In this article, we explore how on-chain liquidity is gradually changing the competitive landscape between decentralized exchanges (DEX) and centralized exchanges (CEX) through technological innovation. From AMM to vAMM, Peer-to-Pool, and then to the evolution of Order Book, these mechanisms provide users with a better trading experience while solving core problems such as slippage, impermanent loss, and price discovery.
We particularly emphasize that deep liquidity is the main factor for CEX to succeed in its competition with DEX. The success of $Trump once again proves that on-chain liquidity is becoming increasingly abundant, and behind it is the increasingly diverse group of liquidity providers. We analyzed the development trend of LP Vault modularization and specialization, and this innovation is providing deeper liquidity support for long-tail assets and mainstream assets on the chain. By analyzing successful cases such as Hyperliquid and Elixir, we show how on-chain liquidity has become a key driving force for the further development of DeFi, and may eventually subvert CEXs dominance in the trading market.
introduction
Exchanges have always been the cornerstone of the capital market, but centralized exchanges (CEX) have always faced many criticisms. First, their operating methods violate the core values of blockchain decentralization and transparency; second, high listing fees, malicious dumping after absorbing a large number of project tokens, and misappropriation of user assets are common. In the past, due to the imperfect on-chain infrastructure, users needed an efficient, convenient and low-cost trading platform, so CEX became the first choice. However, with the gradual maturity of on-chain infrastructure, including the continuous improvement of core components such as automated market makers (AMMs), oracles, high-performance public chains, cross-chain bridges, and security audits, trading activities on CEX will gradually move back to the chain.
DEX to CEX Spot Trading Volume, source: The block
As shown in the above figure, the spot trading volume ratio of DEX/CEX has reached a historical high of 20% in January 2025.
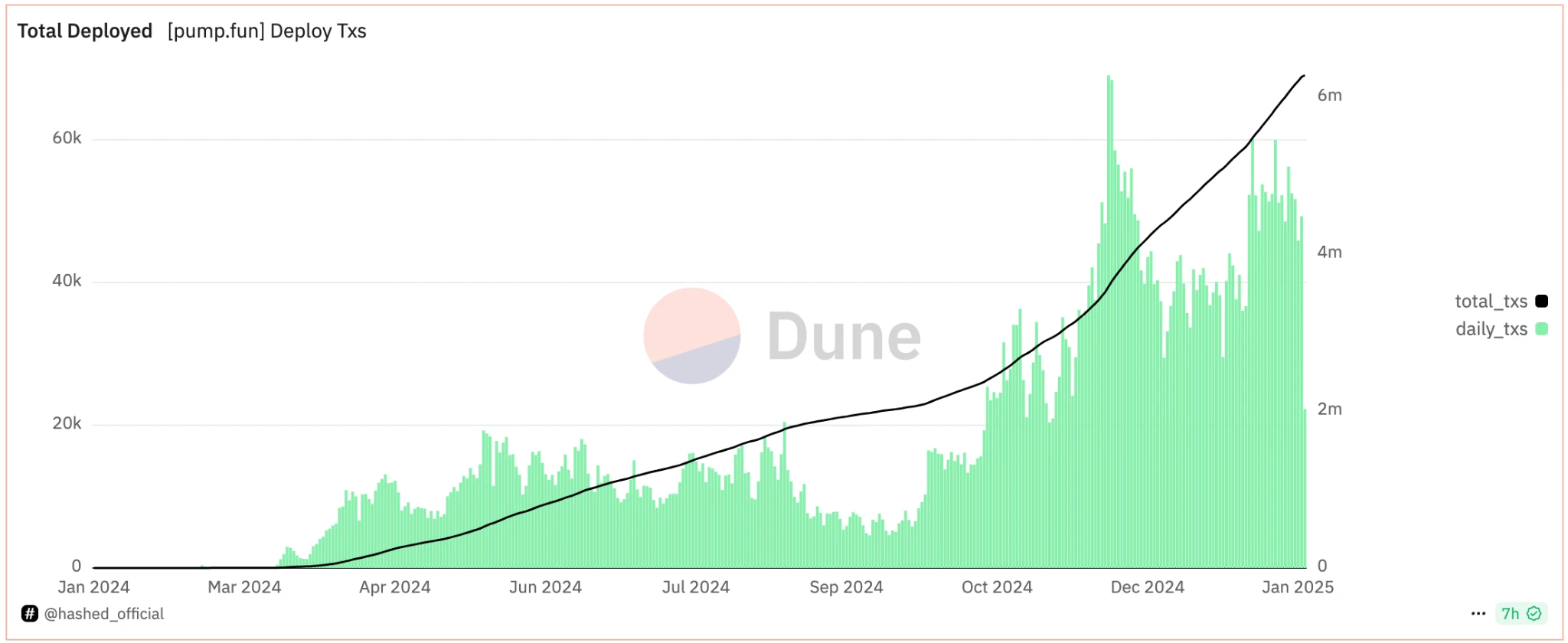
Pump.fun token issuance statistics, source: Hashed
Take Pump.fun as an example. The daily issuance of its on-chain token Launchpad has repeatedly hit new highs. If Hyperliquids achievement of $10 billion in FDV through on-chain Launch was a successful exercise, then the more iconic event was the successful issuance of Trump tokens on the chain. Trump tokens achieved $70 billion in FDV in 24 hours, with on-chain liquidity of up to $700 million, and all of this happened on the chain. More importantly, its token price is less affected by centralized exchanges, which cannot manipulate prices by obtaining free tokens.
In this regard, the founder of Bybit said: The future of Web3 and decentralized trading has arrived. In 2025, we will focus on building an on-chain version of Bybit and increase investment in the user experience of the Bybit Web3 wallet (self-custody), while strengthening our on-chain infrastructure.
On-chain Trading Bot statistics
At the same time, on-chain trading tools are also booming. Cross-platform trading tools based on the chain, such as DEXX, GMGN, Photon and BullX, have occupied a certain market share in the trading track with one-click trading, rich on-chain analysis and other functions. In the $Trump market, these tools took over part of the trading flow, and the trading volume hit a record high. The beneficiaries of this market include not only GMGN, whose market share has expanded rapidly, but Moonshot also topped the US App Store download list on the same day, bringing 200,000 new users in a single day.
In essence, these tools are front-end applications that build a user-friendly liquidity aggregation interface, while also providing features such as Anti-MEV and on-chain analysis, which are not the focus of CEX development. This is also the key to why DEX can intercept most of the traffic. Especially in an era when on-chain asset issuance is becoming increasingly popular, these tools solve user pain points by simplifying the cumbersome transaction process on the chain. Whoever can master the traffic entrance will be able to seize the opportunity to become the next generation of on-chain Binance.
LP Vault mechanism is the key to DEX liquidity
These front-end tools rely on a huge supply of liquidity. The success of $Trump, in particular, shows us the core position of liquidity in the on-chain ecosystem. If you are developing an on-chain DEX, you will usually prioritize building your own LP pool while linking existing on-chain liquidity resources. It can be said that the depth of liquidity directly determines the success or failure of DEX in the competition with CEX. Without a sufficiently supported on-chain liquidity environment, the success of $Trump would be out of the question. As the main on-chain liquidity solution, the LP pool has also undergone many improvements and innovations.
The on-chain liquidity solutions, from AMM, which opened the DeFi Age of Navigation, to vAMM, P2P trading mode, on-chain order book, and then to the product evolution of off-chain order book, have always been optimized around liquidity. These solutions seek the best balance between liquidity, user experience (convenience and security), and cost.
In the AMM era, asset prices are determined based on the formula x * y = k. Since Uniswap V3 introduced range-based centralized liquidity, LPs have been able to finely control the price range of funds, greatly improving fund efficiency and even achieving a thousand-fold utilization rate. However, this model also brings new challenges, such as large price slippage and impermanent losses exceeding LP fees.
vAMM Mechanism
In 2019, Perpetual Protocol proposed a new liquidity solution - vAMM (virtual automated market maker). This solution simulates market depth by using a virtual fund pool. Users deposit stablecoin assets such as USDT into the Vault pool, and AMM uses virtual assets and runs based on the classic x * y = k price curve. Under this mechanism, one users profit corresponds to another users loss, successfully solving the mechanism defect of impermanent loss in traditional AMM.
However, since vAMM does not involve real asset transactions, its price mainly depends on the update of the oracle, and it lacks the pricing ability of real assets. This feature makes it only follow the market price, but cannot form prices independently, which has become one of the important factors limiting its scale expansion. From the perspective of professional market makers, pricing power is one of the key factors to measure whether a mechanism can be successfully promoted, and the shortcomings of vAMM in this regard have also become a bottleneck in its development.
GMX LP Vault Profits
The design of vAMM is somewhat similar to the P2P model. Subsequently, GMX innovatively proposed the Peer-to-Pool liquidity mechanism to transfer trading risks to the overall LP holders. In this model, since the overall traders generally lose more than they gain, GMXs LP Vault, as the counterparty of all traders, can still achieve certain profits. However, although this mechanism theoretically has the advantages of unlimited liquidity and zero slippage trading, its biggest problem is similar to that of vAMM, that is, it cannot discover prices independently. This defect has become the ceiling of its growth and limits its further development space.
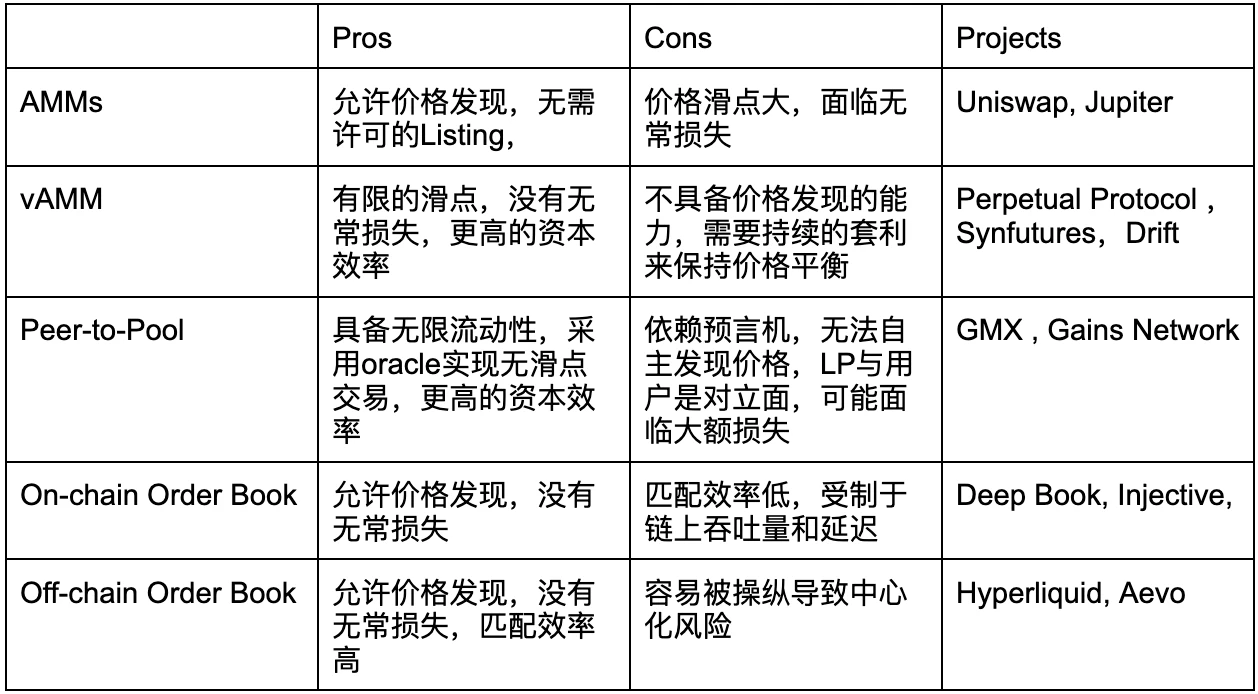
In summary, the above three modes (AMMs, vAMM, P2P) all operate in the form of Vault pools. AMMs have the ability to discover prices independently, while vAMM and P2P, although they solve the problems of slippage and impermanent loss, can only track price indices and cannot set prices independently, which significantly limits their scalability.
On the other hand, the order book model is divided into two types: on-chain and off-chain, and the main trade-off is the centralization risk and efficiency. Taking the full-chain protocol Injective as an example, it provides the best Swap trading experience by coordinating LPs of multiple protocols. Hyperliquid uses off-chain market makers to provide liquidity for the order book, which is similar to the market-making model of traditional CEX. While providing efficient liquidity, the off-chain market-making method also inherits some centralized characteristics.
Diversification and specialization trends of LP Vault
Liquidity is one of the key factors that determine whether a decentralized exchange (DEX) can successfully compete with a centralized exchange (CEX). From AMM to off-chain order books, different mechanisms have made unique innovations in liquidity provision. For example, AMM provides liquidity through token pair pools, vAMM introduces a single asset (such as USDC) pool, and the LP Vault in the Peer-to-Pool mechanism acts as the counterparty to all traders; the on-chain order book uses cross-token pair liquidity aggregation, while the liquidity providers of the off-chain order book have evolved into high-frequency quantitative market makers.
Not only is the form of the LP pool constantly evolving and innovating, the composition of liquidity providers is also quietly changing. According to research by the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), although the LP mechanism operates in a democratic manner, with the emergence of various LP forms (such as AMMs with adjustable ranges and LP Vaults that meet specific functions), liquidity providers are moving towards specialization. Data shows that most liquidity is provided by a small number of mature LPs with professional skills and capital advantages, and their market share has accounted for 65%-85%. In contrast, the participation rate of retail LPs is low, and their yields are significantly lower than those of mature LPs.
LP Vault in Hyperliquid, souce: Hyperliquid
As shown in the above figure, the average annualized return rate of the official LP Vault is 25.81%, but the annualized return rate of the professional HF Vault (High Frequency Trading Vault) has greater potential and broad development space. At present, the liquidity innovation on the chain is making a big leap around the key element of DEX.
In addition to Hyperliquids introduction of off-chain market makers (MM) on the chain, which exponentially improves the user trading experience by combining the high-throughput L1 public chain, there are many innovations based on the LP mechanism that are constantly fermenting. These innovations not only improve the depth and efficiency of liquidity, but also bring users richer functions and better experience, further promoting the development of the DEX ecosystem.
Elixir Workflow, source: Elixir
We noticed that Elixir is leading innovation through a modular LP mechanism. Elixir uses a custom variant of the Avellaneda-Stoikov algorithm to deploy liquidity in decentralized exchange order books. Through these neutral strategies, Elixir is able to provide liquidity for long-tail assets across the entire chain. Users can use this algorithmic platform to become more professional LPs without limiting LPs to a single DEX. Currently, projects such as Injective, dYdX, and Bluefin have been included in its integrated ecosystem.
In Elixirs off-chain components, the system first obtains the order data from the exchange, and the data aggregator verifies the validity of the data and sends it to the verification node. The verification node runs the algorithm to generate orders, and the on-chain audit validator is responsible for auditing the order signature. Subsequently, these orders are sent to the corresponding exchanges for execution.
Compared with Hyperliquid, Elixir provides a more transparent market-making model (MM) due to the existence of on-chain audit nodes. However, the efficiency loss brought about by this transparency is also one of its challenges. Relatively speaking, although Hyperliquids LP Vault is efficient, it lacks scalability, while Elixirs modular LP can provide liquidity for all order books, showing stronger adaptability.
Spicenet Structure, source: Spicenet docs
Elixir is an innovative project that has been under construction since 2021, dedicated to providing a novel and generalizable solution for on-chain order books. Currently, many projects have achieved atomic-level innovations in liquidity architecture. For example, the liquidity networks of Spicenet and Liquorice integrate Solver, Market Maker (MM) and Free Liquidity Pool (NOL), providing global liquidity support with low slippage for order books.
Among them, NOL (free liquidity pool) is essentially the users LP Vault. Users and LPs can deposit funds into different strategy libraries (Vaults) according to their own risk preferences and return targets. These strategy libraries focus on their own unique areas, such as spot trading, futures trading, or cross-book liquidity. In this way, they can alleviate the LVR (liquidity volatility risk) problem when market makers are underpowered, thereby ensuring the stability and efficiency of liquidity.
Liquidity trends
LP Vault is one of the most basic and atomic components of on-chain liquidity and is currently undergoing a transformation of modular innovation. LP Vault integrates multiple front-end DEXs to build a smoother, low-slippage trading experience. Although the traditional AMM model has performed well in the initial liquidity supply of long-tail assets such as Meme due to its simplicity and easy cold start, it is difficult to meet the high standards for mainstream asset liquidity in the current DeFi era. In the process of CEX gradually migrating to DEX, users sensitivity and high requirements for slippage in mainstream asset transactions have become more prominent. The innovation of LP Vault has become the key to solving this pain point. The depth of liquidity directly determines the outcome of the competition between CEX and DEX.
The current trend of on-chain liquidity is that long-tail assets usually rely on AMM LP to provide initial liquidity, and as the market value of assets grows, these assets gradually turn to Order Book for trading. For on-chain Order Book DEX, the liquidity portfolio is becoming more and more diversified. In addition to AMM LP, it also includes off-chain algorithmic market makers built by LP Vault (such as Hyperliquid) or innovative on-chain market makers (such as Elixir). In addition, these DEXs introduce third-party traditional market makers through open APIs to further improve liquidity efficiency.
LP Vault is moving towards specialization and modularization. These specialized LP Vaults not only significantly improve the depth of on-chain liquidity, but also occupy a large share of on-chain liquidity. The innovation of LP Vault brings users a better trading experience, while also providing important support for the continued development of DEX. These advances are jointly promoting the prosperity of the on-chain ecosystem and further narrowing the gap between DEX and CEX.
Disclaimer:
This content does not constitute any offer, solicitation, or recommendation. You should always seek independent professional advice before making any investment decision. Please note that Gate.io and/or Gate Ventures may restrict or prohibit all or part of the Services from restricted regions. Please read their applicable user agreements for more information.
About Gate Ventures
Gate Ventures is the venture capital arm of Gate.io, focusing on investments in decentralized infrastructure, ecosystems, and applications that will reshape the world in the Web 3.0 era. Gate Ventures works with global industry leaders to empower teams and startups with innovative thinking and capabilities to redefine social and financial interaction models.
Official website: https://ventures.gate.io/
Twitter: https://x.com/gate_ventures
Medium: https://medium.com/gate_ventures










