suffered a large price correction in the short term, with a drop of more than 10%. However, from a broader perspective, the changing global economy and the long-term impact of Trumps policies may provide support for the long-term value of Bitcoin and drive its price to gradually rise.
Although Trumps tariff policy has caused short-term market fluctuations and exerted downward pressure on the price of Bitcoin, from a longer-term perspective, the core value of Bitcoin has not changed. With the increasing uncertainty of the global economy, the digitalization trend of the capital market, and especially the development of the decentralized financial system, the demand for Bitcoin as a safe-haven asset will further increase, driving its long-term value up.
Investors should pay attention to global economic policies, market sentiment and the technical progress of the Bitcoin network, and make mid- to long-term plans. Although the market may continue to face certain fluctuations in the short term, Bitcoins safe-haven asset attributes and its potential as digital gold will become its increasingly important role in the global economy. As the global economic environment changes, Bitcoin will continue to be an important asset that cannot be ignored in the global financial system.










