Original source: Shield Chinese Channel
Original editor: SevenUp DAO
This article aims to systematically explain the panorama and competition overview of the LSD track from upstream to downstream, from pledge logic to follow-up deduction and investment opportunities.
The source of the text is Shield Chinese Channel "2023 First Narrative, Ethereum Shanghai Upgrade - Paodingjieniu LSD Ecological Detailed Open Class"
Lecture 1: Who can participate in pledge investment? Talking about the joint pledge model
Jerry:
The theme I shared tonight is - "Who can participate in pledge investment? Let's start with the joint pledge model".
I am Jerry, the current head of Lido CN. Lido is a multi-chain liquidity staking protocol with the core of "Ethereum Staking". In addition to Ethereum, it also supports several public chains such as Polygon. If you want to know more about Lido's news or dynamics, you can follow Lido's official tweet and Lido CN.
1. The basic logic of pledge
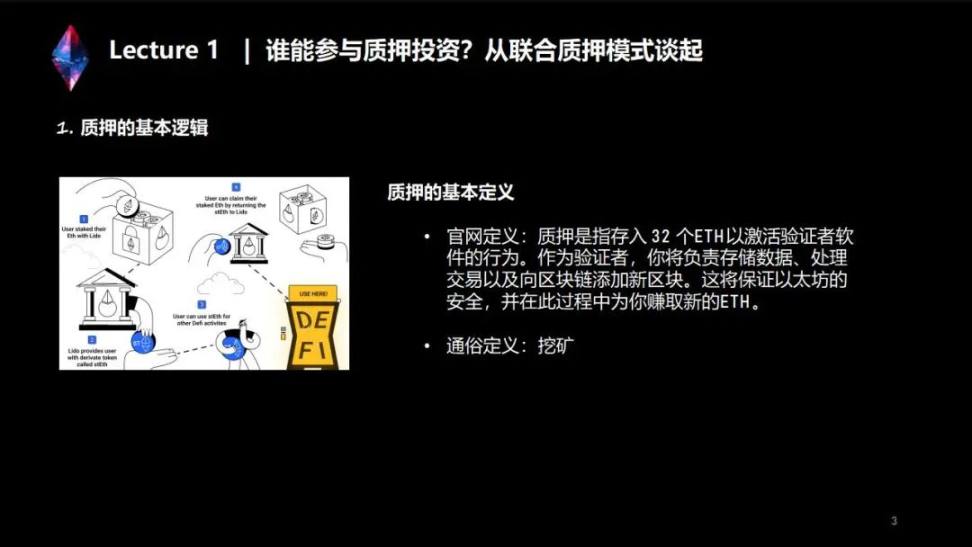
First, explain "what is pledge" - "the basic logic and definition of pledge".
The official website defines it as: Pledging refers to the act of depositing 32 Ethereum to activate the validator software. As a validator, you will be responsible for storing data, processing transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain. This will keep Ethereum safe and you can earn new ETH in the process.
The above is a very official definition, and the easy-to-understand definition is: mining, in the POW era or the current Bitcoin network, miners complete consensus tasks by purchasing or operating computing power equipment, while in the POS of Ethereum In this era, verifiers have replaced the roles or responsibilities of miners, completing consensus tasks by staking Ethereum or running verification nodes, and obtaining certain benefits.
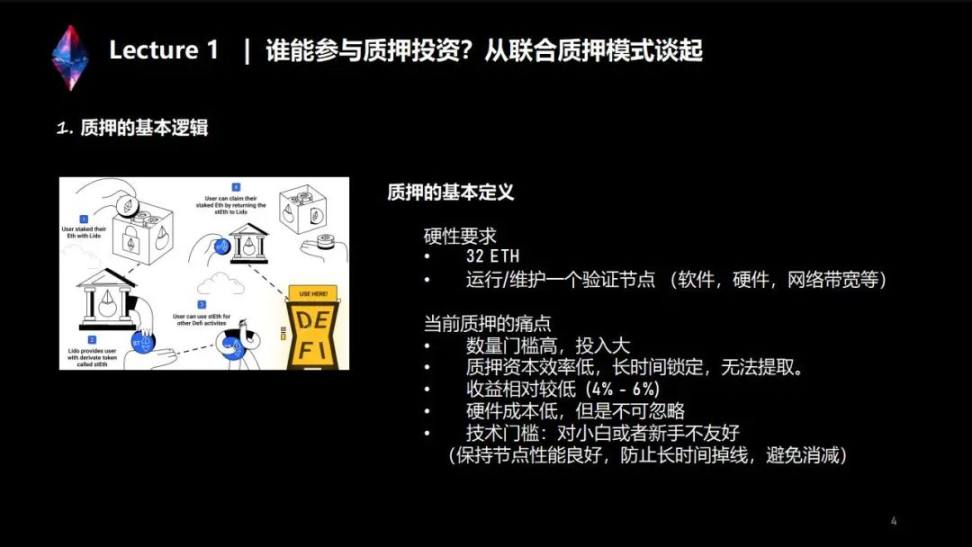
Several important points can be extracted from the "basic definition of staking":
First, if you want to participate in the pledge, you must have 32 ETH, and each verification node needs to deposit 32 ETH before it can be activated.
Second, if you want to run a validator, you need to set up your own infrastructure:
software,You need nodes in the execution layer and nodes in the consensus layer;
hardware,You need to have a computer with good performance and large enough hard disk capacity;
Internet broadband(This will be covered in more detail later in the course).
Through the above rigid requirements, we can summarize some pain points of currently running a verification node:
1. Ethereum has a quantity threshold.It requires a verification node to have at least 32 ETH, which is not a small amount, and the limit of the number prevents many friends who do not have 32 ETH from participating in the pledge.
2. For friends who are already running verification nodes, their 32 ETH and the earnings on the beacon chain are currently completely locked on the beacon chain.Cannot be withdrawn, cannot be transferred.It has been more than two years since the beacon chain was launched, and the ETH pledged by the first node has been locked for more than two years.
3. Earnings.In a bear market, it is only 4% -6%, but in a bull market it may reach 8% or higher. But we have not experienced that time after all, so compared with some other DeFi projects, its returns are relatively low, but at the same time the risks are relatively low.
4. About hardware cost.The current 32 Ethereum investment, compared with the mining machine in the POW era, its hardware input cost is relatively low.
5. Technical threshold or operation and maintenance costs.For friends who want to run nodes, you must at least have some knowledge about computers, such as how to use the command line to interact with nodes; how to keep your nodes online for 24 hours; whether to perform node backup ; If there is a problem with the node, how to troubleshoot and other issues. Another point is to understand the overall mechanism of Ethereum staking, including how its income is calculated, which situations will cause punishment, or which situations will cause slash.
2. Various types of pledge

With pain points, various solutions will emerge in the industry:
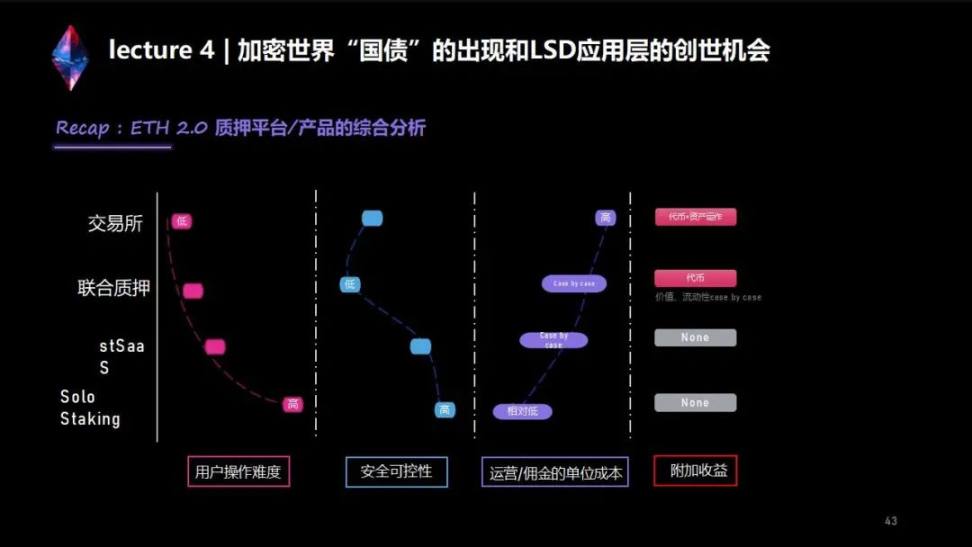
The first type is an independent validator (solo staking); the second type is a pledge-as-a-service platform (stSaaS); the third type is a joint pledge mechanism (pool staking, which can be understood as a joint pledge agreement); The fourth type is the pledge service of the centralized institution.
I think that "existence is reasonable", each type of pledge scheme has different advantages and disadvantages, and can solve the current problems of pledge from different angles.
People who want to participate in staking or evaluate staking projects need to be aware that solutions are not "black and white" and that every solution involves certain trade-offs. What is more important is to start from the problem you want to solve, and see whether the project proposal is sustainable and long-term, and whether it meets regulations and market demand.
Next, I will give you a deeper understanding of the four types of staking by analyzing the pros and cons of each type of staking scheme.
(1) Independent Verifier (Solo Home Staking)

advantage:
advantage:
1. Own all control rights. The control rights mentioned here are actually the verification private key and withdrawal private key of the verifier's own management node. When a node performs a consensus task, it needs to use the verification private key to confirm the signature (similar to the fact that you have completed a certain task, you need to sign your name on the task list to tell others that this task is completed by you), in This private key is often used during node operation. For the withdrawal private key, it corresponds to the withdrawal address. When the pledge reward can be withdrawn, it will be automatically transferred to your withdrawal address. When you want to transfer your reward from this address, you must use it Withdrawal private key.
2. No platform or third party will charge commissions, because you own all the income rights of the nodes.
shortcoming:
shortcoming:
The above-mentioned pain points are all summarized from independent verification nodes, such as high quantity threshold, large investment, low efficiency of pledge capital, long-term lock-up and inability to withdraw, relatively low income, hardware cost and technical threshold, for Xiaobai Or maybe newbies aren't that friendly. The next three types will introduce the concept of a third party or platform.
Generally speaking, the advantage of an independent verifier is that it has complete control and income rights, and conforms to the concept of decentralization. But its disadvantages are also obvious, including high quantity threshold, low pledge efficiency, long-term lock-up and other issues.
(2) Staking as a service platform (stSaaS)

For users who have 32 ETH and want to participate in staking but do not want to build such infrastructure or operate and maintain nodes, stSaaS is a relatively reasonable cooperation model. Its cooperation model is that the user provides 32 ETH, keeps the private key for withdrawal, and the pledge-as-a-service platform helps the user operate and maintain the verification node and keep the verification private key of the node, and finally charges some commission.
shortcoming:
shortcoming:
1. The quantity threshold is still 32 ETH; 2. Your 32 ETH are still locked for a long time and cannot be transferred; third, you need to distinguish the operation and maintenance capabilities of the platform, because the verification private key is controlled by the platform. The benefits you can get depend on the operation and maintenance capabilities of the platform; the last point is that if you want to quit the verification node service, you need the platform to use its verification and sign the withdrawal agreement, so the platform has the right to terminate the service to some extent.
(3) Pool Staking

If you don't have 32 ETH, what should you do if you want to participate in the pledge? One way is for everyone to gather together, one for you, one for me, and make up 32 nodes, and let the third-party service provider help to operate and maintain nodes; After collecting enough 32 ETH, deposit it into the pledge pool. The pledge pool will deposit the user's ETH into the Ethereum pledge contract, activate the verification node operated by the third party, and manage the withdrawal private key through the contract or multi-signature mode. In this mode, the pledger can pledge any amount of ETH, such as 0.01, and then enjoy the benefits, only need to pay some commissions, but do not have any private key.
There are two ways for nodes to join the pledge pool protocol: the first is the DAO whitelist mechanism, that is, professional node operators voted by DAO join these network protocols to help operate and maintain verification nodes; the second is Similar to the mortgage system, among the 32 ETHs corresponding to each verification node, the operator needs to provide 16/8, and then match the remaining half from the pledge pool to form 32 ETHs.
Its advantages are:
1. There is no quantity threshold, 0.1 ETH (or even less) can participate;
2. There is no technical threshold, and the operation and maintenance work is left to the person who runs the node;
3. The risk of pledge can be further dispersed through the pledge pool. The verification node group of this pledge pool will include a variety of node clients, geographically and hardware devices are also diverse. It can be understood that the ETH you pledged is actually scattered on multiple nodes. If If a node is punished or slashed, it will have little impact on your pledged Ethereum.
4. Joint pledge agreements usually issue their own LST tokens (Liquid Staking Tokens), which represent the staker's pledge share. This kind of token can be circulated in the secondary market. If there is good liquidity, your pledged deposits and rewards can be circulated at any time without locking, because pledged deposits and rewards are reflected in LST tokens. This kind of token can be well circulated in the secondary market, so you can sell LST tokens to cash out the pledge at any time without waiting. In this way, a kind of "soft exit" is achieved. Moreover, some LSD tokens can also be used to participate in DeFi projects. In addition to obtaining pledge income, you can also get some additional rewards, such as providing liquidity, such as mortgage LST tokens for loans, so that the utilization efficiency of assets becomes very high. (Note: This only represents the re-pledging method that exists objectively, and does not constitute investment advice. Please carefully consider the risks)
The disadvantage is still from the perspective of private key management, the current pledger does not own any private key. Later we will also explain how protocols like Lido solve such problems.
(4) Centralized organization pledge service

shortcoming:
shortcoming:
These institutions provide staking services, and the transparency may be reduced. Users need to fully trust these institutions, because for users, this kind of service is a kind of "black box". Users cannot determine whether these institutions are actually staking their ETH, nor can they determine the status of commission charges. For users who use Lido for staking, the Lido protocol will charge 10% of the staking reward as a commission. These centralized platforms may charge a higher commission, such as 20% or 25%. Even the commission collection of some platforms is unknown.
In addition, compliance issues also need to be considered. Centralized exchanges have a large amount of ETH reserves, which may be used for quick withdrawals, that is, when users want to withdraw funds, the institution will first borrow these reserves to meet the needs of users, and then transfer them from the Ethereum beacon Withdraw their Ethereum back on-chain. This method is completely "black box" for users, and there are certain compliance risks.
Finally, although these institutions also issue tokens like LST, the contract authority is owned by the institution.
3. Detailed explanation of the joint pledge model represented by Lido
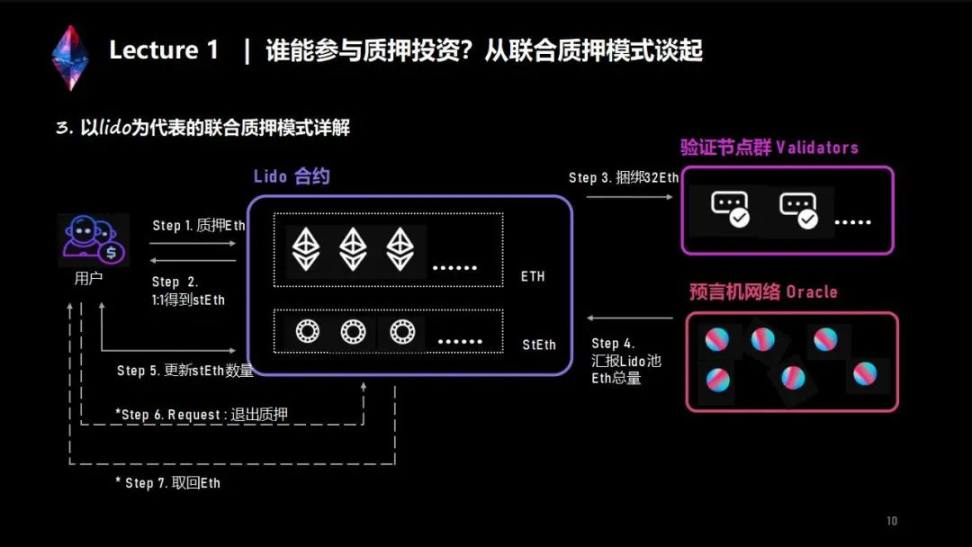
Lido is a decentralized liquidity staking protocol that can be classified as a joint staking category.
First, let's take a look at the entire workflow of Lido, and then divide the workflow into several small fragments for an in-depth analysis.
Step 1: The user pledges ETH through Lido.
Step 2: The user gets 1:1 stETH.
Step 3: Lido integrates the fragmented ETH into 32, and uses it to activate the configured nodes.
Step 4: Rewards, Lido will use the oracle machine to report the total amount of ETH on the current beacon chain every day, and summarize the total amount of ETH held by Lido
Step 5: Use the formula to update the amount of stETH on each staker's address
Step 6: Exit, after Shanghai is upgraded, the pledger can withdraw from the pledge
Step 7: Wait for Lido to process and get back ETH.
Next, let's go from one to seven and look down step by step to see some details inside.
Step 1: Pledge ETH - the market volume of pledge and liquidity pledge
The goal of Lido is to allow more people to participate in the pledge, to simplify and equalize the pledge, so that more users can participate in protecting the network security of Ethereum. This involves the market volume of pledge and the market structure of liquidity pledge.
Market volume of overall staking activity:
In terms of horizontal comparison, the current total amount of Ethereum pledged is about 16.9 million ETH, with a scale of 27 billion US dollars. The pledge rate is only about 14%, and the pledge penetration rate is actually very low. From the picture on the left, we can see the pledge rate of some other POS public chains, such as Solana reaching 70%, BNB Chain reaching 97%, Avalanche reaching 64%, Cosmos hub reaching 62%, Polygon is relatively low but can reach 40% % .
There are certain reasons for the current low pledge rate of Ethereum: one is that withdrawals are currently not available; the other is that the entire pledge process is still systematically imperfect, so many people have the intention to participate in the pledge, but they are still waiting to see . With the improvement of the industry ecology and the upgrading of Shanghai, the amount of pledges on Ethereum will usher in a considerable increase. I personally expect the Ethereum pledge rate to reach 30%, and the optimistic case may reach 40%. If the price of ETH can return to a high level, then the scale of the pledge market can also be expected to reach 100 billion.
But it must be stated that this process cannot be completed within a short period of a few months, not overnight. The rules of Ethereum limit the number of nodes that can join the network or exit the network every day. It is positively related to the number of verifiers in the whole network. The more verifiers in the whole network, the more verifiers allowed to enter the network every day. more and more. This in disguise limits the number of ETHs that can be activated every day: at present, a maximum of more than 50,000 ETHs can be activated per day, and about 18 million ETHs are newly added to the network in a year. Assuming no node exits, a maximum of 18% can be added in a year.
What is the current structure of the liquidity staking market?
The liquid staking discussed here refers to the "liquid staking agreement", that is, you deposit ETH, the platform or agreement gives you liquid staking tokens, and fully deposits your ETH to the pledge deposit contract to activate validator participation This protocol for consensus tasks. There are a lot of players in the current liquid staking protocol, and there are many new players who have recently launched or are about to launch. Liquidity staking agreements account for about 40% of the overall staking market, and Lido's current liquid staking market share is about 75%.
The market share of liquid staking is expected to continue to rise. There are several reasons: first, staking income is a real income; There is a view that it can be regarded as the basic income of DeFi in the future, helping users to obtain superimposed income (DeFi income + pledge income); finally, a little advantage compared to the cliché is that there is no pledge threshold for the liquid staking agreement, anyone Anyone can participate, especially those who can absorb users who do not have 32 ETH.
Step 2: Get stETH—analysis of the value and liquidity of stETH
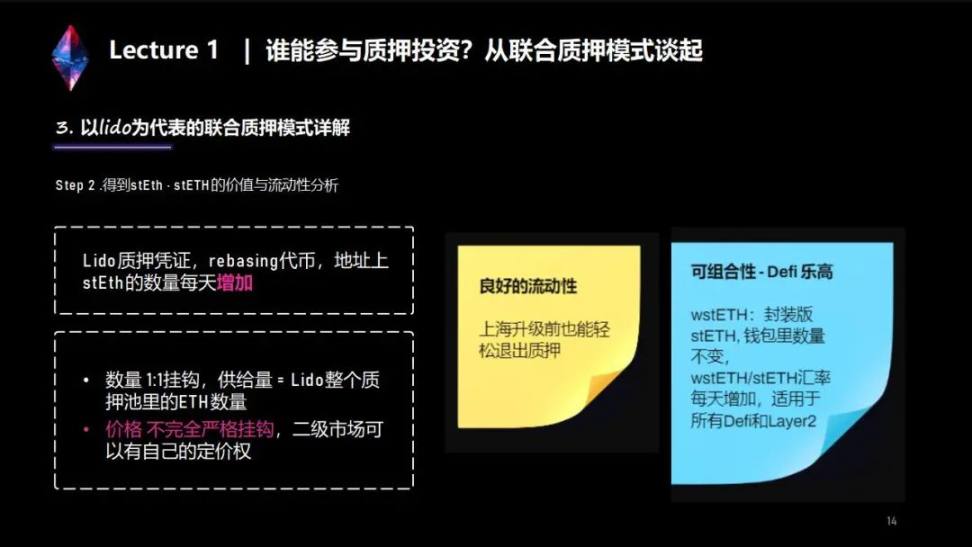
stETH is Lido's pledge certificate, which has the following characteristics:
First, it is a rebasing token. Translated into Chinese, rebasing can be interpreted as "rebase", which means that the tokens you hold have a characteristic: the amount of stETH on your address will automatically increase every day, and the extra part is actually your pledge of the day The income is reflected, but there will be no related transactions with reward distribution on the address.
Second, the supply of stETH is exactly equal to the amount of ETH in the Lido pledge pool, which is a 1:1 backup.
Third, when you pledge, Lido will send you 1:1, but the secondary market has the pricing power of stETH, and there may be some discounts or premiums on stETH, depending on how the market sets prices, which is related to Lido itself. A protocol of 1:1 is irrelevant.
Fourth, stETH has relatively good liquidity, and pledgers can smoothly withdraw from the pledge through the secondary market before the upgrade in Shanghai. For example, the current exchange rate of stETH to ETH is 0.9999, which is a very low discount only in case.
Worthy of attention is wstETH, the packaged version of stETH. Holders of wstETH can also have the same pledge income as stETH. For example, if stETH is 5% per year, then wstETH holders will also get 5% per year. But the amount of these wstETH in the hands of holders will not change. The 5% income is reflected in the exchange rate of wstETH to ETH, and the exchange rate will increase every day, so if you hold wstETH, you will find that your price against the legal currency is getting higher and higher, and more and more valuable.
Both stETH and wstETH have good composability, similar to the attributes of DeFi Lego, and there are currently two mainstream ways to play on the market:
The first way to play is to provide liquidity under Curve balance. When you get a part of the pledge income, you will also get LDO rewards. The overall income will normally be higher than the income of holding stETH alone.
The second method is borrowing. Currently, many platforms such as AAVE and Maker DAO support stETH or wstETH lending. In the high-efficiency mode of the V3 version that AAVE recently launched on the mainnet, the loan rate of wstETH can be as high as 90%. Based on this, it is not difficult to imagine that borrowing can be derived into a cyclical pledge method to further increase the overall pledge income. There are also projects (such as DefiSaver, InstaDapp, Oasis.app, IndexCoop) that have made recurring pledges into a product, allowing users to complete recurring pledges with one click.
A brief introduction to "circular pledge": it refers to the user mortgages stETH to AAVE V2 to lend Ethereum. Out of ETH, and so on. In this mode, a leverage of about 3.2 times can be obtained, and in the high-efficiency mode of AAVE V3, it can even reach a maximum leverage of 10 times. But you must pay attention to the risks in the revolving loan, including but not limited to the discount risk of stETH and ETH. If there is a large discount, users may be liquidated. Although this situation is an extreme event, users still need to do more research and consider it carefully.
Finally, I would like to talk about the imagination of liquid mortgage tokens.
I often think, is it possible that there are some things that "before using ETH to complete, and then stETH can do it for you"? For example, new projects need to provide liquidity. The current mainstream approach is to open a trading pair related to ETH on a decentralized exchange. Is it possible to use stETH to initialize this liquidity, so that the liquidity provider can still get a part of the pledge income, why not?
Step 3: Bundle 32 ETH Lido contract rights management and node management

There are two aspects worthy of attention in this step: the first is the management of contract authority, and the second is the management of nodes.
(1) Contract authority management
Lido's relevant contract permissions are managed using the Lido Dao Aragon on-chain voting system:
At present, anyone can initiate a vote. The voting period lasts for three days. You can vote freely in the first two days. In the last 24 hours, you can only vote against it, or vote for it instead of against it. This two-phase approach, similar to a timelock, prevents this lightning governance problem. Whether it is a contract upgrade or a parameter update, it needs to be voted on the chain first, so Lido's contract authority is not in the hands of a few people or multi-signatures, but in the hands of the entire LDO holder.
Some people may worry about the security of Ethereum pledged in Lido. This involves the management of the withdrawal private key. After July 2021, all verification nodes' withdrawal private keys point to a contract address controlled by Lido DAO. Therefore, the upgrade of the contract can only be executed after voting on the Aragon chain. Its security is guaranteed, and the possibility of the withdrawal private key being hacked is very small.

(2) Node management
Carrier:
In terms of node management, Lido currently has 29 whitelisted node operators (organizations have merged their businesses). The 29 operators include the development teams of Prismatic Labs, ChainSafe, and Nethermind, which are Ethereum clients.
Node shares:
At present, the share of each node does not exceed 2% of the pledged amount of the entire network. The nodes are more like a node alliance, based on the Lido framework for node maintenance, they have enough autonomy (such as the choice of client use, the choice of MEV repeaters, etc.).
Whitelist mode:
At present, we can see that Lido has adopted a whitelist mode. In this mode, you must first apply to join a node such as Lido, and then Lido has a team in charge of node selection to screen and finally provide this candidate list. Finally, let all DAO or LDO holders vote. If the vote is passed, you can enter the Lido network.
Screening process:
1. Due diligence, no white label operators: (the node behind it is not your own entity)
2. There is no connection between the law and the reality: there is no legal or physical connection between nodes or operators. A good example is BlockDaemon and AnyBlock. They are treated as one operator after the business merger .
3. Geographical and judicial decentralization: Lido hopes to have some node operators on a larger geographical scale (seven continents or all over the world), which are geographically dispersed enough; Some countries directly shut down the entire Lido network to the verification nodes. In this case, the only way to minimize the impact is to make it sufficiently decentralized.
4. The share of node operators < 1% of the total pledged amount: Lido has a principle that after Shanghai is upgraded, the share of each node operator should not exceed 1% of the total pledged amount of the entire network.
5. Diversification of node operation methods: For example, some people may choose cloud service (cloud service), some people will build their own computer rooms, and some people will choose the way of hosting machines. Lido wanted to diversify its operations so that one type of operation had the least impact.
6. Diversification of clients: Lido released the usage of current clients in the fourth quarter, and the diversification of clients in the Lido consensus layer is actually better than that of the entire network.

The current whitelist node management mode prevents nodes from joining Lido's network without trust, and Lido is also committed to improving this. Some time ago, the V2 version announced by Lido introduced the concept or structure of "stake routing", which is to introduce this kind of structural adjustment for nodes that do not need to be trusted.
Pledge routing: use a modular approach to isolate and manage node groups, making Lido an aggregator of verification nodes. Based on the pledge routing, everyone can design or develop the corresponding node module, as long as the DAO passes the vote, it can go online.
Recently Lido is testing the integration of Obol and SSV's DVT. Some will ask the question: Which DVT technology will Lido end up using?
This modularity or staking routing already gives a good answer. If the DVT technologies of both parties are good enough, Obol can apply for a DVT module of its own, and SSV can also apply for a pledge module of its own. In this way, the degree of decentralization of Lido will be further strengthened. Not only DVT technology, developers can also design such node modules based on this mortgage or on-chain reputation system. Finally, through this combination of multiple modules, Lido can be further decentralized and at the same time strengthen the Lido network. elasticity.
Step 4/5: Reward Generation and User Reward Distribution Issues

1. Source of income
There are currently two sources of income for pledgers: one is the income of the consensus layer, and the other is the income of the execution layer.
The income of the execution layer is the priority transaction fee or the reward of MEV; the income of the consensus layer is the amount of additional issuance of ETH.
For the consensus layer, as the pledged amount of the entire network increases, the income of the consensus layer will decrease; for the execution layer, if Lido-related verification nodes generate blocks, they will get priority transaction fees other than EIP 1559, and There may be incentives for MEV. At present, Lido will assign all the rewards of these two parts of the execution layer to an address, and re-pledge all the balance on this address to the Lido protocol at a fixed time every day, allowing users to share this income, which currently accounts for approximately Lido pledges 20% of user revenue.
Regarding the benefits of MEV, Lido has developed a framework for MEV rewards, and each verification operator abides by this framework to make the rewards of MEV transparent enough. If a verification node produces a block, it can also go back and find out how much MEV rewards it has obtained.
2. Distribution of proceeds
When Lido distributes income, there is an oracle network. The oracle network will summarize the balance of Lido-related nodes on the beacon chain at around 8:00 Beijing time to obtain the total amount of ETH in Lido's entire pool, thereby updating each The amount of stETH of the staker.
So why do we use oracles?
Because the balance status of the current beacon chain cannot be directly synchronized to the execution layer, a third party needs to be introduced. The introduction of a third party will cause some trust issues, so the Lido community is also discussing the use of ZK, that is, zero-knowledge proof technology to optimize the oracle level so that it does not require trust.
3. User balance formula
When a user pledges, for example, pledges an ETH, the Lido contract does not record the pledge of an ETH, but immediately calculates the pledge share that the user will get when he pledges an ETH, and records it in the Lido contract. Therefore, after the oracle sums up the total amount of ETH in the pool every day, it will update the user's balance according to this formula. When the user opens the wallet after nine o'clock every day, you will find that your stETH has changed. By calculating the pledge share, you can get the latest amount of stETH.
Step 6/7: Regarding redemption of ETH after Shanghai upgrade

At present, everyone can already "redeem" your ETH, through unofficial forms, through the secondary market like Curve, and exit the pledge by directly converting stETH into ETH or other tokens.
Lido has released some designs for withdrawals, which will be launched after the upgrade in Shanghai. In the official design, the upgraded withdrawal module in Shanghai will be divided into two modes:
The first mode is called the Turbo mode, which can be understood as a regular mode. The user initiates a withdrawal, and within a few hours or a day or two, Lido will exchange it for the user at a ratio of 1:1 by obtaining enough ETH. into ETH, users can get back their own ETH.
The second mode is a mode called Bunker. The Bunker mode is designed to protect the interests of most stakers in extreme cases. The calculation of the Slashing mechanism is very complicated and takes a while to determine. Based on this, if there is a large-scale Slashing (Lido's current network has been running for more than two years and has not encountered any Slashing), the pledger's withdrawal function will be suspended. Lido needs a certain amount of time to calculate these losses, and finally the stakers will jointly bear this part of the loss. Lido will turn on the Bunker mode to prevent some pledgers during the Slashing period from applying for withdrawal immediately because they can obtain information on the chain first or obtain information first, avoiding the identification of this loss, and this loss will eventually be apportioned to other pledgers. would lead to some injustice.
Lecture 2: Who can become a verification node? Another possibility brought by stSaaS
Kenway:
I'm the co-founder of XHash. The main business of XHash is Ethereum POS non-custodial pledge service, which mainly serves customers who are willing to participate in Ethereum pledge and create Ethereum consensus.
Let's explore in this lesson - who can be a validator? Another possibility brought by stSaaS.
secondary title
1. "Rights" - what are the benefits?
The first is to contribute to the decentralization of the Ethereum ecosystem. Because you are a solo staker, your voting rights and the right to generate blocks are all in your own hands, and the centralization of the validators of the entire Ethereum will become decentralized, which contributes to the decentralization of the entire Ethereum ecology contribute.
The second is to be able to capture all the benefits. Because I didn't find a third party to cooperate with, let them collect part of the handling fee. From a more technical and low-level perspective, let’s talk about the parts of the proceeds in the staking process:
The first is that the bottom layer is divided into two parts: one part is called the execution layer revenue, and the other part is called the consensus layer revenue.
The income of the execution layer is that if your verifier is selected to produce a block, the fee of the entire transaction in this block will be obtained, that is, the Transaction Fee in the second line of the first row on the left.
The benefit of the consensus layer is that even if your validator is not selected as a block producer, you can still vote on the blocks on your related chain. As long as you correctly participate in these votes, you can get a tiny consensus layer income. Although this income is relatively small, it will occur every four minutes, and the accumulation will account for the majority of the entire pledge income.
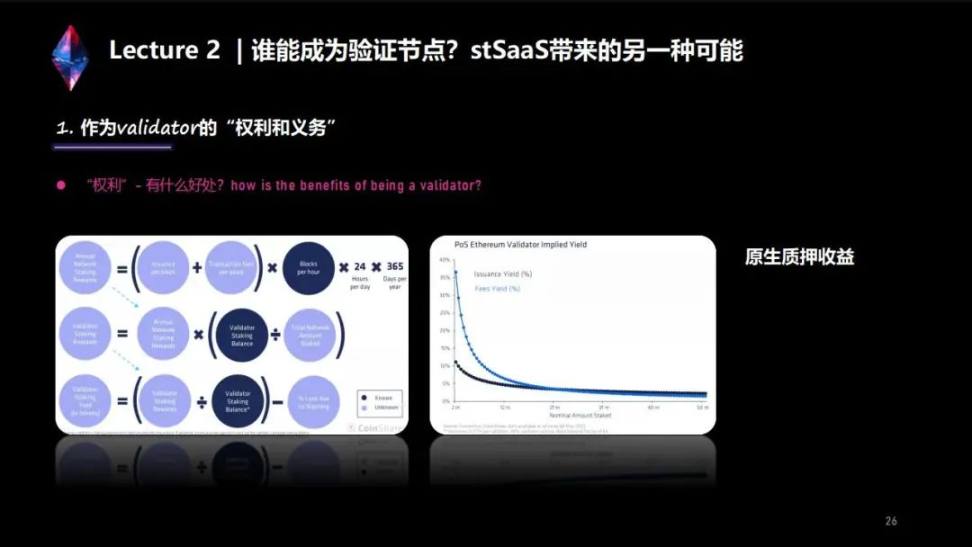
From the formula we can see:
1) Consensus layer income (Issuance) + execution layer income (Transaction Fee) = all income in a block, all income in this block multiplied by the number of blocks produced each year, is the participation in the entire network every year Staking rewards (Annual Network Staking Rewards).
2) After this income is substituted in, look at the ratio of your Validator to the entire network income, that is, your Validator Staking Balance (for example, you only have 32 ETH) divided by the total number of pledges on the entire network (Total Network Amount Staked) is your ratio; the ratio multiplied by the annual network staking rewards (Annual Network Staking Rewards) is your validator rewards (Validator Staking Rewards).
3) Divide the profit (Validator Staking Rewards) by a principal you pledged (Validator Staking Balance), which is your annualized rate of return (Validator Staking Yields).
But at this time, there may be some losses: such as the loss caused by offline time or the loss caused by Slash. Subtracting this percentage gives you the annualized percentage of a validator's earnings in a year.
secondary title
2. "Obligation" - What Should a qualified Validator do?

Being a solo staker comes with some obligations - you run your hardware, ie run your node. There is a hardware requirement.
Hardware requirements: The client needs an 8-core CPU, about 32 G of memory, and a 2 TB solid state drive. This is just a basic requirement. For more stability, you need to increase the hardware configuration. In reality, the required hardware configuration is often much higher than these.
Skills: First of all, you must understand what Ethereum pledge is. In the process of generating these pledges, you need to operate some GUI programs and some command line programs. You must understand these basic operations.
Network: It is necessary to ensure that the nodes are online, which requires a relatively good network. According to current observations, maintaining normal node synchronization may require a network bandwidth of 10 megabytes, and it must be kept online all the time. If you are a solo staker, such as using your own server at home, you need to have a relatively stable network. But in most cases, this kind of home network may not be so stable, there will be some cases of disconnection, and sometimes the disconnection time will be longer, which will affect your online rate. Once your online rate is affected, Your yield will also be affected.
Power supply: Because the server needs to be online 7*24 hours, the power supply must be reliable. If possible, it is best to configure a UPS to ensure the online rate. Another situation is that if the node is writing the database or writing some software on the hard disk when the power is off, problems may occur. If it is restarted after the power outage, it may not be able to re-synchronize. It will take some time to re-synchronize, and the time may decrease. It is relatively long, according to the current situation, it may take two to three days to actually synchronize one.
Client upgrade: Because the client will continue to release new versions, and the Ethereum network will continue to have hard forks, you need to continue to pay attention to the upgrade of these clients, so as to normally upgrade your execution layer client and consensus layer client end. For MEV, if you want to get more MEV income, you need to configure multi-party MEV-Relays, access some reliable and relatively stable MEV-Relays on the network, and maximize the revenue of the relay. There is a problem of technical difficulty and time and energy.
secondary title

1. Basic definition of stSaaS
If some friends have 32 ETH and want to participate in Ethereum staking, but do not have the time and energy to operate, then Staking as a Service (stSaaS) may be a better option. By definition, it is a hosting service for nodes. Customers need to go to the Ethereum official website to download the pledge key generation program, and generate two keys—one is the private key for withdrawing coins, and the other is the private key for pledge.
After generating these private keys, you need to keep your private key for withdrawal, that is, the corresponding mnemonic, and pledge 32 ETH to the deposit contract of Ethereum.
Finally, the pledge fee needs to be handed over to the stSaaS operator, and a certain service fee should be paid to the operator. There may be several charging methods for service fees, such as monthly fees, fixed monthly fees in US dollars; most of them charge a percentage of revenue as fees.
secondary title
2. stSaaS: trade-off of controllability and node operation obligations
Ethereum will generate two keys during the pledge process.

One is the coin withdrawal key, which is the corresponding mnemonic phrase. As long as you protect your mnemonic phrase, your coin withdrawal key will not be leaked, and only this mnemonic phrase can store your The pledged principal (that is, 32 ETH) is withdrawn. In the process of generating your pledge private key, you can also directly specify an ETH withdrawal address. Once specified, this withdrawal address cannot be modified, that is to say, you can only mention this withdrawal address when withdrawing , which will ensure maximum security.
The pledged ETH will be visible on your validator. Your consensus layer income can now also be seen on the validator. After the upgrade in Shanghai, the entire network will periodically select all verifiers. If your verifier is eligible—the so-called eligibility means that you have specified a withdrawal address, then the network will go to the round-robin Select these verifiers, and transfer the income on your consensus layer to the withdrawal address you specified. According to the current verification time, this process is estimated to be rounded in about five days, which means that the income of your consensus layer will be automatically mentioned to the withdrawal address you specified in about 5 days. But this is only after the upgrade in Shanghai, and in the current situation, neither your principal nor the income on the consensus layer can be withdrawn.
The other one is the pledge key. Why does Ethereum officially separate the withdrawal key from the pledge key? Because the pledge key is going to fulfill the verifier's voting, block production and other rights, it needs an online Key. Separating the withdrawal key from the pledge key can ensure that the withdrawal key is offline and in a state of not being connected to the Internet, ensuring security to a greater extent. The pledge key needs to be online all the time to fulfill the rights of the verifier, but the pledge key does not have the right to withdraw ETH, he only has the right to execute the verifier.
The withdrawal key is separated from the pledge key, giving these stSaaS service providers a possibility—as a solo staker, you only need to hand over the pledge key to these pledge service providers, and the service provider will start the node for operation and maintenance. Compared with solo stakers, finding stSaaS service providers is a less secure solution. Because the pledge key is given to the service provider, but this transfers the operational obligations and the risk of punishment to the verifier. If you choose a not-so-good pledge service provider, you may suffer losses. For example, the loss of the verifier caused by the offline server, or his poor operation, or even the problem of double voting, will bear the risk of a slash. Therefore, stSaaS has certain risks compared to solo staking, so choosing a safe and reliable pledge service provider is a very important issue.
Another question is, as a supporter of Ethereum, is it better to choose a top ten service provider, or to choose a service provider with better quality, but maybe not so high in the ranking?
This issue has also been discussed a lot in the entire Ethereum ecosystem. According to the current consensus in the industry, it is a better choice to choose a company although there are not many nodes and the ranking is relatively low, but its own pledge service is excellent, that is, the quality is guaranteed. Because this can achieve a greater degree of decentralization of Ethereum's pledgers.
3. Ethereum official website: What to consider to pick a atSaaS provider
1. Open source: Open source, that is, some necessary programs, such as the fast pledge program that may be developed, is it 100% open source, if it is not open source, it may steal some of your pledge private keys, etc., causing certain risks ; If it is open source, the degree of trust is higher.
2. Audited: For example, whether the code for his profit distribution and some background operation codes of the entire pledge have been audited. If there are some large audit companies, it will be safer.
3. Bug bounty: Is there an open mechanism that allows others to report bugs? If there is such a mechanism, this service provider may be a more trusted service provider.
4. Battle tested: Is there a reliable and stable pledge service provider that has been in operation for a long time and has been proven by time.
5. Self custody: Do you really pledge by yourself? Because there are many white-label pledge service providers on the market. They don’t really act as validator nodes, but rent other people’s servers, and he collects part of the income from them. Can't choose.
6. Permissionless: Is it permissionless, that is, he has not done some KYC audits, and some specific customers cannot access it, because Ethereum also emphasizes the feature of consensus without permission and anti-censorship.
7. Diverse client: The diversity of pledge nodes, you can take a look at the pledge nodes behind the service provider. Because everyone knows that now each node actually has multiple development teams working on it. If everyone uses the same mainstream client from the same development team, if there is a problem with this client on the network, you can It may lead to the collapse of the entire Ethereum network. However, if two or three development teams are selected as clients, it may greatly increase the diversity of clients and make a certain contribution to the security of the entire Ethereum.
Lecture 3: The potential crisis and approach of the pledge model
Robert:
secondary title
A quick warm up: Summary of various staking methods
Now there are mainly four pledge methods, and there are mainly three core logics.
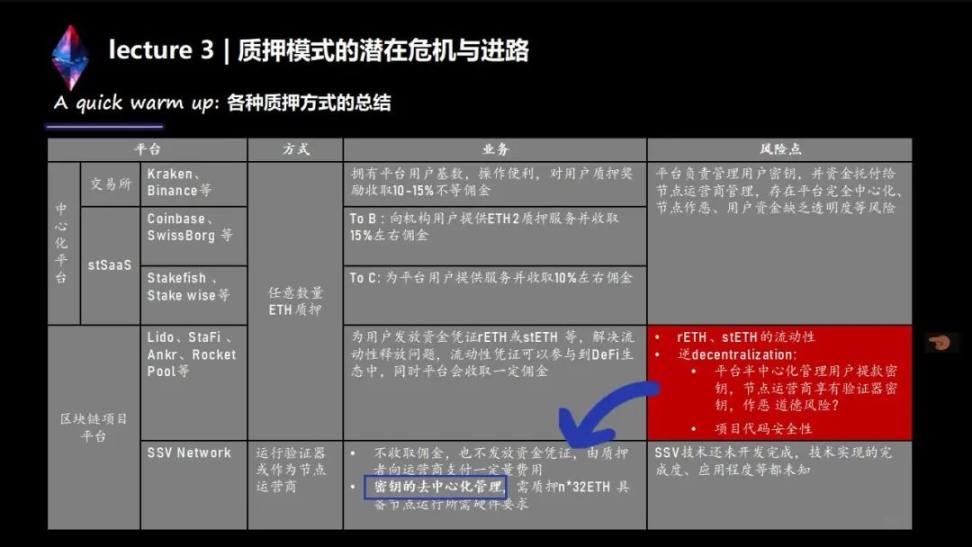
1. Exchange model: The exchange model, such as Kraken, has been banned. The main thing is that you give them the coins, and then they help you to do the pledge. After the pledge, you will be given a certain amount of profit. The middle profit often has a false high and a high value, and its real income may not match its actual value. Scaled earnings are sent to you, so it's very opaque. My position is actually very disapproving of this centralized pledge method. Regarding the judgment of the SEC, I personally think that there should be no major problems, and it is a relatively fair judgment.
2. Similar to the trust model: the second method is similar to the trust model. Both domestic and foreign partners have used this kind of trust. It is called trust in China, and it should be called trust overseas. This model is that you give them the coins, and they will give the proceeds to the trust, and then you will withdraw the shares. This method is also OK, more suitable for large funds. After Kraken was banned, we can see that Coinbase is also very excited, especially their CEO tweets almost three times a day to explain why they don't do what Kraken does.
We can know that they are different after in-depth research, but it is the same model as Kraken, except that the way of distributing revenue is different, and its transparency is the same as Kraken.
3. Blockchain project platforms: such as the existing Lido, Ankr, and Rocket Pool. In fact, SSV has granted grants to more than a dozen projects, all of which are similar to this project. They belong to TOC, and the core problem to be solved is the problem of liquidity. The track of LSD, liquid staking derivatives, you can understand it as a derivative of liquidity. The core problem of the derivative of liquidity is that after it locks your liquidity, there can be a solution when you need liquidity. And this kind of solution is called "emergency plan" in Chinese words, or this kind of solution may be temporary. In the future, after the upgrade of Ethereum to Shanghai, whether this method will become mainstream, I personally have doubts.
Two logics: The first logic is that with the development of the market, new products and new projects are constantly emerging, which is why it was only 13.77% before the upgrade of Ethereum Shanghai (a little higher in the past two days) . Because a certain person who was unwilling to mention his name deposited some ETH in it, which increased the pledge rate a little. The problem is that it still hasn't reached more than 14%, which is very unsafe for a POS, and its robustness is very low. The logic is that if Ethereum wants to solve its own centralization problem, after upgrading to Shanghai, it must make its nodes more decentralized, which requires a product - ssv.network.
The core logic here is to hope that in this market, after the upgrade in Shanghai, there will be 100, 1,000, or 10,000 of these existing LSD protocols in the future, entering a state of contention among hundreds of schools of thought. If DVT technology such as SSV is used, we are also very welcome. If not, I think there will be other solutions in the market in the future, and we can make a comparison.
I also welcome everyone to participate in the testnet of our ssv network. You can experience it. Select four nodes among the tens of thousands of nodes and pledge your 32 ETH to get relevant benefits, and all the benefits It's all for you. You don't need to set up nodes, you don't need to manage nodes anymore, you just need to use DKG's distributed private key sharding technology to distribute your private key to four operators, and then they will hold your Validator Key to sign, you no longer have to worry about losing your private key, and you don’t have to worry about losing your coins (but the private key for withdrawals must be kept well). You also don't have to worry about being slashed, as the chances of being slashed are very low.
1. Why we need SSV?

Why do we need SSV after the upgrade in Shanghai? Personally, I think "it's not that SSV needs Ethereum, but that Ethereum needs SSV."
Two logics: The first logic is that the current pledge rate of Ethereum is 13.77%, or around 14%. Everyone should think deeply about why this is. There must be two layers of logic, which we call "first principles", that is, the conclusion can be reversed to reason and process. The "conclusion" is that Ethereum only has a pledge rate of 13.77%. Why? The core reason is that its liquidity is not enough and it cannot enter and exit freely.
After the upgrade in Shanghai, it has free entry and exit. I think that if Ethereum wants to maintain its anti-censorship and distribution, then it needs SSV's DVT technology to increase the breadth of its node distribution, which can be distributed all over the world. There are Ethereum nodes.
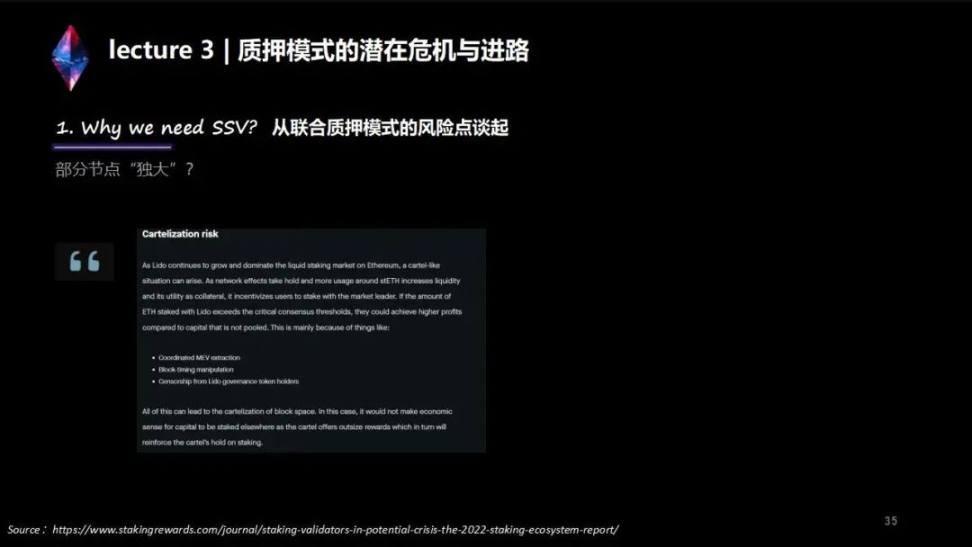
Another point is the risk of the Ethereum joint pledge model. One point we can call dominance, also can be called monopoly. Monopoly needs to be solved by innovation. The source of innovation is emergence, and the source of emergence needs diversification. After the upgrade in Shanghai, we need one hundred, one thousand or even 10,000 LSD track projects to emerge and serve us. We are the customers, and they are just one of the merchants. If the market share is still the same in the future, I personally understand that Ethereum will not have a particularly good development. This is the core risk.
2. The technical principle of the solution: SSV as a technical term

Another point is the solution to the risks of the pledge model. Because from the perspective of SSV, we hope to solve this problem. If the private key is not in your hands, you will not be able to sleep at night. The problem that SSV solves is to keep your withdrawal private key in your own hands. If your private key is not lost, your coins will not be lost. This is the core "don't trust, just verify".
The three core technologies of SSV are very simple logic, but it is difficult to do it.
1. Secret Shared Validator(SSV)
It is a technique of sharding your private key. After Ethereum is converted to POS, it has two layers of chains. The first layer chain we can call it a consensus chain, and the second layer chain we can understand it as an execution chain. On this basis, the logic of his POS is divided into two layers. After we adopt DVD technology in the future, we can split its private key into two parts. That is, when your private key is transferred to POS, if you have 32 ETH, if you want to participate in the Ethereum POS node, your private key can be split into a withdrawal private key and a signature private key. SSV only does one thing, which is to give your withdrawal private key to yourself for storage, and split your signature private key into four parts. This uses the SSV technology, and we split it into four parts Give it to four nodes, and we use 3/4 of the online rate of these four nodes, and your signature can be successful.
2. DKG Technology
The second technology is actually DKG technology, which can be understood as a signature private key generation technology. If the node technology of SSV is used, a key of a node can be split into four fragments, and these four fragments are handed over to these four nodes. These four nodes are selected by you from tens of thousands of nodes. Yes, it can be based on your own risk appetite or your rewards, or you don’t choose it if you think it’s expensive, or you can choose it if you think it’s safe and expensive, and you can also choose fees A little lower, less secure, you can even choose China, the United States, Japan, Singapore or even Europe, you choose one in each country, and then we can do 3/4 of these four nodes verification. This solves the Byzantine attack problem.
3. The third point is the multi-signature wallet technology,The technology of the MPC wallet is also very difficult, but after it is implemented, it is a very simple technology for users.
3. The specific implementation of the solution: SSV.network as a POS ecological participant
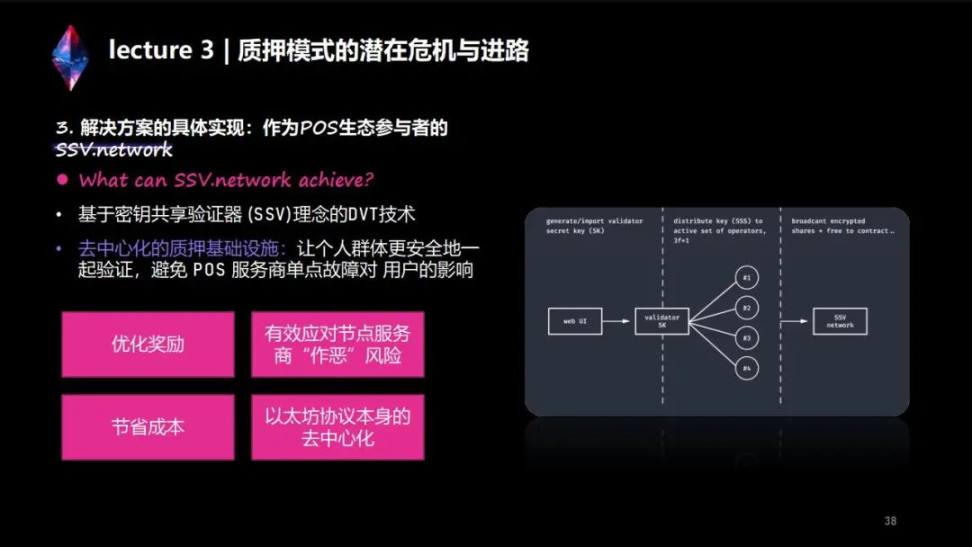
There are three core technologies of DVT: SSV, DKG and MPC. These three technologies are the core technologies of SSV, and this is also the technical basis on which we can survive and provide services to Ethereum, or to any of you who want to be an LSD track in Ethereum in the future.

We can take a look at DVT's plan. DVT's initial name was not DVT but SSV. It was later changed to DVT with the SSV network.
At that time, the place in the first document of V God Zhuan POS was DVT. I personally understand that Vitalik is able to realize that the security of Ethereum is based on its own nodes that are sufficiently distributed. We can recall the recent SEC chairman’s strict scrutiny of the blockchain. The SEC recruited a traditional financial person who knows the blockchain best to join the SEC, and now he supervises our decentralized blockchain technologies. I personally think that he knows what blockchain is better than me, and the supervision he does is very neutral and precise. In the LSD track, he chose the most accurate Kraken to supervise. This also shows that the pledge model needs to be more decentralized.

DKG technology allows four machines to share a private key, so that your private key for withdrawing coins is in your hands, and your validator key is stored and verified together in four nodes, and each node only masters one of your verifications A shard of the private key.
Multi-party secure computing technology is a very critical technology in the industry, and it is also a technology that V God values very much. Multi-signature wallets are very useful for some dAPPs of Web3, which can make your capital transfer safer and more convenient.
The technical team of SSV and the technical team of the Ethereum Foundation often communicate together. SSV and Ethereum are a very good symbiotic relationship. We hope that in the future there will be some products in the middle layer that can be experienced by all our users, and SSV can also provide services for everyone.
Lecture 4: The emergence of "national debt" in the encrypted world and the creation opportunity of LSD application layer
BlueWharf:
I'm BlueWharf, Contributor for Shield. I would like to use another dimension to tell you—what kind of product is the current Ethereum mining under POS from a financial perspective?
Recap: A comprehensive analysis of ETH 2.0 staking platforms/products
1. Risk-free income assets are born in the encrypted world

In the era of POW, your money needs to be invested in buying machines, maintaining mining machines, etc., coupled with a series of factors such as policies, power instability, and local relations, so in the era of POW, whether it is BTC mining or Ethereum Fang mining, we think it is a risky investment, not a very suitable underlying asset.
But after arriving at POS, your principal no longer needs to be spent on any valuable entity, and you will no longer face any risk of returning the principal. At the same time, after throwing it in, the rate of return of mining is very stable, the whole process is very transparent and clean, and you don’t need to bear any series of operational risks such as computer room maintenance.
In the traditional world, there is a very large risk-free income asset, namely the national debt of various countries. We believe that the emergence of Ethereum POS mining has actually introduced a large-scale risk-free underlying asset similar to national debt in the traditional world to the entire encrypted world.
What kind of huge impact will this matter have? We can first take a look at what role does national debt play in the traditional world, especially in the traditional wealth management market?
In the traditional wealth management market, we often see two very common bank wealth management products. One is a fixed-income product, which deposits 100 yuan and gives everyone 102 yuan at the end of the year. This 2 yuan is interest.
However, I often see another product called "Fixed Income +". Your 100 yuan is still 100 yuan, and your 2 yuan may become 3 yuan, 4 yuan, 5 yuan, or 6 yuan. , How did this process come about? In fact, around 19 years ago, because China’s economic development was very fast, so the interest rate was very high. You may get 5.6 points for fixed income, but as the GDP declines, the loan interest rate will not go up. The closing space is basically within 4 points. Therefore, if you still want to earn more than 5 points of income, the "fixed income +" product has become a very popular financial product in the market since 2019. The entire global volume of "Fixed Income +" is very large, possibly tens of trillions of dollars.
Now we need to understand how the national debt in the traditional world plays an important role in the product of "fixed income +". Normally, if you buy this wealth management product and give the broker 100 yuan, he will first use your 100 yuan to buy risk-free products like government bonds. But there are many kinds of government bonds here, such as US dollar government bonds, RMB government bonds, and some other very large types of bonds, which everyone thinks are relatively safe bonds. After investing in treasury bonds, he will give you the first yield of treasury bonds. For example, the yield of treasury bonds is 3% per annum. What will everyone do after getting the 3% annualized income?
We have written about the whereabouts of the mainstream in banks. They usually use the 3% annualized interest part to invest in the primary and secondary markets, including stock investment, stock index futures, treasury bond futures, convertible bonds, etc. Previously, the Hong Kong stock market was relatively hot for new listings, and there will be some demand for new listings and fixed increase categories, so that this 3% will become even higher.
Of course, there is another common destination in the traditional market. We collectively call it quantitative trading, but in fact it is divided into several types. For example, some are quantitative hedging transactions. Most of the hedging transactions are likely to be low-risk. ; There are also some term arbitrage or CTA strategies mixed with subjective market judgments.
This is how the "fixed income +" products in the traditional world are born and the role of national debt here. If there is no safe underlying asset such as national debt, many "fixed income +" products cannot be produced.
2. Problems that need to be solved to realize fixed income + in the encrypted world
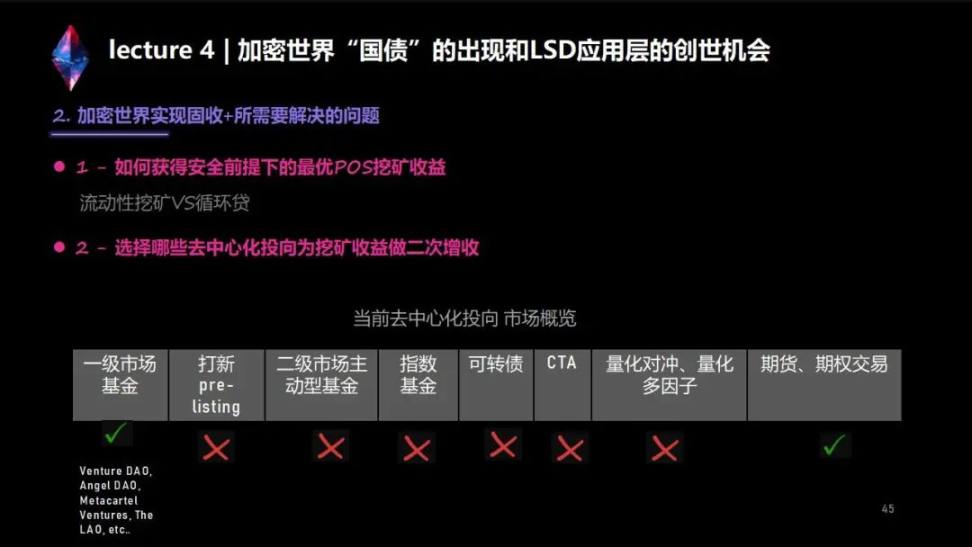
We have just finished the introduction in the traditional world. Then in the Crypto world, POS mining has brought the entire national debt-level, large-scale risk-free assets. In the Crypto industry, "fixed income +" is a huge application scenario in the entire traditional world. How should this thing be designed? There are usually two unavoidable questions: The first question is how we can obtain the income of the first layer of fixed income. The second question is that we have to consider how to increase the income a second time after we get this fixed income.
1. How to obtain the optimal POS mining income under the premise of safety
In the current environment before the upgrade in Shanghai, Shield believes that the optimal POS mining has a big premise, called the security premise, because if we want to deliver such a Protocol, it cannot be easily manipulated by others. Because your entire data is on the chain and is transparent, it can calculate your current positions and various situations. If you design a Protocol that can be easily calculated by others, we think that Protocol is a security risk.
In this case, there are currently two common strategies in the market.
The first strategy: use the proceeds from Lido to do this, and use the proceeds from the staking protocol to do liquidity mining on Curve. This is a relatively common strategy.
The second strategy: use the lending agreement to do revolving lending, because revolving lending can add higher leverage, so that from the perspective of yield, it will be higher than the yield of liquidity mining just now. But its higher rate of return actually comes from your increased leverage. There are two risks in this matter. One risk is that the price difference between stETH and ETH just mentioned will lead to liquidation, which mainly depends on whether you are greedy or not. If you are very greedy, then judging from the current situation, there is a probability that you will be penetrated and lead to liquidation. If you are not greedy and your leverage ratio is low, it will be relatively difficult to be broken down.
But we think that the greater risk here comes from the fact that the essence of your revolving loan is to increase leverage. If you want to earn it back, you have to unleverage. The point now is that even the liquidity of the wstETH trading pair on AAVE is about 110 million US dollars, but a relatively large proportion of the trading pair pool of AAVE may come from revolving loans. That is to say, seeing that it has a liquidity of 100 million US dollars, it is very likely that the 50 million US dollars of liquidity here is actually revolving from the revolving loan, and it does not really have such a large liquidity. This also means that the biggest risk here is that if someone lends 50 million or 70 million at one time, the pool will not be enough. You will find that leverage is difficult to untie.
Shield believes that under such circumstances, a large-amount revolving loan strategy may face the risk of unleveraging. Therefore, Shield currently provides you with a strategy that may not be the highest rate of return, but you can lie down and sleep, that is, a dynamically adjusted pledge mining + liquidity mining strategy.
Before the Shanghai upgrade, these are the points we are currently involved in finding the optimal mining income. With the upgrade of Shanghai, there may be some bigger changes in the market, and the number of mining routes will increase. But before Shanghai's upgrade, we were most concerned about the security range.
2. How to use the optimal income to further add value
Because the money of the DeFi project must flow to the DeFi destination, let's traverse whether the financial management scenarios in the traditional world can be applied to the DeFi world. For those scenarios that can be done in the traditional world, in the current DeFi world, there are only funds + futures/options trading in the primary market. However, the governance level and rate of return of venture DAO-like primary market funds at this moment may still be affected by various subjective factors. However, most income-increasing strategies such as new pre-listing, active funds in the secondary market, index funds, convertible bonds, CTA, quantitative hedging, and quantitative multi-factors currently have no solid solutions in the Crypto industry, or are not suitable for decentralized The way of organization is used for governance and decision-making, so there is no large-scale volume.
And futures trading and options trading can now be done. The problem with futures trading is that it involves complex position management issues, and there may be a risk of liquidation, especially on the chain. Moreover, it is very subjective, and we don’t think it should be the preferred direction at present.
The rest is the option trading strategy. The option trading strategy determines how to buy and how to return. The whole thing can be recorded on the chain. Therefore, it is currently the most transparent value-added solution with a relatively higher degree of risk control.
3. Exploration and practice of Shield Staking Vault in encrypted asset fixed income + products

After doing these analyzes, Shield has launched a product called Shield Staking Vault, which we mainly use to solve the following two problems:
The first question: Focus on "fixed income", that is, to help everyone discover and aggregate the optimal mining income based on market dynamics. After the upgrade in Shanghai, this agreement may become the mining entrance of the entire Ethereum. Based on underlying protocols such as Lido, we will continue to find the optimal mining path for users who want to mine ETH POS.
The second question: To further develop "Fixed Income +", based on the analysis just now, we choose an option strategy with a relatively high winning rate to help everyone do the secondary value-added of ETH POS mining income.
Liquidity mining is a simple strategy. We do Lido’s pledge income on the first layer, that is, pledge mining. The second layer takes this stETH and ETH transaction pair to do Curve’s liquidity mining. We will receive three Layer income: The first layer is the income of transaction fees, the second layer is the income of liquidity rewards, and the third layer is the reward income of Curve (low, negligible). However, the transaction fee income obtained by staking mining on Lido, the income from liquidity mining on Curve, and the income from liquidity rewards are actually changing dynamically. Shield will monitor the data and realize dynamic adjustments, so that achieve the highest yield.
After earning the income, I will give everyone a second choice. There are also multiple gears to choose from.
First: If you are a conservative person, you can only do the aforementioned pledge + liquidity mining.
Second: If you are a person who guarantees capital, it is OK, and the interest part can let go of yourself and take a chance on the benefits brought by the market, then it is the second tier, we call it a moderate product, and the interest part is used as an option value-added strategy .
Third: If you want to get a higher annualized return, you may have to bear the pressure of a part of the principal, for example, 90% of the capital preservation, and then take out 10% of the principal, plus the mining income, to do it together Market options options.
In the process of the last two gears, the option value-added strategy just mentioned will be introduced. At present, we have selected an option strategy called wedding cake. As shown in the schematic diagram, its strategy looks like a cake. Simply put That is, within the scope of the blue line, there is money to be made. As long as the market trend falls within the range of the blue line, there is money to be made. This is a weekly strategy with such a rate of return every week. If the price in the second week reaches the highest level of the cake, you can get an annualized rate of return of 15%, but this actually means that your current price starts from the middle of the cake. If you start from the left and right sides of the cake and choose whether to go long or short, then the middle layer of the cake is not 15% annualized, but 200% annualized.
In the case of this strategy, as long as it falls within the range of the blue line, it is profitable. For ETH, our strategy probably means that only if it falls by 25% in a single week, or rises above 25% in a single week, will it be possible to fall outside the blue line. If you expect this probability to happen, just don't buy it this week. As long as this small probability event is discarded, most of the time, the price of ETH will fall within the scope of this blue line, so this strategy is a relatively stable option income strategy. But Clarify, but there are no absolutes in any transaction, and there are still risks in extreme situations, which require investors to carefully consider.
Four



