introduction
dappOS is committed to building a complete Web3 intent layer to help users simplify operations and achieve institutional-level execution efficiency. The three core components of the Web3 intent layer are: operations, assets, and transactions. Previously, dappOS has launched the intent operating system (IntentOS) and intent assets (Intent Asset), realizing the intentionality of operations and assets. Based on these product technology accumulations, dappOS now launches the intent exchange IntentEX to further help users realize transaction intentionality and improve the key components of the dappOS intent layer ecosystem.
The core advantage of IntentEX is that it allows ordinary users to directly enjoy institutional-level liquidity resources, with faster transaction execution and lower fees, and the experience is close to the CEX level.
1. Background
The current market is in the midst of a new asset and MEME boom, and users have a strong demand for on-chain transactions. However, many existing on-chain exchanges have difficulty providing users with sufficient liquidity, slow execution, and high fees. These problems have seriously affected the user experience. The core reason for these problems is that the trading liquidity of an asset is often dispersed among various exchanges, and users cannot enjoy the liquidity of the entire market for the asset in one exchange.
The emergence of dappOS intent exchange intentEX (https://portal.dappos.com/trade) solves these problems of liquidity, transaction costs, and transaction efficiency, and truly helps users realize transaction intentions.
2. The principle of intentEX
The core design innovation of intentEX is that, based on the traditional order book exchange, it additionally delegates the users limit order as an intent task to the nodes in the dappOS intent execution network, and allows the nodes to complete transactions on any chain. This design not only fully utilizes the trading liquidity advantages of professional institutions, making the tokens in intentEX substantially have liquidity that is better than all CEX and DEX, but also gives users faster transaction speeds and lower execution fees.
2.1 Release Intent Task
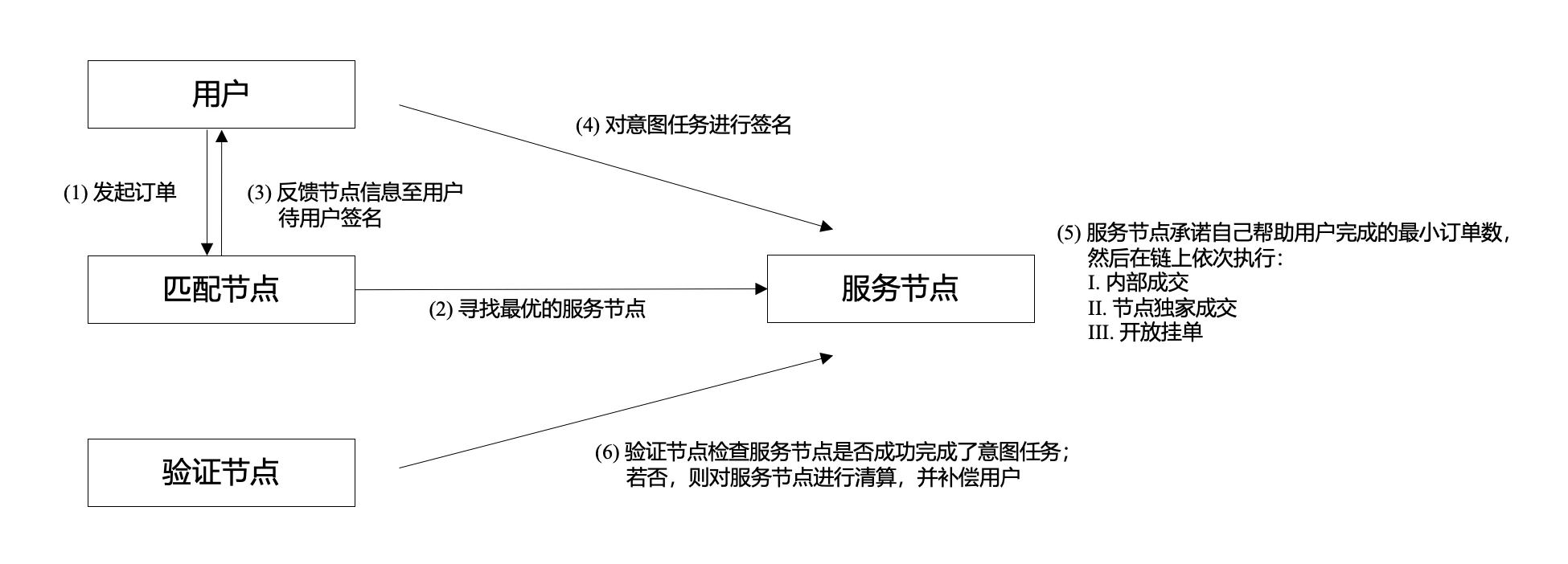
When a user places a limit order on intentEX, it is equivalent to publishing an intent task in the dappOS intent execution network. The matching node in the network will match the intent task to the service node with the strongest overall competitiveness. When selecting a service node, the matching node will comprehensively consider various factors, such as: the nodes margin, execution cost, execution speed, and how many orders the node is willing to accept for each price deviation from the market.
After the user completes the signature, the service node that confirms that it has received the intent task will promise an order amount that it guarantees the user can successfully complete according to its own situation. Due to the constraints of the OMS mechanism of the dappOS intent execution network, once the service node completes the signature and confirms the exclusive transaction amount, if it is not fulfilled in the end, the node will be liquidated. Therefore, usually at this stage, the user can consider that the part of the order promised by the service node has been completed without waiting for the final on-chain confirmation. When the users quotation is near the market, since the service node tends to promise to complete all orders, the speed of user order execution can be higher than the block speed of the public chain itself.
2.2 On-chain order processing
After completing the commitment, the service node will complete the order processing on the chain according to the following three steps under the system constraints:
Internal Fill: If there is a matching order in the intentEX order book, the system will directly match the order. Some orders that fail to be filled at this stage will enter the next stage.
Node Exclusive Fill: For the remaining orders, the service node will have the exclusive right to fill them within a certain period of time. If the number of orders that the service node promised to fill is not completed during the internal filling stage, the service node needs to fill it on its own, otherwise it will face liquidation of the dappOS network. The service node can also fill more orders than it promised during this stage.
Open Order: The remaining orders will be posted to the intentEX market for other users to trade.
If a service nodes execution speed is too slow, or the number of orders it promises to help users complete is small, its competitiveness in the matching node will be reduced, making it difficult to receive more orders. This mechanism helps service nodes tend to promise to help users complete more orders and complete transactions faster.
2.3 A specific case
To make it easier for readers to understand, here is a specific scenario as an example - suppose that the total amount of the sell order of $A token in intentEX is 990 U, and the price is 9.9 U; the total amount of the sell order is 1010 U, and the price is 10.1 U.
At this time, the user initiates a limit buy order of 300 10 U. This buy order will be published as an intention task to the dappOS intention execution network, and the matching node in the network will assign this task to the current optimal service node.
Assuming that a service node successfully competes for this intent task, it needs to promise a minimum number of orders that it can help users complete (for example, 250 $A buy orders). The specific amount of this commitment is generally related to the nodes strategy and the current depth of the $A token in all other trading markets. For example, this node is willing to promise to help users complete at least 250 buy orders, which may be because: the intentEX market currently has 100 sell orders that can be completed immediately; and after observing all other DEXs and CEXs, it found 150 $A tokens with a cost of less than 10 U after taking into account the relevant fees.
From the users perspective, 250 of its 300 limit buy orders were completed when the service node submitted the commitment to the network, which is faster than the block speed of the public chain itself. In this example, the market depth of $A is not large, but in more cases, when the market depth is sufficient, the node will promise to help users to complete all orders near the market, so that users can find that all their orders can be completed immediately.
Next, the service node will execute the transaction according to the following process:
1. Internal Fill
100 of the user’s 300 10 U limit buy orders will be matched with intentEX’s existing 100 9.9 U sell orders and traded directly at 9.9 U.
2. Node Exclusive Fill
Since the node has made a commitment to help users complete at least 250 orders, at this stage it needs to help users complete at least the remaining 150 orders, otherwise it will face liquidation.
This is where the advantage of intentEX comes into play: compared to leaving the users remaining unexecuted orders on the market and waiting for other market makers to arbitrage, the professional service nodes in the intent execution network directly assume this role. This allows users to have the liquidity of the $A token in the entire market, and on the other hand, it also allows users orders to be traded faster.
3. Open Order
If the matching service nodes of the last 50 10 U limit buy orders are unwilling to execute the transaction, they will appear in the buy order of $A token of intentEX.
Generally speaking, this situation will only occur when the users order price is far away from the market price, or when the liquidity of the relevant token in all trading markets is relatively insufficient.
3. Core advantages of intentEX
1. Institutional-grade full-market liquidity
dappOSs professional service nodes can observe and match user orders in real time in CEX and DEX across the entire market. Therefore, token transactions within intentEX have full market-level liquidity.
Compared with pure on-chain price inquiry designs such as routers, intentEX combines high-quality on-chain and off-chain liquidity, bringing institutional-level liquidity capture capabilities. In this way, each users order can quickly access the best price source, achieve a higher transaction rate and faster transaction execution, and enjoy the liquidity of the entire market.
Compared with other intent architecture designs, dappOSs unique OMS mechanism allows nodes to take on tasks without incurring capital costs (as long as the intended tasks can be completed, funds can be used simultaneously for multiple businesses, and there is no need to pledge funds specifically like acting as an LP) and the cost of dealing with order grabbing, which reduces the overall operating costs of nodes and makes the entire system more efficient.
2. Fast execution speed
IntentEX uses the liquidity of its entire platform to quickly match the market price, providing users with faster transaction speeds than conventional on-chain transactions. The execution efficiency of intentEX benefits from the professional service nodes of the dappOS intent execution network. In general, signature confirmation can be completed within 500 milliseconds from the completion of the users signature, which is even faster than the speed of the public chain. This greatly reduces the transaction waiting time and enables users to complete transactions faster.
Compared with other intentional architecture designs, this transaction speed and smooth experience that is superior to the public chain brings users a convenient experience that is closer to that of centralized exchanges.
3. Low transaction fees
IntentEX relies on the professional service node network of dappOS, which greatly optimizes the transaction fee, with the cost as low as 0.1%, which is much lower than the fees of most on-chain exchanges. This makes intentEX a more economical choice for users when trading on the chain.
4. Decentralization and transparency
All intentEX transactions are publicly recorded on the chain, ensuring the transparency and credibility of the system. The decentralized mechanism in the dappOS intent execution network ensures the reliable execution of orders. Even if a service node fails, other nodes can be seamlessly connected to ensure the success of the transaction. Through this decentralized structure, intentEX provides users with a more stable trading experience that does not rely on the stability of a single point server.
4. intentEX and dappOS ecosystem
IntentEX is an important part of the dappOS ecosystem. It is a product launched by dappOS to help users realize transaction intentions after realizing operation intentions and asset intentions.
The previous article has explained in detail the specific implementation of intentEX based on the dappOS intent execution network. For the detailed principles of the dappOS intent execution network, please refer to: https://dappos.gitbook.io/docs/dappos/how-dappos-works
In addition, USDT, BTC, and ETH used in intentEX are actually dappOSs intent assets, namely intentUSD, intentBTC, and intentETH. In this way, users can enjoy interest income even when they hold these mainstream assets and do not trade them, and it does not affect users immediate use of these mainstream assets for trading. For the detailed principles of dappOS intent assets, please refer to: https://dappos.gitbook.io/docs/dappos/intent-task-frameworks/intent-assets










