As the futuristic concept of DAO has set off waves of innovation in the Web3 world, this innovative paradigm rooted in blockchain technology has not only reshaped our understanding and imagination of traditional organizations, but also incubated star projects such as Compound and MakerDAO that have changed the rules of the industry. From project owners to institutional investors to ordinary cryptocurrency players, everyone has paid close attention to and shown great interest in DAO. It is like a key that opens the mysterious door to the future organizational form. However, whenever we try to define DAO, it changes into new forms in different contexts and application scenarios, making it difficult to understand.
However, what exactly is a DAO organization? What are its advantages and limitations?
How to create a DAO organization? What procedures need to be met?
Which countries or regions have clear laws and regulations to regulate DAO organizations?
Can the DAO organization be used as the token issuing entity of the RWA project?
The Crypto Salad team has been deeply involved in the cryptocurrency industry for many years and has rich experience in dealing with complex cross-border compliance issues in the cryptocurrency industry. In this article, we will combine the laws and regulations of various countries and the teams practical experience to sort out and answer the above questions from the perspective of professional lawyers.
1. What exactly is a DAO organization? What are its advantages and limitations?
DAO organizations are very new to many people outside the industry, so there is no so-called strict definition of this concept. Specifically, the DAO organizations mentioned by cryptocurrency players, the DAO organizations in the sense of blockchain technology, and the DAO organizations in the sense of legal norms may have completely different corresponding concepts.
Therefore, only by returning to the DAO expression itself for semantic analysis can we understand its common essence in different scenarios and contexts. DAO refers to a decentralized autonomous organization. Therefore, organizations with the following two characteristics can theoretically be identified as DAO organizations: decentralization + autonomy. The following article will compare DAO organizations with traditional companies, and analyze the core essence of DAO organizations from the two perspectives of decentralized organizational structure and autonomy governance model, so that everyone can better understand the uniqueness of DAO organizations.
1. “Decentralized” organizational structure
Under my countrys traditional corporate system, the highest decision-making power of a company lies in the hands of the shareholders meeting. Shareholders delegate the management power of specific company affairs to directors to exercise, and form a centralized management body such as the board of directors, which is responsible for making decisions on important matters during the companys operations. Finally, the board of directors implements the decision by hiring corporate executives and employees.
The decentralized nature of the DAO organization is reflected in the fact that the DAO does not have a centralized decision-making and management body like the traditional corporate system, but rather all members of the organization share the management and decision-making power over the DAO organization.
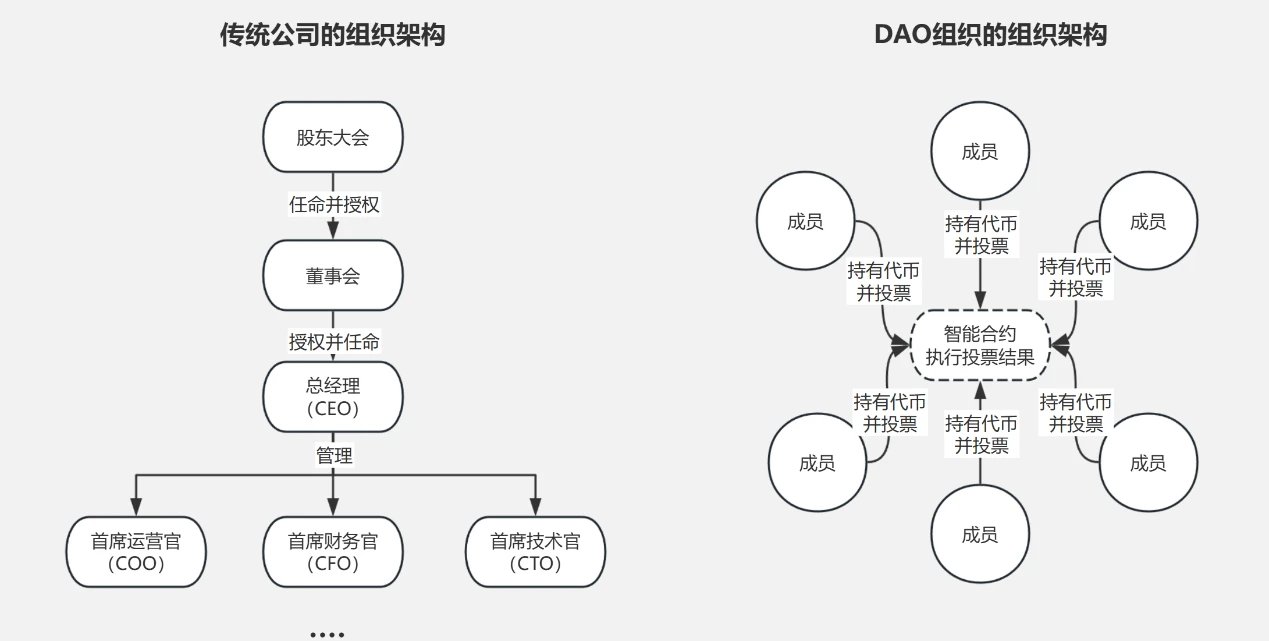
(Diagram comparing the organizational structure of traditional companies and DAO organizations, for reference only)
At the same time, the DAO organization does not need to be responsible for the interests of specific stakeholders (such as shareholders) and does not have a centralized interest orientation. Among them, every member of the organization who holds the DAO organizations governance token can share the benefits of the organizations development through token appreciation or internal incentives. Take Uniswap as an example. As one of the largest defi trading platforms on the chain, the DAO organizations governance token UNI has brought considerable benefits to its members and further motivated them to build the entire organization.
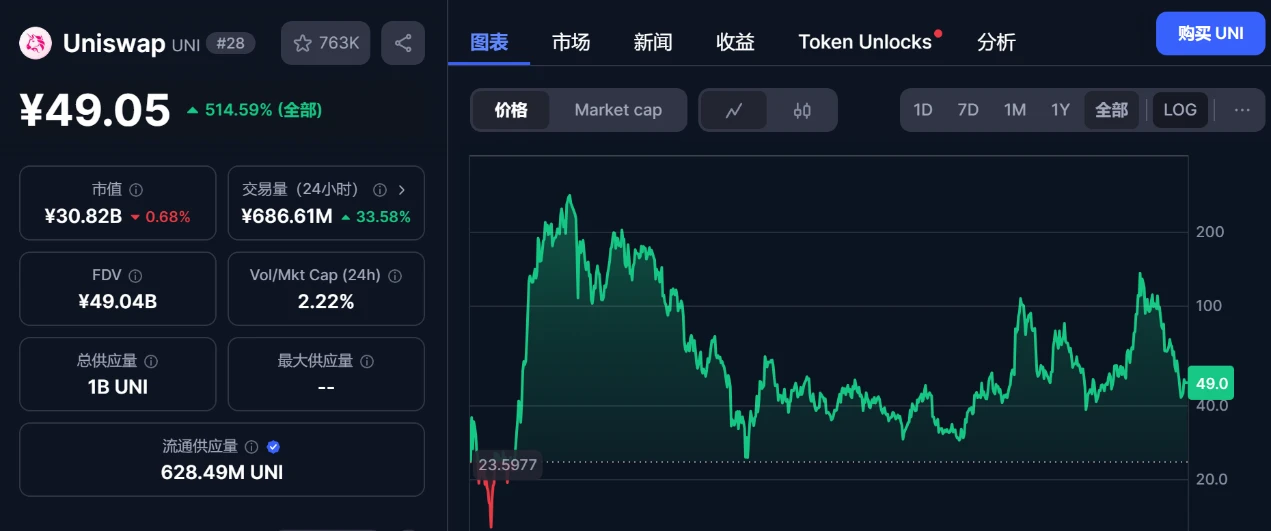
(The above picture shows the price trend of UNI tokens) Source: CoinMarketCap
So, how does the DAO organization achieve a decentralized organizational structure?
After the operational management rules of the DAO organization are established, they will be written into the corresponding smart contract and run autonomously through blockchain technology. In theory, once the smart contract is written and deployed on the chain, it will continue to run automatically, and the operational management rules cannot be changed at will, thus eliminating the possibility of intervention by centralized management agencies.
At the same time, the smart contracts that write the governance rules are completely open source on the chain. Therefore, all community members, including other players on the chain, can query the smart contracts of the DAO organization and all the operation and management rules of the organization through the blockchain. Through the technical tool of smart contracts, the DAO organization has achieved complete transparency of management rules and got rid of the black box decision-making model of centralized management agencies.

(The above picture shows the relevant information and part of the code of the Governor smart contract of the DAO organization Compound) Source: Compound project official website
Compared with traditional companies, what advantages can a decentralized organizational structure bring to DAO organizations?
In the management model of traditional companies, how to avoid the ethical risks of corporate directors, senior executives, etc. and ensure that they act in the overall interests of the company is a difficult problem that can never be completely solved.
In order to ensure that individuals or centralized management agencies that hold major power in the company do not act against the overall interests of the company due to their own selfish interests, they need to be regulated from various aspects such as internal governance models and external regulatory frameworks.
The establishment of a board of supervisors in the companys organizational structure is, to a certain extent, to solve this problem. For example, Article 78 of my countrys Company Law stipulates that the board of supervisors shall exercise the following powers: When the behavior of directors and senior managers harms the interests of the company, require directors and senior managers to correct it. However, a new problem has arisen - the supervisors are responsible for supervising the companys directors and senior managers, so who will supervise the supervisors, and how to ensure that the supervisors can effectively perform their supervisory duties? At this time, it is no longer possible to completely solve this problem only by starting from the internal structure of the company, so the intervention of an external regulatory system is needed. Article 180 of my countrys Company Law clearly stipulates the diligence obligations and loyalty obligations of directors, supervisors, and senior managers. Even so, this internal and external combination of methods still cannot completely solve the problem.
However, based on blockchain technology, DAO organizations use coded, automatically-running operational management rules to replace centralized management decision-making bodies. At the same time, DAO organizations also use governance tokens to allow members to share the benefits of organizational development, so that the interests of decision-makers and the overall interests of the organization are consistent. Therefore, DAO organizations avoid the moral hazard issues mentioned above from the root.
2. “Member autonomy” governance model
The member autonomy here refers to the internal governance system within the organization that can achieve autonomy through its members, breaking away from the bureaucratic organizational governance model under the traditional corporate system.
How to achieve internal autonomy in an organization?
In short, DAO organizations generally achieve autonomy through internal voting. Members holding DAO governance tokens can propose proposals and participate in voting. Specifically, organization members can initiate a limited-time vote on a specific proposal within the framework of governance rules, and ultimately decide whether the proposal will be implemented based on the public voting results of organization members (i.e., governance token holders). The entire process above is automated through smart contracts.
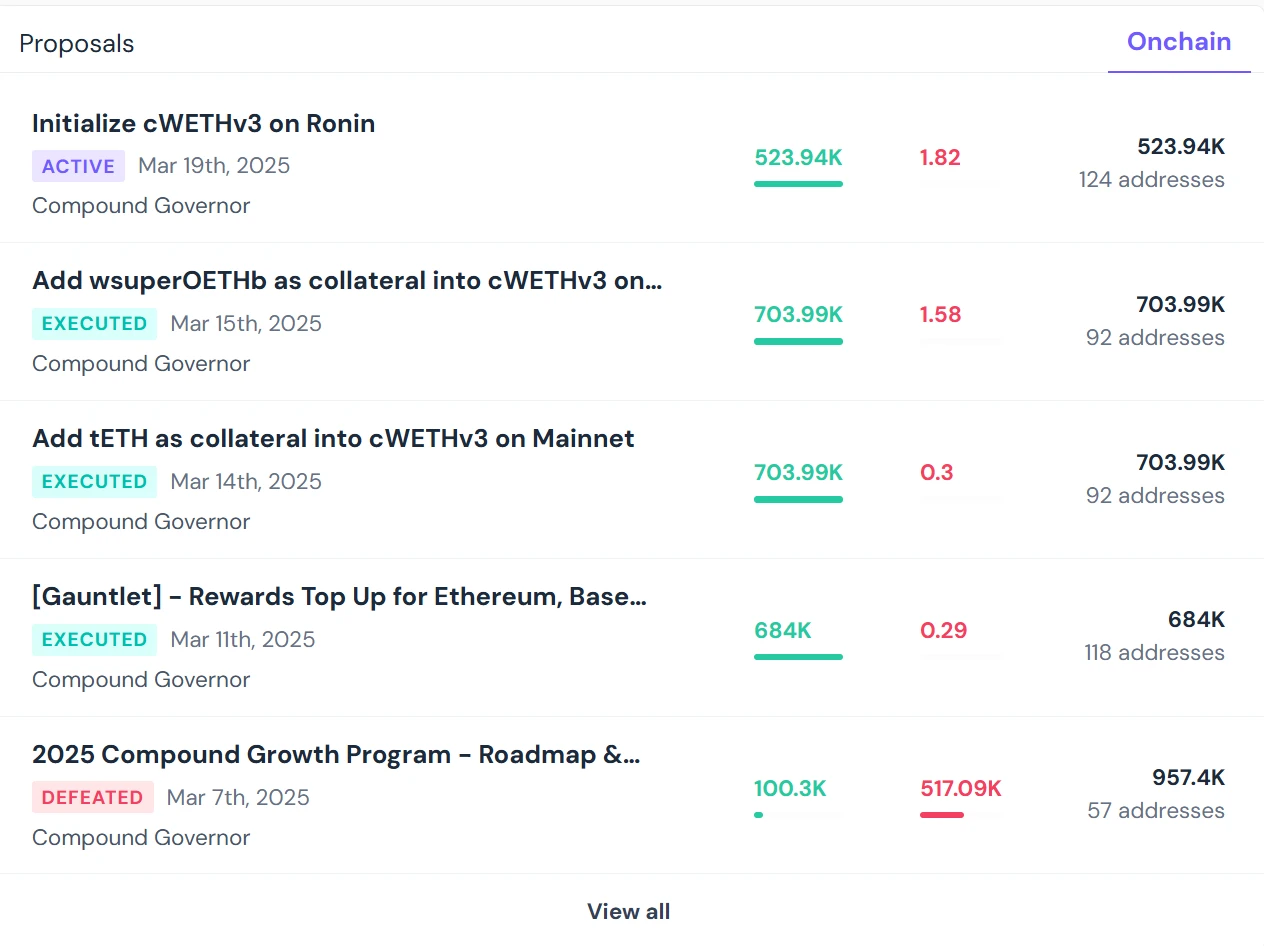
(The above picture is the public interface of the proposal voting of the DAO organization Compound)
Source: Compound project official website
Although the voting modes of DAO organizations are very similar, the specific voting rules are different. Some DAO organizations will adopt the one coin, one vote method to set the voting weight. Some DAO organizations will also adopt special calculation methods to calculate the voting weight, such as the quadratic voting mechanism, to reduce the influence of large coin holders on the final voting results. At the same time, mainstream DAO organizations will adopt a delegate voting method, so that token holders can entrust their voting rights to the corresponding representatives to vote uniformly, so as to improve the overall voting efficiency of the organization.
It should be noted that in the actual implementation process, DAO organizations will not adopt a completely community-autonomous system model from the beginning. For many DAO organizations that have just been established or are in the early stages of project operation, considering that the governance structure of the DAO organization has not been fully perfected and there are fewer members within the DAO organization, the founding team of the DAO organization will generally temporarily choose a centralized governance method, and the founding team will be responsible for the initial operation management and decision-making of the project. When the DAO organization matures, the founding team will gradually transfer the management authority in their hands to other members of the organization through other means such as distributing governance tokens.
So, what are the advantages of member autonomy compared to the traditional corporate governance model?
Under the traditional corporate bureaucracy, the companys operational decisions largely rely on the business judgments made by directors or senior executives. However, when the judgments and decisions of senior executives are transmitted to the executive level, there will inevitably be deviations. This is an inevitable problem when instructions are transmitted from top to bottom. Moreover, the situations and information known by employees at the executive level are difficult to convey directly to decision makers, and the channels for information exchange from bottom to top will also be blocked. Therefore, this governance method of traditional companies is likely to cause a subtle misalignment between the companys senior decision-making and the actual business level. If this misalignment is not corrected in time, it is likely to cause the entire company to lose its competitiveness and go to extinction.
The DAO organization, through member autonomy, eliminates the differences and barriers between the ranks and levels of the organization members, thereby promoting equal communication among the members of the organization and forming a communication atmosphere and model similar to that of the community. At the same time, the DAO organization makes decisions by publicly voting on proposals, which can ensure that the organizations decisions reflect the views and cognition of the majority of members in the organization. Although the views of the majority are not necessarily correct, this mechanism can indeed avoid the negative impact of one-man dictatorship in theory and increase the enthusiasm of members to participate in organizational construction and communication.
After the community voting decision is completed, the smart contract will faithfully and automatically execute the contents of the proposal, and also solve the problem of the difficulty of implementing the decision-making-execution approach.
In short, the above two core characteristics complement each other and are indispensable. Without a decentralized organizational structure, the so-called autonomy of organizational members will inevitably become a show of performance nature due to the intervention of centralized management agencies, lacking practical significance and value. If it is separated from a rigorous, reasonable and sustainable autonomy model, then the decentralized organization will become a tree without roots, and it will be difficult to maintain the normal operation and development of the organization.
From the perspective of higher-level humanistic care and organizational development concepts, the significance and value of DAO organizations are by no means limited to within the organization.
In order to maximize the interests of shareholders, traditional companies have a tendency to pursue unlimited capital appreciation and scale expansion. While pursuing higher profits and larger scale, companies are bound to reduce the importance of individuals to the entire system, otherwise the entire enterprise development will be exposed to huge risks. Therefore, traditional companies will eventually lead to individuals being constantly instrumentalized and eventually reduced to screws. This organizational form naturally puts the company and employees on opposite sides and constantly intensifies the contradictions and conflicts between the two.
The blockchain technology that DAO organizations rely on has broken away from the companys centralized management organization and bureaucratic management model, and to a certain extent has overturned the traditional paradigm of organization and individual opposition and manager and employee opposition in the company system. The two core characteristics of the DAO organization introduced above enable the DAOs organizational purpose and goals to return to the individuals self-exploration and social needs, rather than blindly pursuing the organizations own profit and expansion.
People as ends rather than means, this humanistic ideal and vision is also one of the deep reasons why so many Web3 entrepreneurs and participants are willing to follow or even believe in DAO organizations.
However, DAO organizations also have their own limitations
First, since the DAO’s smart contract is deployed on-chain and is completely open source, this ensures the transparency of the organization’s operating rules to the organization’s members, but it also facilitates malicious attacks by hackers. If there is a loophole in the DAO’s smart contract and the loophole is exploited by hackers, it may cause the DAO organization to suffer huge losses. The most typical case of this limitation is the huge theft of “The DAO”.
Around 2016, a DAO organization called The DAO was created on the Ethereum mainnet. This DAO organization is essentially a community-controlled, decentralized investment fund. The DAO raised more than 11.5 million ETH by selling its own community tokens as its investment fund, which is jointly managed by its members.
However, not long after The DAO began operating, it was hacked due to a smart contract vulnerability and about 3.6 million ETH was stolen. According to the ETH price at the time, the total loss caused by this hacker attack exceeded 60 million US dollars, which was the largest hacker attack in the world at that time. This incident dealt a huge blow to the Ethereum community. In order to recover the related losses, the Ethereum community had to vote to approve a hard fork. In summary, the security risks of the DAO organization cannot be ignored.
Secondly, DAO organizations need to make decisions through voting. In order to ensure that members of the organization can fully participate in the voting decision, the DAO organizations proposal voting is generally set for a longer period of time. Therefore, overall, its operational decision-making efficiency is lower than that of traditional corporate entities.
Finally, although DAO is widely recognized and used in the blockchain field, in most countries and regions, DAO does not have a very complete financial and legal regulatory framework. This leads to the establishment and operation of DAO on the chain, which may face certain legal compliance risks in the real world off the chain, such as liability, taxation, financial compliance and other issues. However, there are still a few countries and regions that have adopted a more open and advanced attitude towards this organizational form and have formulated corresponding regulatory frameworks, which will be elaborated in detail later.
2. How to create a DAO organization? What processes need to be met?
After understanding the characteristics of the DAO organization itself, we can further analyze how to create a DAO organization in practice. Although the creation method and process of each DAO organization are different, most of them include the following four steps:
Establish the purpose of the DAO organization and its operating and management rules.
Write the operation and management rules of the DAO organization into the smart contract.
Since the contract cannot be modified after it is created and running, technicians need to conduct rigorous testing and auditing of the smart contract before they can put the contract online.
Inject funds into the DAO organization.
The DAO organization will set up a fund-raising method based on a pre-set governance framework, and generally complete initial financing by selling DAO organization governance tokens.
After the smart contract is deployed to the corresponding blockchain, the DAO organization is officially established.
After completing the above steps, the creation of a DAO organization is theoretically completed. However, it should be noted that the completion of the creation of a DAO organization mentioned here does not mean registering and establishing a DAO organization under the legal system. In most cases, the DAO organization on the chain does not have the legal status and corresponding behavioral capacity under the actual legal framework. How to register a DAO organization recognized by official laws and regulations, as well as the relevant regulations of various countries and regions, will be elaborated in detail later.
3. Which countries or regions have clear laws and regulations to regulate DAO organizations?
1. United Arab Emirates (UAE)
RKA DAO in the UAE is a free zone established for virtual asset companies by the government of Ras Al Khaimah. At the end of 2024, RKA DAO issued a set of rules and regulations called the DAO Association Regulations , which provide a clear legal framework for DAO organizations in the UAE.
In this legal framework, the DAO organization clearly has an independent legal personality . According to Article 8 of the DAO Association Regulations and related regulations, the DAO organization adopts the underlying legal form of a guarantee company, and its legal personality is completely independent of the organization members and token holders. Specifically, the DAO organization can legally and independently acquire, hold or abandon property, and independently establish legal relationships with the outside world, and bear corresponding legal responsibilities.

(The above picture is the original text of Article 8 of the DAO Association Regulations)
At the same time, the law and regulations also put forward clear technical requirements for DAO organizations, requiring DAO organizations to be deployed on a permissionless distributed ledger and all software codes to be open source. This regulation also further clarifies the uniqueness of DAO organizations in terms of technology compared to other traditional organizational forms.

(The above picture is the original text of Article 14 of the DAO Association Regulations)
In addition, this law and regulation also provides detailed regulations and explanations for the internal governance structure and external regulatory framework of the UAE DAO organization. For example, Articles 92 and 99 of the DAO Association Regulations stipulate that the official registrar and third-party auditors shall conduct compliance supervision and financial review of DAO organizations.

(The above picture is the original text of Article 92 of the DAO Association Regulations)
By analyzing the DAO Association Regulations, it is not difficult to see that the UAE government attaches great importance to the Web3 industry and is at the forefront of the world in supervising and regulating this field. Combined with the recent news that the Abu Dhabi sovereign fund invested 2 billion US dollars in Binance Exchange, the future development prospects of the Web3 industry in the UAE and even the Middle East are very exciting.
2. United States
On April 21, 2021, Wyoming Governor Mark Gordon officially signed Wyoming Senate Bill No. 38, the Wyoming Decentralized Autonomous Organization Supplement Act . First, the bill clearly defines the DAO organization: A decentralized autonomous organization is a limited liability company whose articles of association contain a statement that the company is a decentralized autonomous organization as described in subsection (c) of this section.

(The above picture is the original text of the DAO Organization Supplementary Act 17-31-104)
It can be seen from this that the DAO organization stipulated in the bill can be directly registered as a limited liability company . At the same time, in order to highlight the characteristics of the DAO organization itself and allow the DAO organization to get rid of the various restrictions brought about by the limited liability company form, the bill specifically stipulates that the DAO organization needs to clearly attach the following statement in the charter:
“The rights of DAO members may differ materially from the rights of members of other limited liability companies. The Wyoming DAO Supplemental Act, the underlying smart contract, the Articles of Incorporation, and the Operating Agreement, as applicable, may define, reduce, or eliminate fiduciary duties and may restrict the transfer of DAO ownership interests, exit from the DAO, dissolution, and liquidation of the DAO.”

(The above picture is the original text of the DAO Organization Supplementary Act 17-31-104)
In addition, this bill also makes relevant provisions for the establishment, operation, dissolution and other stages of DAO organizations. However, by comparison, it can be seen that the completeness and strictness of this regulation are slightly inferior to the UAEs DAO Association Regulations.
On April 20, 2022, the U.S. state of Tennessee also passed legislation to amend Title 48 of the Tennessee Code, Companies and Associations, in which § 48-250-103(a) clearly stipulates that a limited liability company (LLC) can register as a decentralized organization by adding a specific statement to its articles of association. In terms of the legal nature of DAO organizations, the legislative model of Tennessee is similar to that of Wyoming.
In addition, countries such as the Marshall Islands and Malta have also issued laws and regulations related to DAO organizations, but due to their limited influence, they will not be discussed here.
4. Can DAO organizations be used as the token issuer of the RWA project?
Regarding this issue, we need to analyze it in conjunction with the definition of DAO organizations in the previous article. If the DAO organization has been registered as an independent legal entity in accordance with local laws and regulations, in theory, as long as the DAO organization meets local financial compliance requirements, it can complete the token issuance. Of course, the specific situation should be comprehensively judged in conjunction with the project itself and local regulatory policies, laws and regulations.
If the DAO organization only exists on the chain and there is no corresponding legal entity off the chain, then this type of DAO organization cannot directly serve as the token issuer of the RWA project, and the DAO needs to be legally packaged (Legal Wrapper) in the early stage of the project. This is because the on-chain DAO organization, as the issuer of currency, will face tax risks and will most likely fail to pass the financial compliance review of relevant financial institutions. The so-called legal packaging specifically means setting up a separate legal entity such as a limited liability company or foundation, and transferring some of the functions of the DAO organization to the off-chain legal entity through an agreement or a specific architecture design, and finally completing the currency issuance.
5. Crypto Salad Interpretation
DAO, a novel organizational form, has developed relatively maturely on the chain, and many star projects have been born. However, if DAO organizations want to further deepen their connection and interaction with the real world, the relevant laws, regulations and regulatory frameworks still need to be further improved. At the same time, project parties that are operating DAO organizations or are interested in DAO organizations should also pay more attention to the compliance requirements of the real world.
The Crypto Salad team is committed to providing the most professional legal services to practitioners in the crypto industry, protecting the legitimate rights and interests of clients to the greatest extent, and avoiding unnecessary legal risks. Our goal is to help clients make more money and avoid pitfalls. If they win, they win comfortably, and even if they lose, they can lose clearly.
This article only represents the personal views of the author and does not constitute legal advice or legal opinion on specific matters.










