Abstract: This article discusses the role and function of blockchain technology in the process of computer forensics. At the same time, it discusses the mechanism and principle of its function with actual cases.
With the wide application of Internet technology and various information technologies, especially the prosperity of the Internet + era, new industries such as Internet finance, e-commerce, and industrial Internet are gradually replacing the development of traditional industries. People are enjoying the benefits brought by the new era. With the coming high-efficiency work and high-quality life, computer crimes are also emerging.
As a high-tech crime, computer crime requires extremely high computer expertise and strong anti-investigation capabilities for criminals, so the evidence collection of computer crimes has always been a technical problem.
1. Computer Forensics and Blockchain Technology
The evidence of computer crime is stored in the computer hard disk in the form of electronic data, which is often confused with other important files in the computer, such as program codes, logs storing computer operation records, etc., so it is very difficult to extract computer evidence.
The blockchain is a structure that does not depend on a specific center. It uses a distributed node consensus mechanism to complete the verification and storage of data, and dynamically adjusts and accurately searches for retained data evidence, which solves the practical problem of electronic evidence preservation in procuratorial work. Reliable preservation of evidence, traceable operations, irreversible tampering, and efficient search are realized through technologies such as blockchains trusted timestamp, Merkle event fork tree, POW consensus mechanism, and hash encryption. well applied to judicial practice.
2. Overview of Computer Forensics
Computer forensics is not only a legal issue, but also a technical issue. It is necessary to combine the particularity and generality of computer forensics, and study the various links of computer on-site survey, acquisition, preservation, use, review and confirmation to ensure the objectivity and integrity of computer forensics. Legitimacy and relevance.
Judd Robbins, a well-known American computer forensics expert, defines computer forensics as computer forensics and forensic identification is the application of computer investigation and analysis techniques to the determination and acquisition of potential and legally effective evidence. The Maoqiu Institute of Science and Technology believes that computer forensics refers to the use of computer software and hardware related technologies for criminal acts such as computer intrusion, sabotage, fraud, and attacks, in a manner that complies with legal norms, and is acceptable to the court. The process of identifying, acquiring, transmitting, storing, analyzing and presenting digital evidence persuasively present in computers and related peripherals and networks.
(1) Process of computer forensics
image description
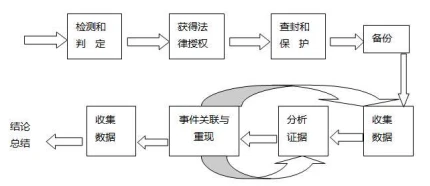
(Figure 1 Computer Forensics Process)
The fragility of digital evidence makes the authenticity and security of digital evidence questionable. Therefore, in the entire forensic investigation, certain operating procedures and techniques must be followed to ensure that the presented evidence is correctly analyzed and that the original evidence has not been tampered with from beginning to end. The specific process is as follows:
1. Detection and judgment:This stage is mainly through the combination of IDS technology and network deception technology to discover the attack behavior on the evidence on the network, and to identify the attack behavior, determine whether the behavior is an illegal attack, and then take corresponding measures.
2. Legal authorization:Although this process does not involve any technical issues, because the evidence obtained by computer forensics will be applied to the law, the legality of the obtained evidence must be paid attention to. Without the process of legal authorization, the collected evidence may be judged as invalid. For example, a video or recording secretly recorded by a mobile phone may be judged invalid according to Article 57 of the Criminal Law.
3. Seizure and protection:This stage is mainly to prevent the criminal subject from destroying or tampering with digital evidence after the criminal act is discovered. Before the advent of blockchain technology, the tampering of digital evidence was very hidden and difficult to detect. Perhaps a modification of punctuation marks may lead to digital evidence. invalidation of evidence. Therefore, before blockchain technology is applied to the computer forensics process, the seizure and protection of devices that store data evidence is the top priority.
4. Data backup:In order to avoid the destruction of the original data, the original media is not used in forensics, but the mirroring of the original media, byte stream backup and other methods are used. For example, use the DD command of Linux or UNIX system for disk backup.
5. Collect and analyze data:The sources of digital evidence mainly include systems, networks, and other digital devices. The evidence extracted from the system mainly includes existing normal files; hidden files, password-protected files and encrypted files; system log files; chat room logs; Email; backup media, etc. These collected data do not fully meet the needs of current evidence. Through techniques such as comparison method and keyword analysis, the relevance of the same event can be found and useful data can be extracted.
6. Event correlation and reproduction:Based on the data collected and initially analyzed in step (5), a timeline is established through the intervals of system time and standard book swords to determine the correlation between events.
7. Organize and archive data:The data in step (6) is sorted and archived for submission to the court as evidence.
8. Summary:Propose countermeasures to prevent similar cases from happening, improve safety measures; summarize technically and learn from experience.
The above is the computer forensics process compiled by Maoqiu Technology based on the research and work experience of the judicial department. From the process, we can conclude that the process of computer forensics involves complicated steps and procedures, and a little carelessness may lead to data loss or damage. How to prevent data from being tampered with or lost has become a problem that must be considered now.
(2) Classification of computer forensics
According to the different storage methods and locations of electronic evidence, the objects of computer forensics work can be divided into three categories, namely, hard disk forensics, Internet forensics and mobile phone forensics.
1. Hard disk forensics:image description
Figure 2 Hard Disk Forensics
2. Internet forensics:image description
Figure 3 Internet crime
3. Mobile phone evidence collection:image description
Figure 4 Mobile phone crime
All of the above are different types of computer forensics. However, with the development of 5G networks, big data, and Internet of Things networks in the future, more methods for storing data will appear. As a value Internet, blockchain has unique characteristics and these The interactive integration of new technologies provides a safer and more complete solution for computer forensics.
3. Overview of blockchain technology
Blockchain is an intelligent peer-to-peer network that uses distributed databases to identify, disseminate and record information. The core point is distributed multi-copy and non-tamperable information. Its advantages lie in decentralization, distribution, and common identification, which can ensure data It is safe, efficient, authentic, and reliable. At the same time, it uses cryptographic methods that cannot be tampered with forged decentralized sharing. By using encryption algorithms, trusted timestamps, data structures, and common identification mechanisms, point-to-point Each node in the network participates in various activities on an equal footing.
(1) The core technology of blockchain
image description
Figure 5 Basic Architecture of Blockchain
The point-to-point protocol communication is used at the network layer. During this process, the blockchain data structure and distributed network that cannot be tampered with and forged, the common identification mechanism, and trusted time stamps are all representative features of the blockchain. The specific core technology of the blockchain is organized as follows:
1. Trusted timestamp:Blockchain technology requires that data blocks must have time stamps, which enables the blocks on the blockchain to be arranged in chronological order. Relying on trusted time stamps can effectively prove the existence of block data, which helps to form unreliable The tampered and forged blockchain database lays the foundation for solving the time-sensitivity problem in electronic evidence, and can be used as the basis for the existence of electronic data in procuratorial technology.
2. Hash encryption:Blockchain technology is stored in the blockchain by performing hash function operations on the original data.
3. P2P network:Each node in the P2P network is equal in status, and each node undertakes functions such as verification, dissemination, and storage. According to the amount of data stored by the node, it can be divided into full nodes and light nodes. The full node stores the most complete block data of the blockchain, can update the main chain in real time, and independently implements query, update, verification, etc. without relying on any other nodes.
4. Data block:A data block generally includes two parts: a block header and a block body, where the block header contains effective information such as target hash value, consensus mechanism, Merkle root, and trusted timestamp.
5. Smart contract:A smart contract is an information-sharing program code deployed on the blockchain that encapsulates various rules, starting conditions, and corresponding behaviors. It has the characteristics of decentralization, automation, and strong scalability. It will run automatically once it is started. The scalability of smart contracts makes it possible to connect more application services.
6. Merkle tree:The Merkle tree quickly summarizes and verifies the integrity of the data, so that there is no need to encapsulate all the data, and the Merkle root is formed recursively on the hash value, which greatly improves the efficiency of the blockchain, and can also run the entire network node incompletely. data validation is complete.
The core technologies of the blockchain are not limited to the above six. This article only discusses the core technologies in the blockchain technology that are helpful to computer forensics, and Maoqiu Technology will not list them here.
(2) Application cases of blockchain technology
Since 2015, some international publishers have successively cooperated with blockchain technology companies to start the research and development of blockchain technology application scenarios, especially in the field of copyright. Foreign publishers like PeerReview Blockchain, Artifacts.ai , Scienceroot.com have good technical development results.
1. Peer Review Blockchain——Improve the transparency of peer review
Peer Review Blockchain improves the transparency, recognition and efficiency of the peer review process by storing and publishing key data about the peer review process on a shared platform, while ensuring privacy requirements.
2. Scienceroot——Establish a new academic exchange ecosystem
Scienceroot is a more effective, transparent, and open scientific research ecosystem based on blockchain technology, allowing anyone in the global scientific community to raise funds, interact, discuss research ideas, collaborate, and finally publish their research ideas through this system. work results.
3. The Peoples Bank of China - developing a digital bill trading platform
At the beginning of 2017, the blockchain-based digital bill trading platform promoted by the Peoples Bank of China was successfully tested. Subsequently, the Digital Currency Graduate School under the central bank was established. The central banks blockchain data bill platform introduces digital currency for settlement, and realizes the synchronization of capital flow and information flow of digital bill transactions, thereby realizing DVP bill payment settlement.
4. Beijing Internet Court - the first case of blockchain electronic certificate deposit
On October 30, the first case accepted by the Beijing Internet Court officially opened to hear a dispute over copyright ownership and infringement between Beijing Weibo Vision Technology Co., Ltd. and Baidu Online Network Technology (Beijing) Co., Ltd. In this case, Jinri Toutiao (the parent company of Douyin Short Video) entrusted a third-party electronic platform to carry out the evidence collection work, and a series of technologies including blockchain evidence storage technology and third-party judicial appraisal were used to ensure evidence collection. true.
At present, although blockchain technology has applications in various industries, most of them are still on the surface, and more exploration and research are needed, especially the technical application in the field of computer forensics.
4. Implementation mechanism of computer forensics based on blockchain
image description
Figure 6 block mechanism
The hash encryption and time stamp technology of the blockchain can ensure the authenticity of the data obtained during the computer forensics process and has not been tampered with by humans. The blockchain is composed of blocks. As long as the content on a node is modified, it will cause a change in the hash value. Simply put, after the data evidence for computer forensics uses blockchain encryption technology, a certain point of tampering It will cause the hash of the entire block to change. If you want others to know that the data has not been modified, you need to modify all the blocks (someone will generate hash records if they check it), which is basically impossible.
At the same time, each node of the blockchain can receive data through the hash algorithm and Merkle tree and encapsulate it into a data block with a trusted time stamp, and link it to the main blockchain. In the process of the computer area, through the complete and true acquisition of illegal data on the electronic platform, it is packaged as original data into the blockchain, which can ensure the authenticity and traceability of data evidence.
V. Conclusion
V. Conclusion
references:
references:
1. Cao Min. Overview of Computer Forensics Technology
2. Hu Yong. Application of Electronic Forensics Based on Blockchain in Smart Prosecution
3. Mai Yonghao, Liu Zhijun, Xiang Dawei, Zhang Peng. Systematic Process Specification for Computer Forensics
4. Hua Bin, Xue Dong. Computer Forensics Process Analysis and Research
5. Zhang Tian, Meng Meiren. Analysis of Scenarios and Cases of Application of Blockchain Technology in Academic Exchanges
6. My way is limited. Ten Cases of Blockchain Technology Application










