Original author: Crypto Research
Original translation: Luffy, Foresight News
How much does it cost to trade Bitcoin and other crypto assets? This question sounds simple, but it is not. The vast majority of current markets ignore other participants and often trade at prices higher or lower than other markets show. There are several reasons for this phenomenon:
Lack of data: There is no “official” combined best bid and ask (BBO) price for cryptocurrencies.
Market fragmentation: There are many cryptocurrency trading markets, including centralized exchanges (CEX), liquidity providers (LP), and decentralized exchanges (DEX), and price oracles conflict with each other.
Opportunism: Many market makers ignore their responsibilities to clients to provide “best execution” and instead extract profits and reduce costs from payment for order flow (PFOF).
The chart below shows the cost of buying and selling $25,000, $100,000, $250,000, $500,000, and $1,000,000 of Bitcoin in USD between February and November 2023:
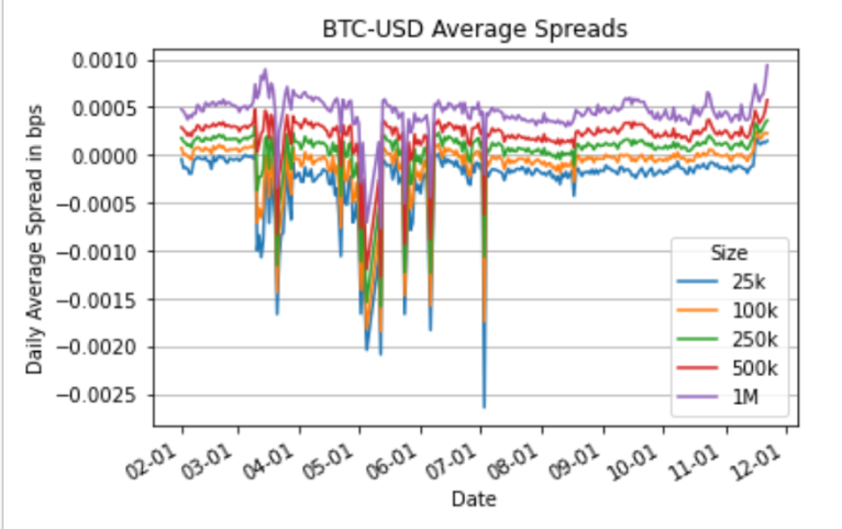
As can be seen in this chart, the small, persistent cost of the $25,000 order is caused by price differences between exchanges, where the bid price on one exchange is often higher than the offer price. Traditional financial markets refer to these as “crossing markets,” which are very rare in most asset classes, but almost always exist in crypto. It is worth noting that most of the time these differences are less than the cost of transferring assets between exchanges and arbitrageurizing away the difference. However, during times of high market volatility, there are often more significant differences. This price difference can lead to a distorted view of the potential costs of trading. Therefore, we created the CoinRoutes Liquidity Index to normalize the data and provide traders with a consistent and fair benchmark for understanding liquidity costs.
We measured the difference in cost between a $25,000 order and a $1 million order based on the best “smart routing” for buying and selling of each size. This is calculated by “walking the order book,” where we keep the complete order book of all major exchanges. The order book is used to add up the sell costs of all bids, sorted from high to low to accumulate $1 million in sales, and the buy costs of all bids, sorted from low to high to accumulate $1 million in buys. We then calculate a time-weighted average from a 5-second sample each day. It’s worth noting that this benchmark assumes optimal order routing, which means it assumes that all exchanges are available for trading at all times and have sufficient inventory of USD, stablecoins, or cryptocurrencies. In reality, this requires sophisticated routing technology and excellent money management.
CoinRoutes Liquidity Index Results:
We calculated the index of perpetual swap contracts denominated in USD and USDT for Bitcoin and Ethereum from February to the end of November 2023 and came to several conclusions:
1) If institutions have access to all markets, then institutional-scale Bitcoin and Ethereum trading costs are quite competitive with global stocks of similar market cap. (Retail investors in Bitcoin and Ethereum pay much higher fees, which is very different from the situation in the stock market, where the spreads paid by different traders are very small)
2) USD spot trading is more expensive than USDT spot trading. Although this trend has eased over the past year, it is still significant.
For Bitcoin, the average cost of $1 million of liquidity in USD has ranged from 5 to 7.5 basis points over the past quarter, while the average cost of $1 million of liquidity in USDT has ranged from 3.5 to 5.5 basis points.
For Ethereum, the average cost of $1 million of liquidity in USD has been between 5 and 9 basis points over the past quarter, while the average cost of $1 million of liquidity in USDT has been between 4 and 8 basis points.
3) Perpetual swap contracts are more liquid and have lower transaction costs. This is not surprising as the swap market has significantly higher trading volumes than the spot market. This also explains why OTC is so popular in the spot market as market makers are able to hedge in the perpetual swap market to create tight spreads.
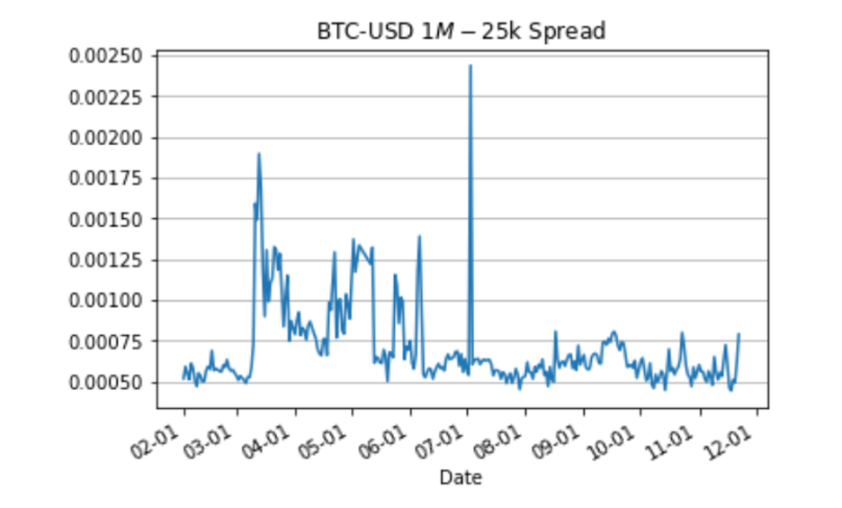
For Bitcoin, the average cost of a perpetual swap for $1 million in liquidity is between 3.5 and 7 basis points for USD-denominated swaps and between 1 and 2.5 basis points for USDT-denominated swaps.
For Ethereum, the average cost of a perpetual swap for $1 million in liquidity is between 4 and 8 basis points for USD-denominated swaps and between 2 and 3.5 basis points for USDT-denominated swaps.
The chart above shows the liquidity cost of buying or selling $1 million of Bitcoin in USD on major cryptocurrency exchanges. Note that there were spikes in liquidity costs during the spring and early summer, primarily on weekends when banking issues made it difficult to move funds across exchanges, but the average cost has stabilized between 5 and 7.5 basis points. Since this is a measure of every cost, it means that the average bid-ask spread for USD-based liquidity is between 10 and 15 basis points.
In summary, achieving best execution in the fragmented cryptocurrency market presents many challenges, including price discrepancies between exchanges and opportunistic behavior by market participants.










