Foreword: Information records such as contracts and transactions have become important structures in the current economic system, but the disadvantage is that they have not kept pace with the digital transformation of the world, so they are like cars stuck in rush hour, in a dilemma. Blockchain is expected to solve this dilemma.
first level title
The charm of the blockchain: to achieve free trade and interaction
Blockchain, the technology at the heart of Bitcoin and other virtual currencies, promises to solve this problem. Blockchain, as an open distributed ledger, can effectively, verifiably and permanently record transactions between two parties. So how does the blockchain work and can it solve this problem? Maoqiu Technology summarizes the five technical characteristics of the blockchain:
Distributed database
Every party on the blockchain has access to the entire database and its complete history. No party controls data or information. Each party can directly verify the records of its trading partners without an intermediary.
point-to-point transmission
Communication happens directly between peers rather than through a central node. Each node stores and forwards information to all other nodes.
Anonymous and transparent
Anyone with access to the system can see every transaction and its associated value. Every node or user on the blockchain has a unique 30+ character alphanumeric address to identify it. Users can choose to remain anonymous or provide proof of their identity to others. Transactions happen between blockchain addresses.
record irreversibility
Once a transaction is entered into the database and the account is updated, the records cannot be changed because they are linked to every transaction record before them (hence the name chain). Various computational algorithms and methods are deployed to ensure that records on the database are permanent, chronological, and available to everyone else on the network.
Computational logic
The digital nature of the ledger means that blockchain transactions can be associated with computational logic and are inherently programmable. So users can set algorithms and rules that automatically trigger transactions between nodes.
It can be imagined whether the above five advantages of the blockchain are the results expected by the general population, with no centralized control and autonomy. When a contract is embedded in digital code through blockchain technology and stored in a transparent and shared database, it is not controlled by a centralized organization and cannot be deleted or tampered with.
In this world, every agreement, process, task and payment will have a digital record and signature, can be identified, verified, stored and shared, and individuals, organizations, machines and algorithms can freely carry out with almost no friction transactions and interactions. This is the beauty of blockchain.
Of course, this is an ideal state. Although now we hear every day that the blockchain will change the traditional business model and will redefine the way companies operate and the economic operation model. This information makes our blood swell and full of passion, but the emergence of new things is always accompanied by some uncertainties. For example, exchanges fail, or get hacked, and these security issues arise.
Through the experience of previous technological innovations, we can find that if the blockchain is to become a revolutionary wave like the Internet, all obstacles must be regulated and governed. Maoqiu Technology Market Research does not believe that it is necessary to plunge into blockchain innovation without understanding what it should be. How to stand firm in this era is a wrong idea.
Although the blockchain is a disruptive technology that can surpass the traditional business model with low-cost solutions, it will take some time for the real transformation of businesses and companies led by the blockchain. As a foundational technology, it may create new foundations for our economic and social systems, and it will take decades to fully penetrate the economic and social infrastructure.
first level title
Looking at the future of blockchain from the perspective of TCP/IP
Before discussing the future course of the blockchain, Maoqiu Technology will take everyone to review the process of technology adoption, especially the typical transformation process of other basic technologies. The following will take distributed computer network technology (TCP/IP) as an example.
Introduced in 1972, TCP/IP first gained a single use case as the basis for email for researchers on ARPAnet, the precursor to the US Department of Defenses commercial internet. Before TCP/IP, telecommunications architectures were based on circuit switching, where a connection between two parties or machines had to be pre-established and maintained throughout the exchange. To ensure that any two nodes can communicate, telecommunications service providers and equipment manufacturers have invested billions of dollars in dedicated lines.
The advent of TCP/IP upended this model. The new protocol transmits information by digitizing it and breaking it down into very small packets, each of which contains address information. Once released into the network, the packet can take any route to the receiver. Intelligent sending and receiving nodes at the edge of the network can break down and reassemble data packets and interpret encoded data. No dedicated leased lines or bulky infrastructure are required. TCP/IP creates an open, shared public network without any central authority or party responsible for maintaining and improving it.
At the time, the traditional telecommunications and computing sectors were skeptical of TCP/IP. Few imagined that robust data, messaging, voice, and video connections could be built on new architectures, or that associated systems could be secure and scalable. But in the late 1980s and 1990s, more and more companies such as Sun, NeXT, Hewlett-Packard, and Silicon Graphics used TCP/IP, in part to create localized private networks within organizations. To this end, they developed building blocks and tools that extended their use beyond email, gradually displacing more traditional native web technologies and standards. As organizations adopted these building blocks and tools, they saw dramatic increases in productivity and productivity.
With the advent of the World Wide Web in the mid-1990s, TCP/IP suddenly entered widespread public use. New technology companies quickly emerged to provide the pipes -- the hardware, software and services needed to connect to now public networks and exchange information. Netscape commercializes browsers, Web servers, and other tools and components that facilitate the development and adoption of Internet services and applications. Sun drives the development of the application language Java. With the exponential growth of information on the network, Infoseek, Excite, AltaVista and Yahoo emerged as the times require, and guide users to understand it on the platform.
Once this basic infrastructure reaches critical mass, a new generation of companies will take advantage of low-cost connectivity by creating Internet services that are attractive alternatives to existing businesses. CNET moves news online. Amazon offers more books than any other bookstore. Priceline and Expedia have made buying airline tickets easier and brought unprecedented transparency to the process. The ability of these newcomers to achieve broad reach at relatively low cost has put enormous pressure on traditional players such as newspapers and brick-and-mortar retailers.
Relying on widespread internet connectivity, next-wave companies create novel, transformative applications that fundamentally change how businesses create and capture value. These companies are built on a new peer-to-peer architecture and create value by coordinating a distributed network of users. Consider how eBay changed online retail with auctions, Napster changed the music industry, Skype changed telecommunications, and Google changed web search by using user-generated links to provide more relevant results.
first level title
Blockchain, a peer-to-peer network based on the Internet
The parallels between blockchain and TCP/IP are clear. Bitcoin enables bilateral financial transactions just as email enables bilateral messaging. Blockchain development and maintenance is open, distributed and shared - just like TCP/IP. A team of volunteers around the world maintains the core software. Like email, Bitcoin first caught on with an enthusiastic but relatively small group.
TCP/IP unlocks new economic value by dramatically reducing connection costs. Likewise, blockchain can greatly reduce transaction costs, and it has the potential to become the system of record for all transactions. If that happens, the economy will once again be fundamentally shifted as new, blockchain-based sources of influence and control emerge.
Think again about how the business works today. Keeping an ongoing record of transactions is a core function of any business. These records track past actions and performance and guide future planning. They provide a view not only of how an organization works internally, but also of its external relationships. Every organization has its own records, and they are private. Many organizations do not have a general ledger of all activity; instead, records are distributed among internal units and functions. The problem is, coordinating transactions between individuals and private ledgers takes a lot of time and is prone to error.
For example, a typical stock trade can be executed in microseconds, often without human intervention. However, settlement - the transfer of ownership of the shares - can take up to a week. Thats because parties dont have access to each others ledgers, nor can they automatically verify that assets are actually owned and can be transferred.

first level title
How long it will take for blockchain to be adopted
If the analogy was with early email, does blockchain have decades to reach its full potential? Fuqiu Technology believes that the answer is yes. We cant predict exactly how many years the transformation will take, but we can guess which types of applications will gain traction first, and how blockchain will eventually become widely accepted. The following hair ball technology research department will take you to find out.
Scholars Marco Iansiti and Karim R. Lakhani of the foreign journal Nature have developed a set of Basic Technology Phase Adoption Analysis framework model, which divides basic technology into four stages, namely four quadrants, and each quadrant represents a stage of technological development. stage.
image description
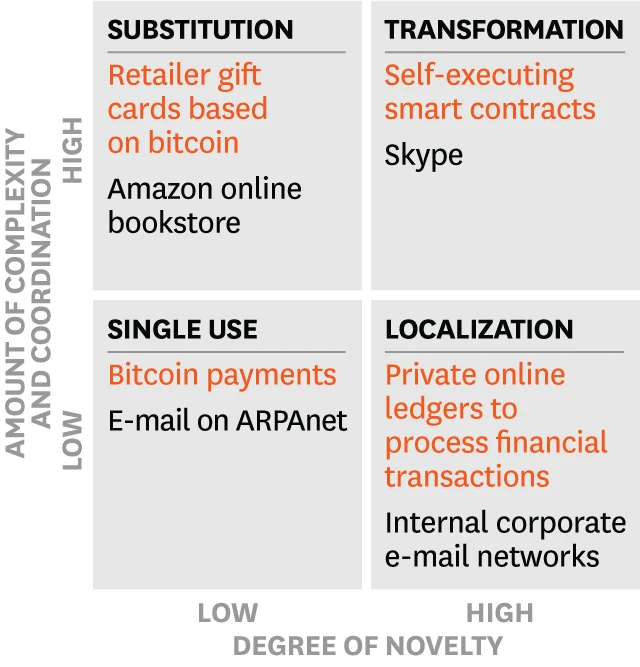
(Basic Technology Phase Adoption Analysis framework model)
epilogue
epilogue
References:
References:
1. Marco Iansiti、Karim R. Lakhani.《The Truth About Blockchain》
2. Liang Guirong. The Current Situation and Development Prospects of the TCP/IP Network Protocol Layer
3. Liu Xingquan. Status and Development of the Stock Market
4. Zhang Wei, Ding Kaiyan. The Essential Characteristics of Blockchain
5. Liu Pingfeng, Xie Kun, Gao Yating, Qin Guishuang, Liu Yujie, Li Xinxin. Using Blockchain to Realize the Management System and Method of Stock Trading










